目录
1. 只出现一次的数字(简单)
1.1. 题目描述
1.2. 解题思路
方法一:位运算

class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
single ^= num;
}
return single;
}
}
2. 多数元素(简单)
2.1. 题目描述
2.2. 解题思路
方法一:哈希表

class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> countNums(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (!counts.containsKey(num)) {
counts.put(num, 1);
} else {
counts.put(num, counts.get(num) + 1);
}
}
return counts;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = countNums(nums);
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> majorityEntry = null;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
if (majorityEntry == null || entry.getValue() > majorityEntry.getValue()) {
majorityEntry = entry;
}
}
return majorityEntry.getKey();
}
}
方法二:排序

class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
方法三:随机化

class Solution {
private int randRange(Random rand, int min, int max) {
return rand.nextInt(max - min) + min;
}
private int countOccurences(int[] nums, int num) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Random rand = new Random();
int majorityCount = nums.length / 2;
while (true) {
int candidate = nums[randRange(rand, 0, nums.length)];
if (countOccurences(nums, candidate) > majorityCount) {
return candidate;
}
}
}
}
方法四:分治

class Solution {
private int countInRange(int[] nums, int num, int lo, int hi) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private int majorityElementRec(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
// base case; the only element in an array of size 1 is the majority
// element.
if (lo == hi) {
return nums[lo];
}
// recurse on left and right halves of this slice.
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2 + lo;
int left = majorityElementRec(nums, lo, mid);
int right = majorityElementRec(nums, mid + 1, hi);
// if the two halves agree on the majority element, return it.
if (left == right) {
return left;
}
// otherwise, count each element and return the "winner".
int leftCount = countInRange(nums, left, lo, hi);
int rightCount = countInRange(nums, right, lo, hi);
return leftCount > rightCount ? left : right;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
return majorityElementRec(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}
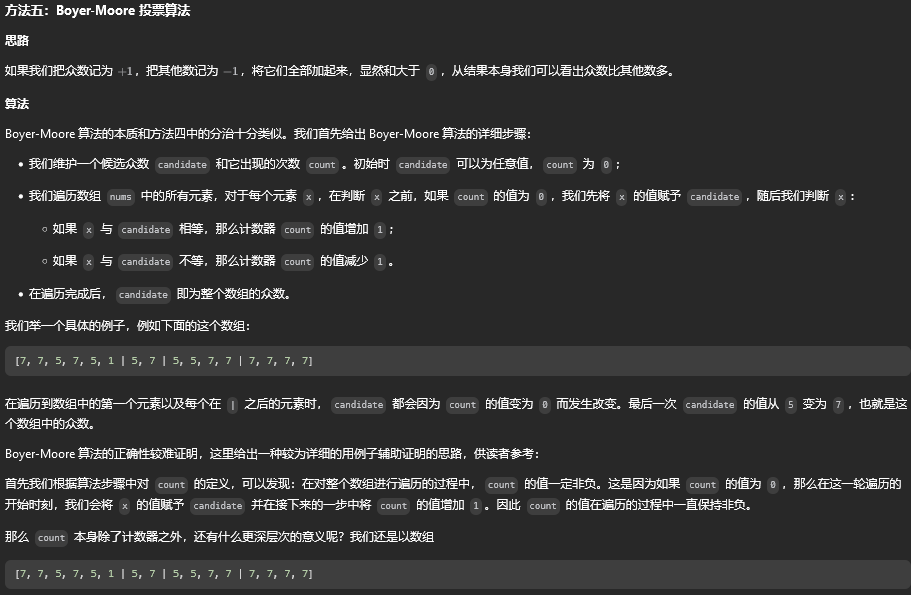
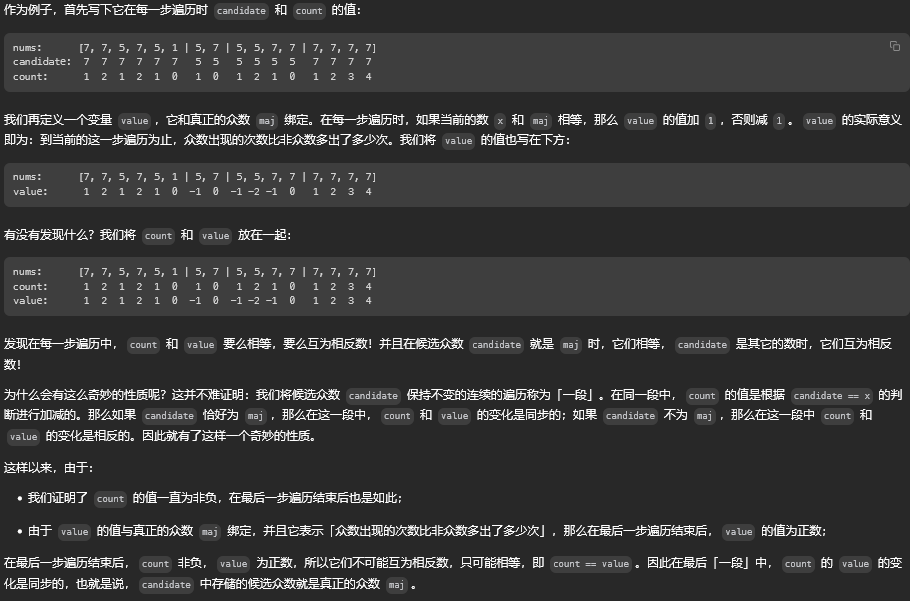
方法五:Boyer-Moore 投票算法
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;
Integer candidate = null;
for (int num : nums) {
if (count == 0) {
candidate = num;
}
count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1;
}
return candidate;
}
}

3. 颜色分类
3.1. 题目描述
3.2. 解题思路
方法一:单指针

class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int ptr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == 0) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[ptr];
nums[ptr] = temp;
++ptr;
}
}
for (int i = ptr; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[ptr];
nums[ptr] = temp;
++ptr;
}
}
}
}
方法二:双指针

Java代码:
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int p0 = 0, p1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[p1];
nums[p1] = temp;
++p1;
} else if (nums[i] == 0) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[p0];
nums[p0] = temp;
if (p0 < p1) {
temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[p1];
nums[p1] = temp;
}
++p0;
++p1;
}
}
}
}
方法三:双指针

Java代码:
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int p0 = 0, p2 = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= p2; ++i) {
while (i <= p2 && nums[i] == 2) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[p2];
nums[p2] = temp;
--p2;
}
if (nums[i] == 0) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[p0];
nums[p0] = temp;
++p0;
}
}
}
}
4. 下一个排列
4.1. 题目描述
4.2. 解题思路

方法一:两遍扫描

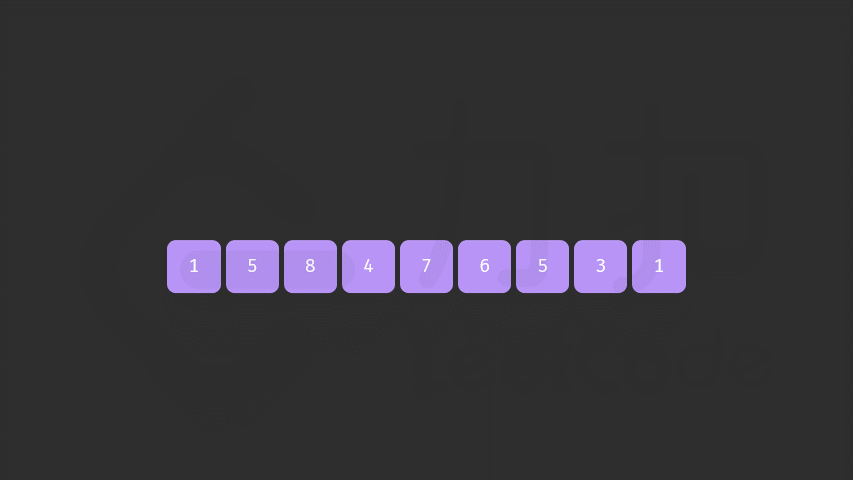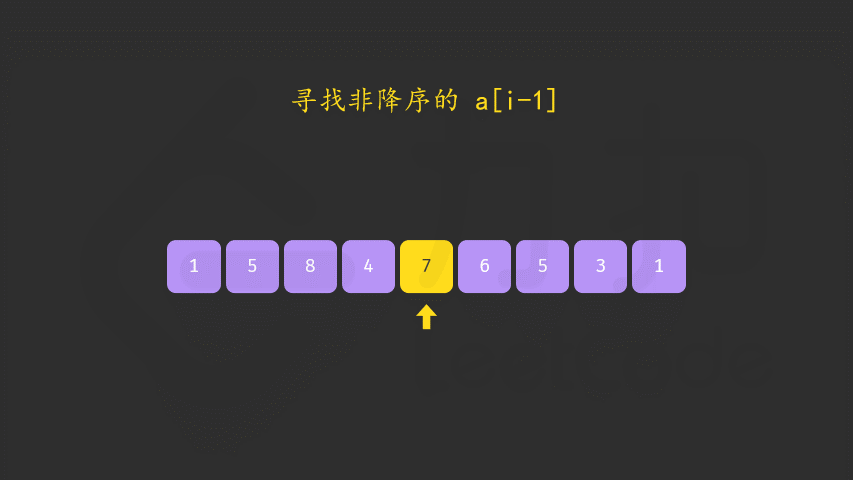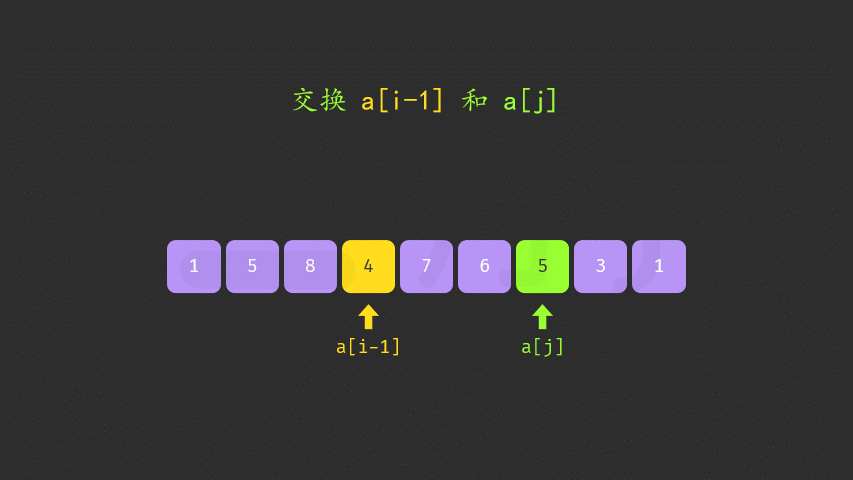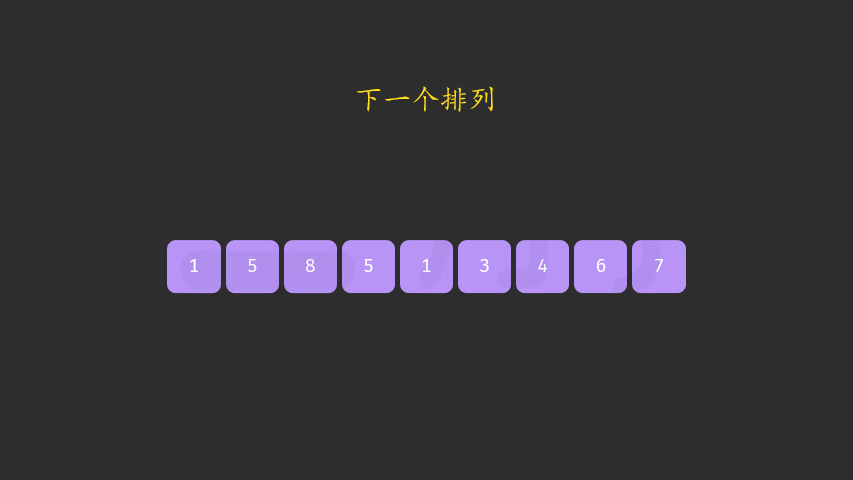
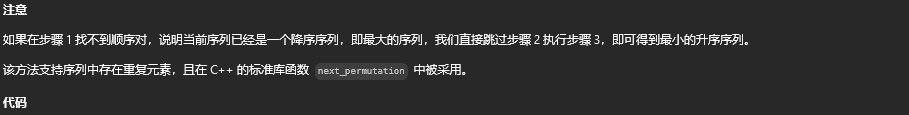
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1]) {
i--;
}
if (i >= 0) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[j]) {
j--;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
reverse(nums, i + 1);
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int start) {
int left = start, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
swap(nums, left, right);
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
5. 寻找重复数
5.1. 题目描述
5.2. 解题思路
方法一:二分查找
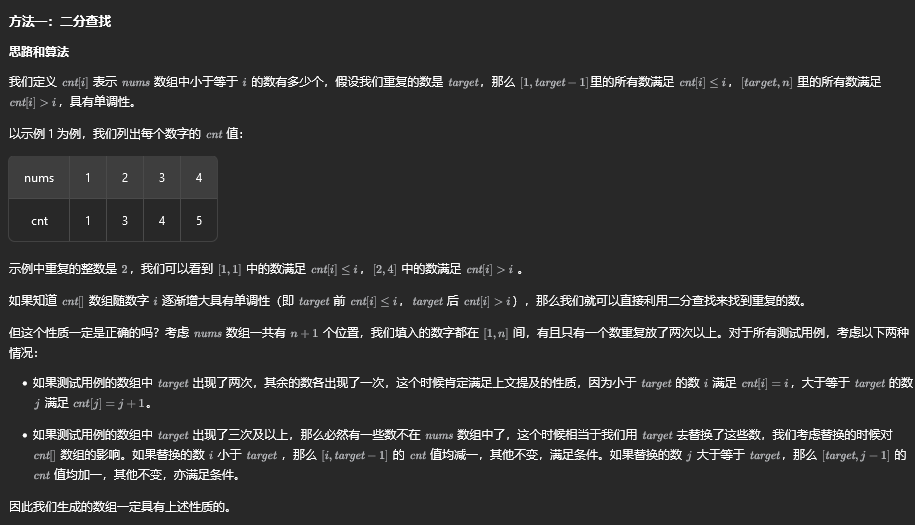
class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int l = 1, r = n - 1, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] <= mid) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt <= mid) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
ans = mid;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
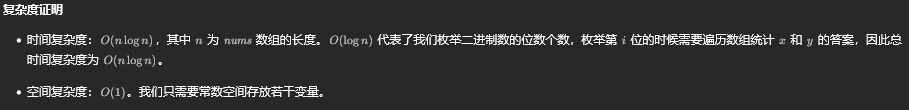
方法二:二进制

class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, ans = 0;
int bit_max = 31;
while (((n - 1) >> bit_max) == 0) {
bit_max -= 1;
}
for (int bit = 0; bit <= bit_max; ++bit) {
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if ((nums[i] & (1 << bit)) != 0) {
x += 1;
}
if (i >= 1 && ((i & (1 << bit)) != 0)) {
y += 1;
}
}
if (x > y) {
ans |= 1 << bit;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
方法三:快慢指针

class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int slow = 0, fast = 0;
do {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
} while (slow != fast);
slow = 0;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
}