二叉树经典面试题::
目录
1.根据二叉树创建字符串

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
string tree2str(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return string();
}
string str;
str += to_string(root->val);
if (root->left != nullptr)
{
str += '(';
str += tree2str(root->left);
str += ')';
}
else if(root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr)
{
str += "()";
}
if (root->right != nullptr)
{
str += '(';
str += tree2str(root->right);
str += ')';
}
//右边为空则不处理
return str;
}
};2.二叉树的层序遍历

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> vv;
int levelSize = 0;
if (root != nullptr)
{
q.push(root);
levelSize = 1;
}
while (!q.empty())
{
//一层一层出
vector<int> levelv;
while (levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
levelv.push_back(front->val);
if (front->left != nullptr)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if (front->right != nullptr)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(levelv);
//当前一层出完 下一层全部进入队列 那么size就是下一层的数据个数
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};3.二叉树的层序遍历II
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root)
{
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> vv;
int levelSize = 0;
if (root != nullptr)
{
q.push(root);
levelSize = 1;
}
while (!q.empty())
{
vector<int> levelv;
while (levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
levelv.push_back(front->val);
if (front->left != nullptr)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if (front->right != nullptr)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(levelv);
levelSize = q.size();
}
reverse(vv.begin(), vv.end());
return vv;
}
};4.二叉树的最近公共祖先
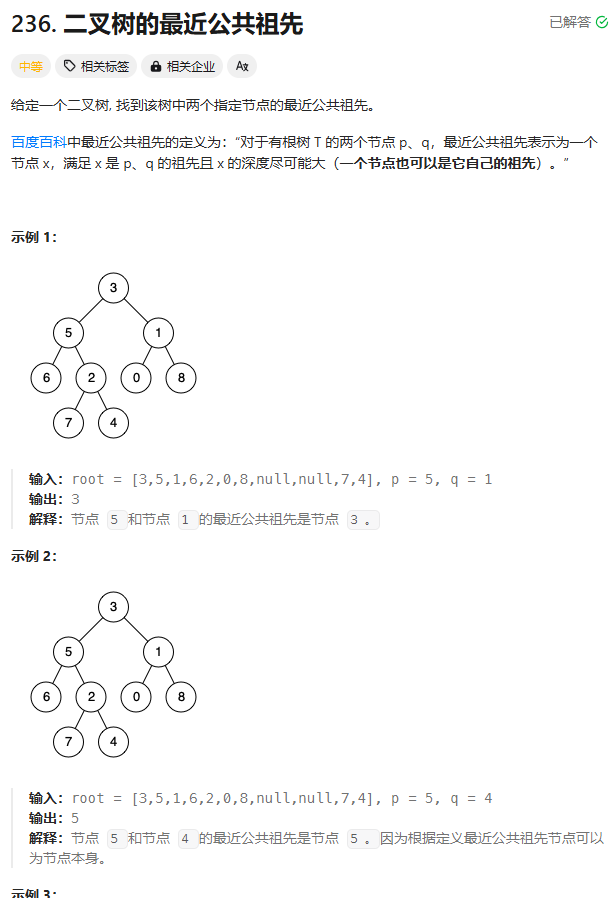
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
bool GetPath(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x, stack<TreeNode*>& path)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
path.push(root);
if (root == x)
{
return true;
}
if (GetPath(root->left, x, path))
{
return true;
}
if (GetPath(root->right, x, path))
{
return true;
}
path.pop();
return false;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
stack<TreeNode*> pPath;
stack<TreeNode*> qPath;
GetPath(root, p, pPath);
GetPath(root, q, qPath);
//找路径相遇点
while (pPath.size() != qPath.size())
{
if (pPath.size() > qPath.size())
{
pPath.pop();
}
else
{
qPath.pop();
}
}
while (pPath.top() != qPath.top())
{
pPath.pop();
qPath.pop();
}
return pPath.top();
}
};5.二叉树与双向链表

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL)
{}
};
class Solution
{
public:
void InOrderConvert(TreeNode* cur, TreeNode*& prev)
{
if (cur == nullptr)
{
return;
}
InOrderConvert(cur->left, prev);
cur->left = prev;
if (prev != nullptr)
{
prev->right = cur;
}
prev = cur;
InOrderConvert(cur->right, prev);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
InOrderConvert(pRootOfTree, prev);
TreeNode* head = pRootOfTree;
while (head != nullptr && head->left != nullptr)
{
head = head->left;
}
return head;
}
};6.从前序与中序序列构造二叉树

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& prei, int inbegin, int inend)
{
//中序区间不存在则是空树
if (inbegin > inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
//划分左右区间
int rooti = inbegin;
while (rooti <= inend)
{
if (inorder[rooti] ==preorder[prei])
{
break;
}
++rooti;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);
++prei;
//[inbegin,rooti-1] rooti [rooti+1,inend]
root->left = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, inbegin, rooti - 1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, rooti + 1, inend);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder)
{
int pi = 0;
return _buildTree(preorder, inorder, pi, 0, inorder.size() - 1);
}
};7.从中序与后序序列构造二叉树

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, int inbegin, int inend, vector<int>& postorder, int& pi)
{
if (inbegin > inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[pi]);
pi--;
//将该子树的中序遍历序列划分为其左子树和右子树的中序遍历序列
int rooti = inbegin;
while (inorder[rooti] != root->val)
{
rooti++;
}
root->right = _buildTree(inorder, rooti + 1, inend, postorder, pi);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder, inbegin, rooti - 1, postorder, pi);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder)
{
int i = postorder.size() - 1;
return _buildTree(inorder, 0, inorder.size() - 1, postorder, i);
}
};8.非递归实现二叉树的前序遍历

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (!st.empty() || cur != nullptr)
{
//准备开始访问一棵树
//访问左路结点
//左路结点的右子树
while (cur != nullptr)
{
v.push_back(cur->val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
//左路结点右子树
TreeNode* top = st.top();
st.pop();
//循环子问题访问右子树
cur = top->right;
}
return v;
}
};9.非递归实现二叉树的中序遍历

struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur || !st.empty())
{
while (cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();
st.pop();
v.push_back(top->val);
//访问右子树
cur = top->right;
}
return v;
}
};10.非递归实现二叉树的后序遍历
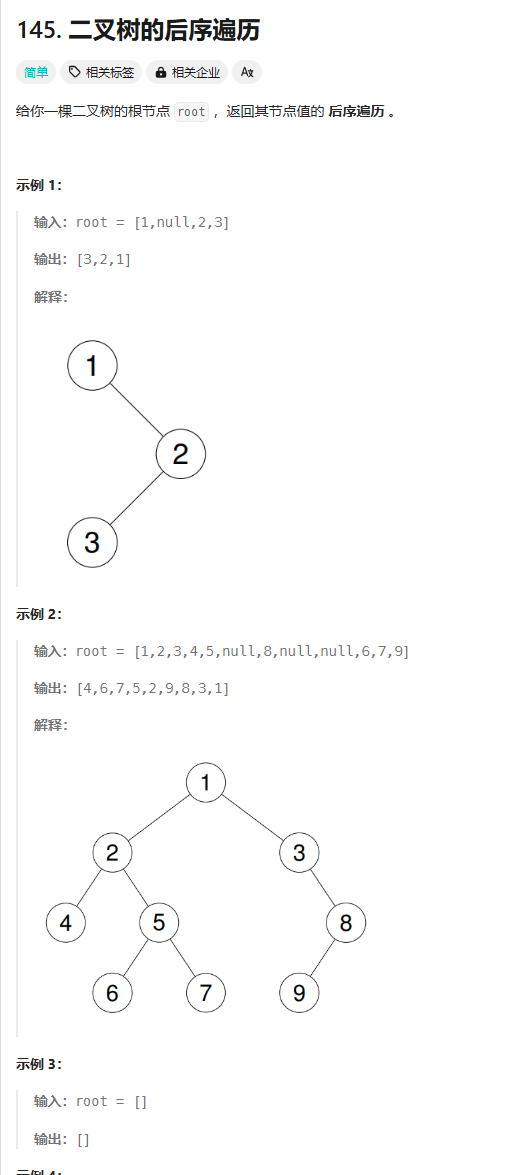
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
while (cur || !st.empty())
{
while (cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();
//1.top的右子树为空或者右子树已经访问过了(上一个访问的结点是右子树的根)
//那么说明右子树不用访问或者访问过了,可以访问根top
//2.右子树不为空且没有访问,则迭代子问题访问
if (top->right == nullptr || top->right == prev)
{
st.pop();
v.push_back(top->val);
prev = top;
}
else
{
cur = top->right;
}
}
return v;
}
};
11.前K个高频单词

class Solution
{
public:
struct Compare
{
bool operator()(const pair<int, string>& l, const pair<int, string>& r)
{
return l.first > r.first;
}
};
public:
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k)
{
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& str : words)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
vector<pair<int, string>> v;
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
v.push_back(make_pair(kv.second, kv.first));
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
stable_sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Compare());
vector<string> ret;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
ret.push_back(v[i].second);
}
return ret;
}
};12.在长度2N的数组中找出重复N次的元素

class Solution
{
public:
int repeatedNTimes(vector<int>& A)
{
size_t N = A.size() / 2;
// 用unordered_map统计每个元素出现的次数
unordered_map<int, int> m;
for (auto e : A)
{
m[e]++;
}
// 找出出现次数为N的元素
for (auto& e : m)
{
if (e.second == N)
{
return e.first;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
13.两个数组的交集I

class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
// 用unordered_set对nums1中的元素去重
unordered_set<int> s1;
for (auto e : nums1)
{
s1.insert(e);
}
// 用unordered_set对nums2中的元素去重
unordered_set<int> s2;
for (auto e : nums2)
{
s2.insert(e);
}
// 遍历s1,如果s1中某个元素在s2中出现过,即为交集
vector<int> vRet;
for (auto e : s1)
{
if (s2.find(e) != s2.end())
{
vRet.push_back(e);
}
}
return vRet;
}
};
14.两个数组的交集II

//哈希表
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2)
{
//为了降低空间复杂度,应该先将元素个数较少的数组放入哈希表
if (nums1.size() > nums2.size())
{
return intersect(nums2, nums1);
}
//1、将nums1中的每个数字以及对应出现的次数放入哈希表中
unordered_map<int, int> um;
for (auto e : nums1)
{
um[e]++;
}
//2、遍历nums2,找出nums1和nums2的交集
vector<int> vRet;
for (auto e : nums2)
{
if (um.count(e)) //该元素在哈希表中
{
vRet.push_back(e); //该元素属于交集
um[e]--; //减少该元素在哈希表中出现的次数
if (um[e] == 0) //该元素的次数已经变为0了
{
um.erase(e); //将该元素从哈希表中删除
}
}
}
return vRet;
}
};
15.两句话中的不常见单词

class Solution
{
public:
vector<string> uncommonFromSentences(string s1, string s2)
{
unordered_map<string, int> um;
//1、将两个字符串拼接起来,中间加一个" "字符串
string str = s1 + " " + s2;
//2、将拼接后字符串当中的单词放入哈希表
size_t start = 0; //字头
size_t pos = str.find(' '); //字尾
while (pos != string::npos) //直到找到字符串结尾
{
string word = str.substr(start, pos - start); //将单词提取出来
um[word]++; //将单词放入哈希表
start = pos + 1; //更新字头
pos = str.find(' ', start); //更新字尾
}
//将最后一个单词放入哈希表
string word = str.substr(start);
um[word]++;
//3、找出哈希表中只出现过一次的单词,即不常见单词
vector<string> vRet;
for (auto e : um)
{
if (e.second == 1) //只出现过一次的单词
{
vRet.push_back(e.first);
}
}
return vRet;
}
};