图论part03
孤岛的总面积


思路:既然某个网格在边界上的岛屿不是孤岛,那么就把非 孤岛的所有岛屿变成海洋,最后再次统计还剩余的岛屿占据的网格总数即可。
dfs:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int res = 0;
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
// TODO 4.dfs遍历逻辑
private static void dfs(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
graph[x][y] = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= graph.length || nextY >= graph[0].length) continue;
if(graph[nextX][nextY] == 1){
graph[nextX][nextY] = 0;
dfs(graph,nextX,nextY);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// TODO 1.生成graph
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// sc.colse();
// TODO 2.仅对四个边进行遍历,遇到陆地的时候将该陆地和与之相邻的陆地全部变为海洋
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][0] == 1){
dfs(graph,i,0);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][m - 1] == 1){
dfs(graph,i,m-1);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[0][j] == 1){
dfs(graph,0,j);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[n - 1][j] == 1){
dfs(graph,n-1,j);
}
}
// TODO 3.遍历图,获取所有岛屿土地数量
int sum = 0 ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[i][j] == 1 ){
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
bfs:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int res = 0;
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
// TODO 4.bfs遍历逻辑
private static void bfs(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
class Node{
int x;
int y;
public Node(int x , int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Node(x,y));
graph[x][y] = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node node = queue.remove();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = node.x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = node.y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= graph.length || nextY >= graph[0].length)
continue;
if(graph[nextX][nextY] == 1){
graph[nextX][nextY] = 0;
queue.add(new Node(nextX,nextY));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// TODO 1.生成graph
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// sc.colse();
// TODO 2.仅对四个边进行遍历,遇到陆地的时候将该陆地和与之相邻的陆地全部变为海洋
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][0] == 1){
bfs(graph,i,0);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][m - 1] == 1){
bfs(graph,i,m-1);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[0][j] == 1){
bfs(graph,0,j);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[n - 1][j] == 1){
bfs(graph,n-1,j);
}
}
// TODO 3.遍历图,获取所有岛屿土地数量
int sum = 0 ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[i][j] == 1 ){
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
沉没孤岛


思路:在这道题之中,我们只需要将图保留两份,一份计算孤岛,计算完之后对第二份图的孤岛进行去除即可。
DFS:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int res = 0;
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
// TODO 4.dfs遍历逻辑
private static void dfs(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
graph[x][y] = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= graph.length || nextY >= graph[0].length) continue;
if(graph[nextX][nextY] == 1){
graph[nextX][nextY] = 0;
dfs(graph,nextX,nextY);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// TODO 1.生成graph
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
int[][] graph2 = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
int num = sc.nextInt();
graph[i][j] = num;
graph2[i][j] = num;
}
}
// sc.colse();
// TODO 2.仅对四个边进行遍历,遇到陆地的时候将该陆地和与之相邻的陆地全部变为海洋
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][0] == 1){
dfs(graph,i,0);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][m - 1] == 1){
dfs(graph,i,m-1);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[0][j] == 1){
dfs(graph,0,j);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[n - 1][j] == 1){
dfs(graph,n-1,j);
}
}
// TODO 3.遍历图,获取所有岛屿土地数量
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[i][j] == 1 && graph2[i][j] == 1){
graph2[i][j] = 0;
}
System.out.print(graph2[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
// for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
// System.out.print(graph2[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
}
}
BFS:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int res = 0;
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
// TODO 4.bfs遍历逻辑
private static void bfs(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
class Node{
int x;
int y;
public Node(int x , int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Node(x,y));
graph[x][y] = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node node = queue.remove();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = node.x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = node.y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= graph.length || nextY >= graph[0].length)
continue;
if(graph[nextX][nextY] == 1){
graph[nextX][nextY] = 0;
queue.add(new Node(nextX,nextY));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// TODO 1.生成graph
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
int[][] graph2 = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
int num = sc.nextInt();
graph[i][j] = num;
graph2[i][j] = num;
}
}
// sc.colse();
// TODO 2.仅对四个边进行遍历,遇到陆地的时候将该陆地和与之相邻的陆地全部变为海洋
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][0] == 1){
bfs(graph,i,0);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if(graph[i][m - 1] == 1){
bfs(graph,i,m-1);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[0][j] == 1){
bfs(graph,0,j);
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[n - 1][j] == 1){
bfs(graph,n-1,j);
}
}
// TODO 3.遍历图,获取所有岛屿土地数量
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(graph[i][j] == 1 && graph2[i][j] == 1){
graph2[i][j] = 0;
}
System.out.print(graph2[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
水流问题
暴力DFS:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int m,n;
// static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{1-,0}};
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
private static void dfs(int[][] graph , boolean[][] visted , int x , int y ){
if(visted[x][y]) return ;
visted[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= n || nextY >= m) continue;
if(graph[x][y] < graph[nextX][nextY]) continue;
dfs(graph,visted,nextX,nextY);
}
}
private static boolean isResult(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
boolean[][] visted = new boolean[n][m];
dfs(graph,visted,x,y);
boolean isFirst = false;
boolean isSecond = false;
// 判断当前的(x,y)节点是否从第一组边界出去
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(visted[i][0]){
isFirst = true;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(visted[0][j]){
isFirst = true;
break;
}
}
// 判断当前的(x,y)节点是否从第二组边界出去
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(visted[i][m-1]){
isSecond = true;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(visted[n - 1][j]){
isSecond = true;
break;
}
}
return isFirst&&isSecond;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(isResult(graph,i,j))
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
暴力BFS:(超时)
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int m,n;
// static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{1-,0}};
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
private static void bfs(int[][] graph , boolean[][] visted , int x , int y ){
class Node{
int x ;
int y;
public Node(int x , int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Node(x,y));
visted[x][y] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node node = queue.remove();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nextX = node.x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = node.y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= n || nextY >= m ) continue;
if(visted[nextX][nextY]) continue;
if(graph[node.x][node.y] < graph[nextX][nextY] ) continue;
queue.add(new Node(nextX,nextY));
visted[nextX][nextY] = true;
}
}
}
private static boolean isResult(int[][] graph , int x , int y){
boolean[][] visted = new boolean[n][m];
bfs(graph,visted,x,y);
boolean isFirst = false;
boolean isSecond = false;
// 判断当前的(x,y)节点是否从第一组边界出去
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(visted[i][0]){
isFirst = true;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(visted[0][j]){
isFirst = true;
break;
}
}
// 判断当前的(x,y)节点是否从第二组边界出去
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(visted[i][m-1]){
isSecond = true;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(visted[n - 1][j]){
isSecond = true;
break;
}
}
return isFirst&&isSecond;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(isResult(graph,i,j))
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
DFS优化:
采用逆向思维,考虑水流从低处往高处可以流通的情况,从而获得第一组边界的流通情况和第二组流水的情况,二者均为true的情况则表明该网格可以从第一组边界和第二组边界流出。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int m,n;
// static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{1-,0}};
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
private static void dfs(int[][] graph , boolean[][] visted , int x , int y , int preH){
// 遇到边界或者访问过的点直接返回
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= graph.length ||y >= graph[0].length || visted[x][y]) return;
if(graph[x][y] < preH) return ;
visted[x][y] = true;
dfs(graph,visted,x+1,y,graph[x][y]);
dfs(graph,visted,x,y+1,graph[x][y]);
dfs(graph,visted,x-1,y,graph[x][y]);
dfs(graph,visted,x,y-1,graph[x][y]);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
boolean[][] firstB = new boolean[n][m];
boolean[][] secondB = new boolean[n][m];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 从上下边界进行DFS
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
dfs(graph,firstB,0,j,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
dfs(graph,secondB,n-1,j,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
// 从左右边界进行DFS
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
dfs(graph,firstB,i,0,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
dfs(graph,secondB,i,m-1,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++){
if(firstB[i][j] && secondB[i][j])
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
BFS(待补充)
建造最大岛屿(待完成)
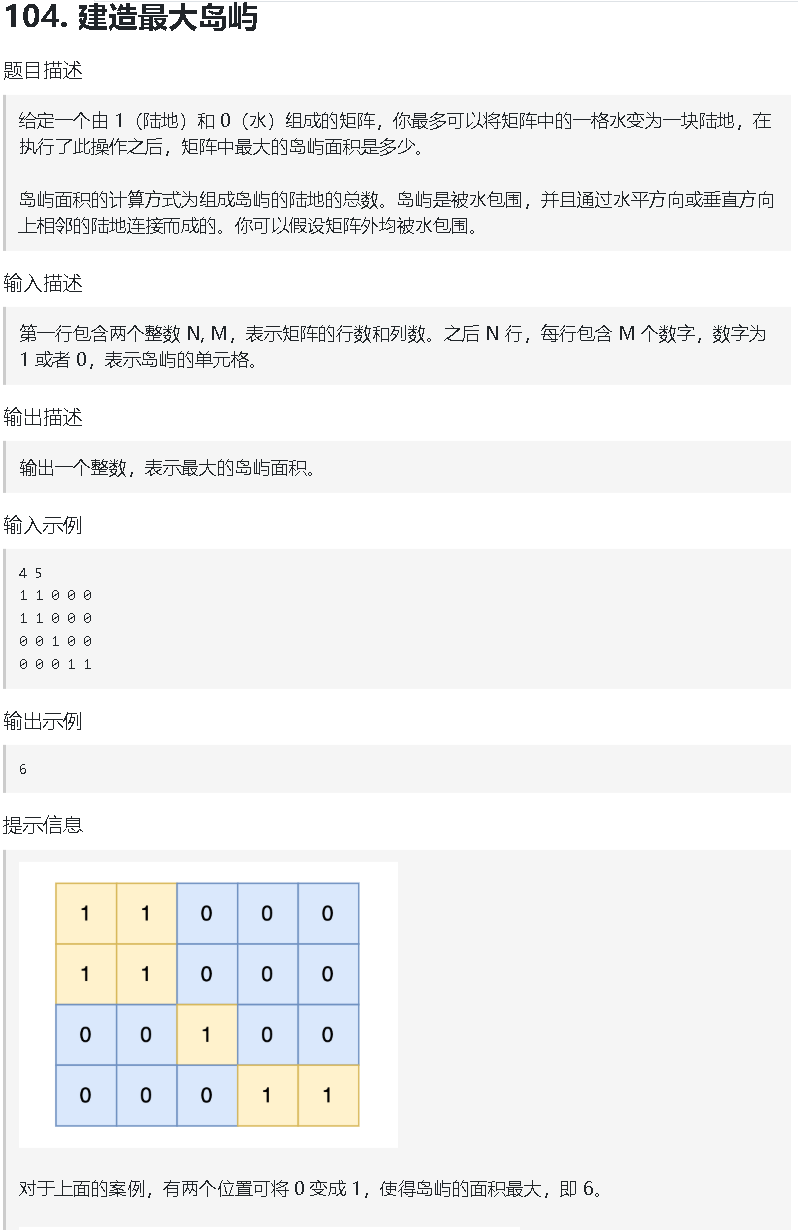
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 该方法采用 DFS
// 定义全局变量
// 记录每次每个岛屿的面积
static int count;
// 对每个岛屿进行标记
static int mark;
// 定义二维数组表示四个方位
static int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
// DFS 进行搜索,将每个岛屿标记为不同的数字
public static void dfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y, boolean[][] visited) {
// 当遇到边界,直接return
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length) return;
// 遇到已经访问过的或者遇到海水,直接返回
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
count++;
grid[x][y] = mark;
// 继续向下层搜索
dfs(grid, x, y + 1, visited);
dfs(grid, x, y - 1, visited);
dfs(grid, x + 1, y, visited);
dfs(grid, x - 1, y, visited);
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
// 接收输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 初始化mark变量,从2开始(区别于0水,1岛屿)
mark = 2;
// 定义二位boolean数组记录该位置是否被访问
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
// 定义一个HashMap,记录某片岛屿的标记号和面积
HashMap<Integer, Integer> getSize = new HashMap<>();
// 定义一个HashSet,用来判断某一位置水四周是否存在不同标记编号的岛屿
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
// 定义一个boolean变量,看看DFS之后,是否全是岛屿
boolean isAllIsland = true;
// 遍历二维数组进行DFS搜索,标记每片岛屿的编号,记录对应的面积
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllIsland = false;
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, i, j, visited);
getSize.put(mark, count);
mark++;
}
}
}
int result = 0;
if (isAllIsland) result = m * n;
// 对标记完的grid继续遍历,判断每个水位置四周是否有岛屿,并记录下四周不同相邻岛屿面积之和
// 每次计算完一个水位置周围可能存在的岛屿面积之和,更新下result变量
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
set.clear();
// 当前水位置变更为岛屿,所以初始化为1
int curSize = 1;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int curRow = i + dir[0];
int curCol = j + dir[1];
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= m || curCol < 0 || curCol >= n) continue;
int curMark = grid[curRow][curCol];
// 如果当前相邻的岛屿已经遍历过或者HashMap中不存在这个编号,继续搜索
if (set.contains(curMark) || !getSize.containsKey(curMark)) continue;
set.add(curMark);
curSize += getSize.get(curMark);
}
result = Math.max(result, curSize);
}
}
}
// 打印结果
System.out.println(result);
}
}

