目录
概述
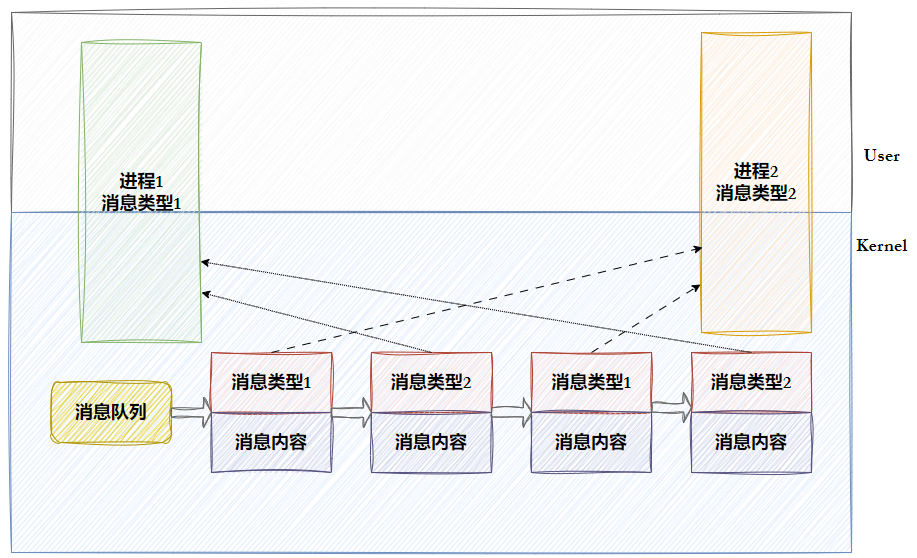
- 消息队列提供了⼀个从⼀个进程向另外⼀个进程发送有类型块数据的⽅法
- 每个数据块都被认为是有⼀个类型,接收者进程接收的数据块可以有不同的类型值
- 消息队列也有管道⼀样的不⾜,就是每个消息的最⼤⻓度是有上限的(MSGMAX)
- 每个消息队列的总的字节数也是有上限的(MSGMNB),系统上消息队列的总数也有上限(MSGMNI)的
通信形式
IPC对象数据结构
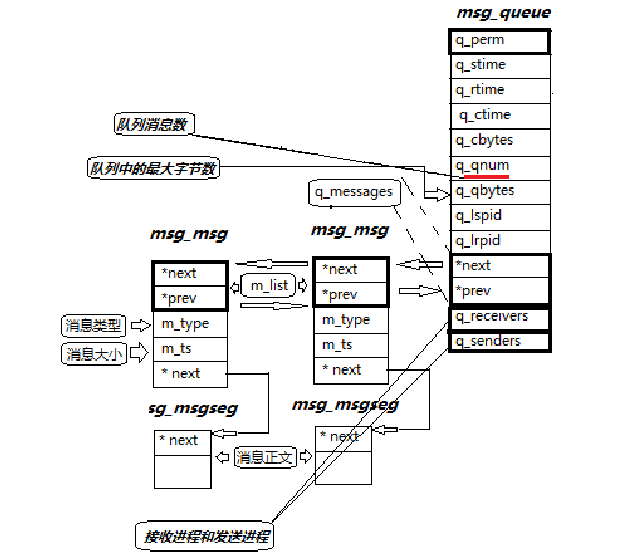
/usr/include/linux/ipc.h ,内核为每个IPC对象维护⼀个数据结构
struct ipc_perm {
key_t __key; /* Key supplied to xxxget(2) */
uid_t uid; /* Effective UID of owner */
gid_t gid; /* Effective GID of owner */
uid_t cuid; /* Effective UID of creator */
gid_t cgid; /* Effective GID of creator */
unsigned short mode; /* Permissions */
unsigned short __seq; /* Sequence number */
};
消息队列结构
/usr/include/linux/msg.h
struct msqid_ds {
struct ipc_perm msg_perm;
struct msg msg_first; / first message on queue,unused */
struct msg msg_last; / last message in queue,unused */
__kernel_time_t msg_stime; /* last msgsnd time */
__kernel_time_t msg_rtime; /* last msgrcv time */
__kernel_time_t msg_ctime; /* last change time */
unsigned long msg_lcbytes; /* Reuse junk fields for 32 bit */
unsigned long msg_lqbytes; /* ditto */
unsigned short msg_cbytes; /* current number of bytes on queue */
unsigned short msg_qnum; /* number of messages in queue */
unsigned short msg_qbytes; /* max number of bytes on queue */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t msg_lspid; /* pid of last msgsnd */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t msg_lrpid; /* last receive pid */
};
消息队列内核表示
接口说明
msgget
NAME
msgget - get a System V message queue identifier
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);
RETURN VALUE
If successful, the return value will be the message queue identifier
(a nonnegative integer), otherwise -1 with errno indicating the error.
参数
- key : 某个消息队列的名字
- msgflg :由九个权限标志构成,它们的⽤⽤法和创建⽂⽂件时使⽤⽤的mode模式标志是⼀⼀样
返回值
- 成功返回⼀个⾮负整数,即该消息队列的标识码;失败返回-1
msgctl
NAME
msgctl - System V message control operations
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgctl(int msqid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf);
struct msqid_ds {
struct ipc_perm msg_perm; /* Ownership and permissions */
time_t msg_stime; /* Time of last msgsnd(2) */
time_t msg_rtime; /* Time of last msgrcv(2) */
time_t msg_ctime; /* Time of last change */
unsigned long __msg_cbytes; /* Current number of bytes in
queue (nonstandard) */
msgqnum_t msg_qnum; /* Current number of messages
in queue */
msglen_t msg_qbytes; /* Maximum number of bytes
allowed in queue */
pid_t msg_lspid; /* PID of last msgsnd(2) */
pid_t msg_lrpid; /* PID of last msgrcv(2) */
};
RETURN VALUE
On success, IPC_STAT, IPC_SET, and IPC_RMID return 0. A successful
IPC_INFO or MSG_INFO operation returns the index of the highest used entry in
the kernel's internal array record-
ing information about all message queues. (This information can be
used with repeated MSG_STAT or MSG_STAT_ANY operations to obtain information
about all queues on the system.)
A successful MSG_STAT or MSG_STAT_ANY operation returns the identifier
of the queue whose index was given in msqid.
On error, -1 is returned with errno indicating the error.
参数
- msgid : 由 msgget 函数返回的消息队列标识码
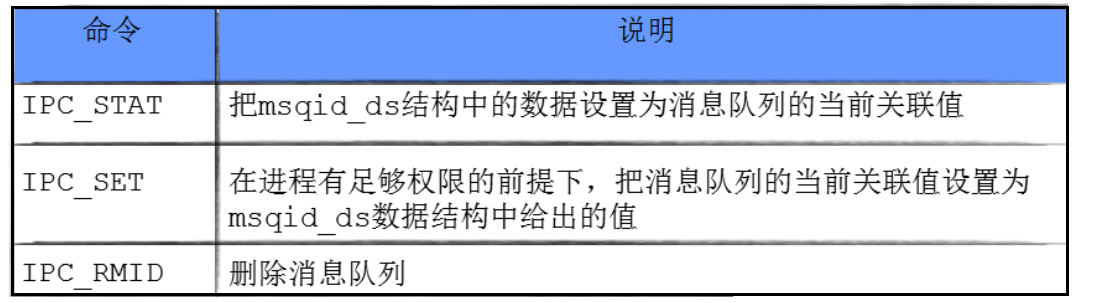
- cmd :将要采取的动作(有三个可取值),分别如下:
- buf : 属性缓冲区
返回值
- 成功返回0;失败返回-1
msgsnd
NAME
msgrcv, msgsnd - System V message queue operations
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);
参数
- msgid : 由 msgget 函数返回的消息队列标识码
- msgp:是⼀个指针,指针指向准备发送的消息
- msgsz:是msgp指向的消息⻓度,这个⻓度不含保存消息类型的那个long int⻓整型
- msgflg:控制着当前消息队列满或到达系统上限时将要发⽣⽣的事情, 0即可 ( msgflg=IPC_NOWAIT 表⽰⽰队列满不等待,返回 EAGAIN 错误 )。
返回值
- 成功返回0;失败返回-1
关于消息主体
struct msgbuf {
long mtype; /* message type, must be > 0 */
char mtext[1]; /* message data */
};
// 以—个long int⻓整数开始,接收者函数将利⽤⽤这个⻓整数确定消息的类型
msgrcv
NAME
msgrcv, msgsnd - System V message queue operations
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
ssize_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp, int
msgflg);
参数
- msgid : 由 msgget 函数返回的消息队列标识码
- msgp :是—个指针,指针指向准备接收的消息
- msgsz :是 msgp 指向的消息⻓度,这个⻓度不含保存消息类型的那个long int⻓整型
- msgtype :它可以实现接收消息的类型,也可以模拟优先级的简单形式进⾏接收
- msgflg :控制着队列中没有相应类型的消息可供接收时将要发⽣⽣的事
返回值
- 成功返回实际放到接收缓冲区⾥⾥去的字符个数,失败返回 -1
msgflg标志位
msgtype=0返回队列第—条信息
msgtype>0返回队列第—条类型等于msgtype的消息
msgtype<0返回队列第—条类型⼩于等于msgtype绝对值的消息,并且是满⾜⾜条件的消息类型最小的消息
msgflg=IPC_NOWAIT,队列没有可读消息不等待,返回ENOMSG错误。
msgflg=MSG_NOERROR,消息大小超过msgsz时被截断
msgtype>0且msgflg=MSG_EXCEPT,接收类型不等于msgtype的第—条消息
样例代码
基本通信代码
MsgQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#define SIZE 1024
#define PATHNAME "/tmp"
#define PROJID 0x4321
#define CREATE_NEW_MSGQUEUE (IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666)
#define GET_MSGQUEUE (IPC_CREAT)
typedef struct
{
long mtype;
char mtext[SIZE];
} msg_t;
class MsgQueueBase
{
public:
MsgQueueBase()
{
}
bool BuildMsgQueue(int flg)
{
_key = ::ftok(PATHNAME, PROJID);
if (_key < 0)
exit(1);
_msgid = ::msgget(_key, flg);
if (_msgid < 0)
exit(2);
return true;
}
bool SendMessage(const std::string& in, long type)
{
msg_t msg;
msg.mtype = type;
memset(msg.mtext, 0, sizeof(msg.mtext));
strncpy(msg.mtext, in.c_str(), in.size());
int n = ::msgsnd(_msgid, &msg, in.size(), 0);
if (n < 0)
return false;
return true;
}
bool RecvMessage(std::string* out, long type)
{
msg_t msg;
int n = ::msgrcv(_msgid, &msg, SIZE, type, 0);
if (n < 0)
return false;
msg.mtext[n] = 0; // 当做字符串
*out = msg.mtext;
return true;
}
bool DeleteMsgQueue()
{
int n = ::msgctl(_msgid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
return n == 0;
}
~MsgQueueBase()
{
}
protected:
key_t _key;
int _msgid;
};
class MsgQueueClient : public MsgQueueBase
{
public:
MsgQueueClient()
{
bool res = MsgQueueBase::BuildMsgQueue(GET_MSGQUEUE); // 获取
(void)res;
}
};
class MsgQueueServer : public MsgQueueBase
{
public:
MsgQueueServer()
{
bool res = MsgQueueBase::BuildMsgQueue(CREATE_NEW_MSGQUEUE); // 创建
(void)res;
}
~MsgQueueServer()
{
bool res = MsgQueueBase::DeleteMsgQueue();
(void)res;
}
};
#define SERVER 1
#define CLIENT 2Client.cc
#include "MsgQueue.hpp"
int main()
{
MsgQueueClient mq;
std::string msg;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter# ";
std::getline(std::cin, msg);
mq.SendMessage(msg, CLIENT);
if (msg == "q") break;
}
return 0;
}Server.cc
#include "MsgQueue.hpp"
#include "ChainOfResponsibility.hpp"
int main()
{
std::string msg;
MsgQueueServer mq;
HandlerEntry he;
he.EnableHandler(true, true, true);
while(true)
{
mq.RecvMessage(&msg, CLIENT);
std::cout << "get message: " << msg << std::endl;
if(msg == "q") break;
he.Run(msg);
}
return 0;
}makefile
.PHONY:all
all:client server
client:Client.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17
server:Server.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f client server结论:
- 消息队列的⽣命周期是随内核的
- ipcs -q && ipcrm -q msgfd
- 消息队列⽀持全双⼯通信
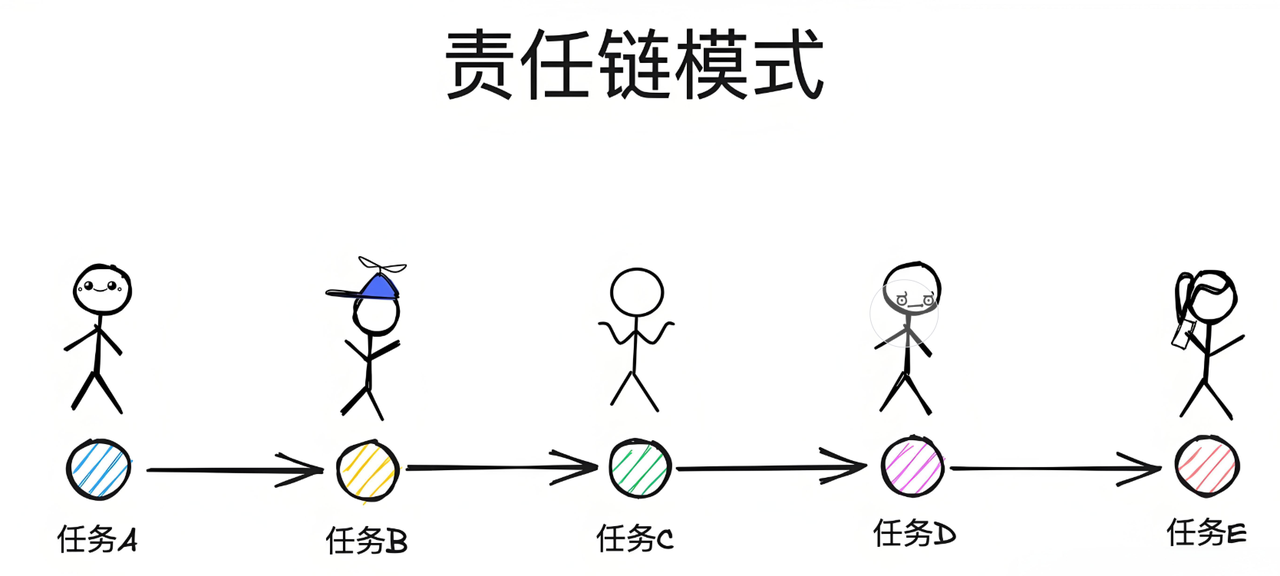
责任链模式
新需求:
- client 发送给 server 的输⼊内容,拼接上时间,进程pid信息
- server 收到的内容持久化保存到文件中
- 文件的内容如果过大,要进行切片保存并在指定的⽬录下打包保存,命令⾃定义
解决方案:责任链模式
⼀种行为设计模式,它允许你将请求沿着处理者链进行传递。每个处理者都对请求进行检查,以决定是否处理它。如果处理者能够处理该请求,它就处理它;否则,它将请求传递给链中的下⼀个处理者。这个模式使得多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免了请求的发送者和接收者之间的紧耦合。
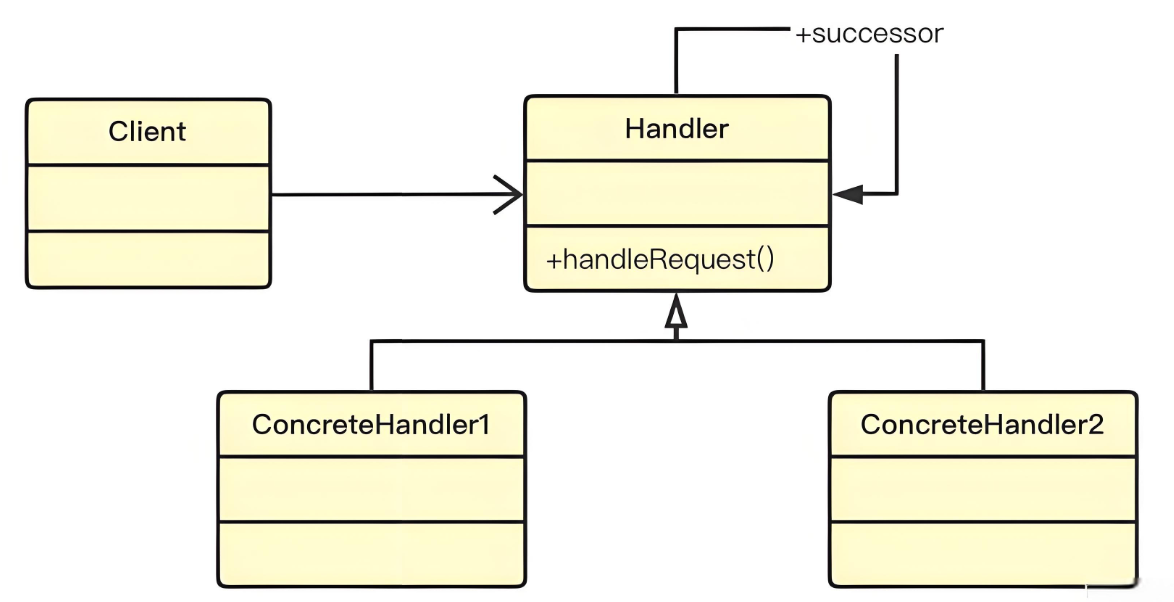
责任链代码结构
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <memory>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <ctime>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
class HandlerText
{
public:
HandlerText() : _enable(true)
{
}
virtual ~HandlerText() = default;
void SetNextHandler(std::shared_ptr<HandlerText> handler)
{
_next_handler = handler;
}
void Enable() { _enable = true; }
void DisEnable() { _enable = false; }
bool IsEnable() { return _enable; }
virtual void Execute(std::string &info) = 0;
protected: // 这里要protected,方便继承
std::shared_ptr<HandlerText> _next_handler;
bool _enable;
};
class HandlerTextFormat : public HandlerText
{
public:
~HandlerTextFormat()
{
}
void Execute(std::string &info) override
{
if (HandlerText::IsEnable())
{
// 开始处理,添加简单的补充信息
std::cout << "Format ..." << std::endl;
// 简单处理
std::stringstream ss;
ss << time(nullptr) << " - " << getpid() << " - " << info << "\n";
info = ss.str();
sleep(1);
}
if (_next_handler) // 如果_next_handler被设置,就交给下一个继续加工处理
_next_handler->Execute(info);
else
std::cout << "责任链节点结束,处理完成" << std::endl;
}
};
std::string defaultpath = "./tmp/";
std::string defaultfilename = "test.log";
class HandlerTextSaveFile : public HandlerText
{
public:
HandlerTextSaveFile() : _filepath(defaultpath), _filename(defaultfilename)
{
if (std::filesystem::exists(_filepath))
return;
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_filepath);
}
catch (std::filesystem::filesystem_error &e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
~HandlerTextSaveFile()
{
}
void Execute(std::string &info) override
{
if (HandlerText::IsEnable())
{
// 开始处理,保存到指定的文件中
std::cout << "Save ..." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
const std::string file = _filepath + _filename;
std::ofstream out(file, std::ios::app);
if (!out.is_open())
return;
out << info;
out.close();
}
if (_next_handler) // 如果_next_handler被设置,就交给下一个继续加工处理
_next_handler->Execute(info);
else
std::cout << "责任链节点结束,处理完成" << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string _filepath;
std::string _filename;
};
const int maxline = 5; // 为了尽快触发备份动作,该值设置小一些
class HandlerTextBackupFile : public HandlerText
{
public:
HandlerTextBackupFile() : _max_line_number(maxline), _filepath(defaultpath), _filename(defaultfilename)
{
}
~HandlerTextBackupFile()
{
}
void Execute(std::string &info) override
{
if (HandlerText::IsEnable())
{
// 开始处理,对文件进行增量备份
std::cout << "Backup ..." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
const std::string filename = _filepath + _filename;
// 1. 打开文件
std::ifstream in(filename);
if (!in.is_open())
return;
std::string line;
int currentlines = 0;
while (std::getline(in, line))
{
currentlines++;
}
// 关闭文件流
in.close();
// 2. 备份
if (currentlines > _max_line_number)
{
std::cout << "消息行数超过" << _max_line_number << ", 触发日志备份" << std::endl;
// 大于才做备份,否则什么走不做
Backup();
}
}
if (_next_handler) // 如果_next_handler被设置,就交给下一个继续加工处理
_next_handler->Execute(info);
else
std::cout << "责任链节点结束,处理完成" << std::endl;
}
void Backup()
{
std::string newname = _filename + "." + std::to_string(time(nullptr));
pid_t id = fork();
if (id == 0)
{
chdir(_filepath.c_str()); // 更改进程路径,进入"./tmp/"路径下
std::filesystem::rename(_filename, newname); // rename比较快,也不影响未来其他继续写入的操作,因为会重新形成文件
std::string tarname = newname + ".tgz";
// 子进程打包备份
std::cout << "打包 : " << newname << " 成为: " << tarname << "开始" << std::endl;
execlp("tar", "tar", "czf", tarname.c_str(), newname.c_str(), nullptr); // 注意这里要以nullptr结尾,注意这里的坑
std::cout << "打包 : " << newname << " 成为: " << tarname << "失败" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
std::string tempfile = _filepath + newname;
std::filesystem::remove(tempfile); // 删除文件原件,只要tar包
}
private:
int _max_line_number;
std::string _filepath;
std::string _filename;
};
class HandlerEntry
{
public:
HandlerEntry()
{
// 构建责任链节点对象
_format = std::make_shared<HandlerTextFormat>();
_save = std::make_shared<HandlerTextSaveFile>();
_backup = std::make_shared<HandlerTextBackupFile>();
// 链接责任链
_format->SetNextHandler(_save);
_save->SetNextHandler(_backup);
}
void EnableHandler(bool isformat, bool issave, bool isbackup)
{
isformat ? _format->Enable() : _format->DisEnable();
issave ? _save->Enable() : _save->DisEnable();
isbackup ? _backup->Enable() : _backup->DisEnable();
}
void Run(std::string &info)
{
_format->Execute(info);
}
private:
std::shared_ptr<HandlerText> _format;
std::shared_ptr<HandlerText> _save;
std::shared_ptr<HandlerText> _backup;
};