typedef int QDataType;
//定义队列结点的结构
typedef struct QueueNode {
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
//定义队列的结构
typedef struct Queue {
QueueNode* phead; //节点结构的指针
QueueNode* ptail; //节点结构的指针
int size; //队列有效元素个数
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
//队列里面只有phead和ptail
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) {
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail!\n");
exit(1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//队列为空,队头队尾都是newnode
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else {
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL; //pq->phead为空,返回true
}
//计算队列里面的有效元素个数
QDataType QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
//QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
//int size = 0;
//while (pcur)
//{
// size++;
// pcur = pcur->next;
// //时间复杂度为O(N)
// //其余的队列接口复杂度都是O(1)
// //尝试换一种方法来实现,达到此接口的时间复杂度为O(1)
//}
//return size;
return pq->size;
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);//传过来的pq不为空 or 有效的队列结构
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//空队列不可取出数据
//只有一个节点
if (pq->phead == pq->ptail)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else {
QueueNode* next=pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//取队列头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);//传过来的pq不为空 or 有效的队列结构
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//空队列不可取出数据
return pq->phead->data;
}
//取队列尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);//传过来的pq不为空 or 有效的队列结构
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//空队列不可取出数据
return pq->ptail->data;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur)
{
QueueNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
//将队列的两个指针置为空,防止变为野指针
pq->size = 0;
}
/////////////////////////上述是自己实现的队列的结构和方法///////////////////////////
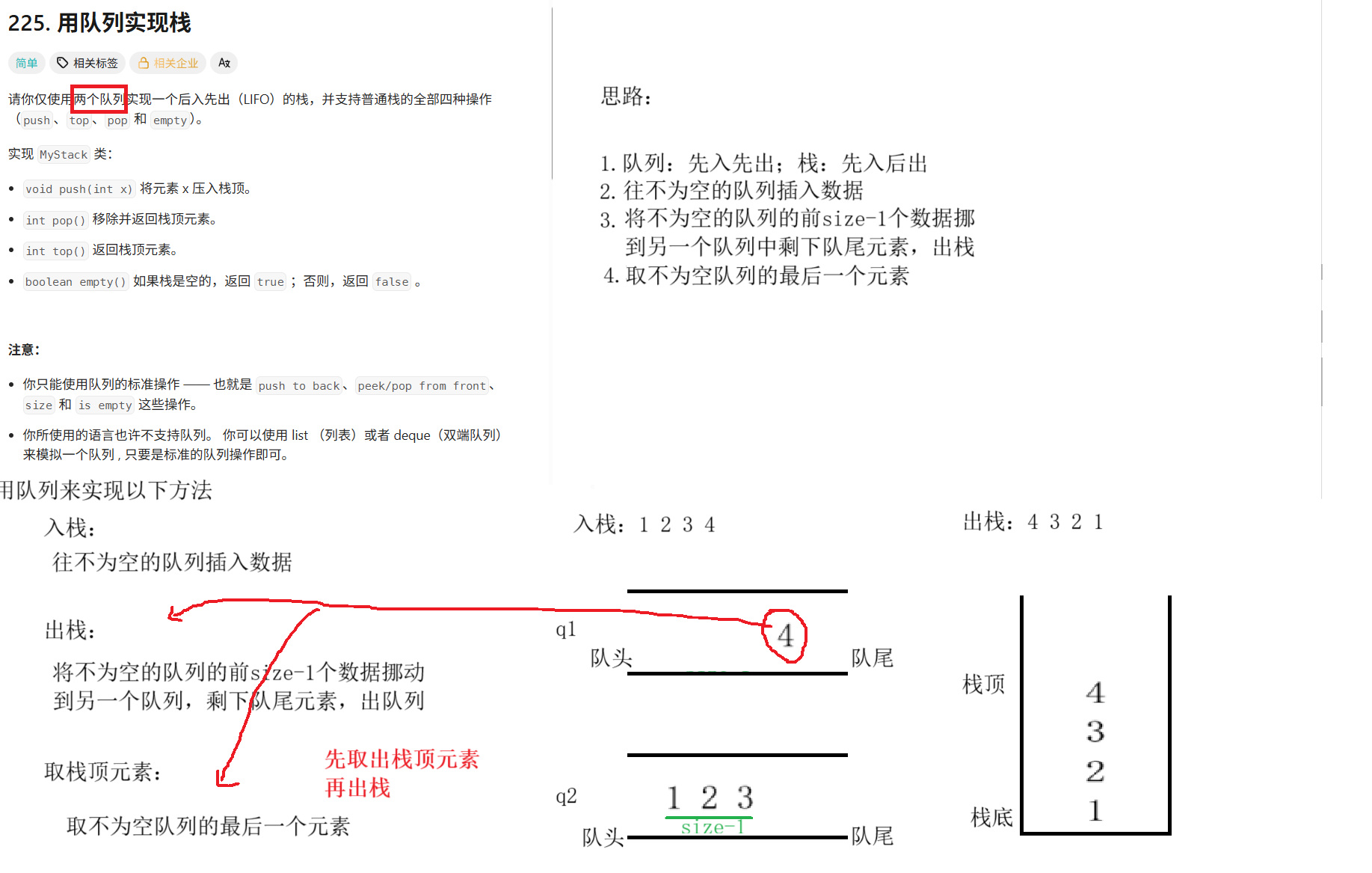
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
//栈的初始化 --- 初始化两个队列
//MyStack* 一位置需要返回当前栈的指针
MyStack* pst=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//入栈
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
// q1不为空队列,往q1里面插入数据
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}else{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
// 出栈 --- 找空队列和非空队列
Queue* emp=&obj->q1; //obj->ql类型为Queue 所以要加上&
Queue* noneEmp=&obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
emp=&obj->q2;
noneEmp=&obj->q1;
}
//非空队列前size-1个数据往空队列里面挪动数据
while(QueueSize(noneEmp)>1)
{
QueuePush(emp,QueueFront(noneEmp));
QueuePop(noneEmp);
}
int top=QueueFront(noneEmp);
QueuePop(noneEmp);
return top;
}
//把不为空队列的队尾元素返回,相当于取栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}else{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj); //obj 通过malloc来的,需要释放
obj=NULL;
}
/**
* Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();
* myStackPush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);
* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);
* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);
* myStackFree(obj);
*/
typedef int STDataType;
//定义栈的数据结构
//栈的底层结构 链表或者是数组都是可以的 但是数组的实现会更加简单(有点像顺序表)
typedef struct Stack {
STDataType* arr;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//栈的初始化
void StackInit(Stack* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//栈的销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) {
if (ps->arr != NULL)
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈 -- 栈顶 -- 顺序表的尾插
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//空间不够 --- 增容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
//扩容
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!\n");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//空间足够 --- 直接插入数据
ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//判空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == NULL;
//top=NULL 返回 true
//top!=NULL 返回 false
}
//出栈 -- 栈顶
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
////////////////////////上述是自己实现的栈的结构和接口实现///////////////////////////
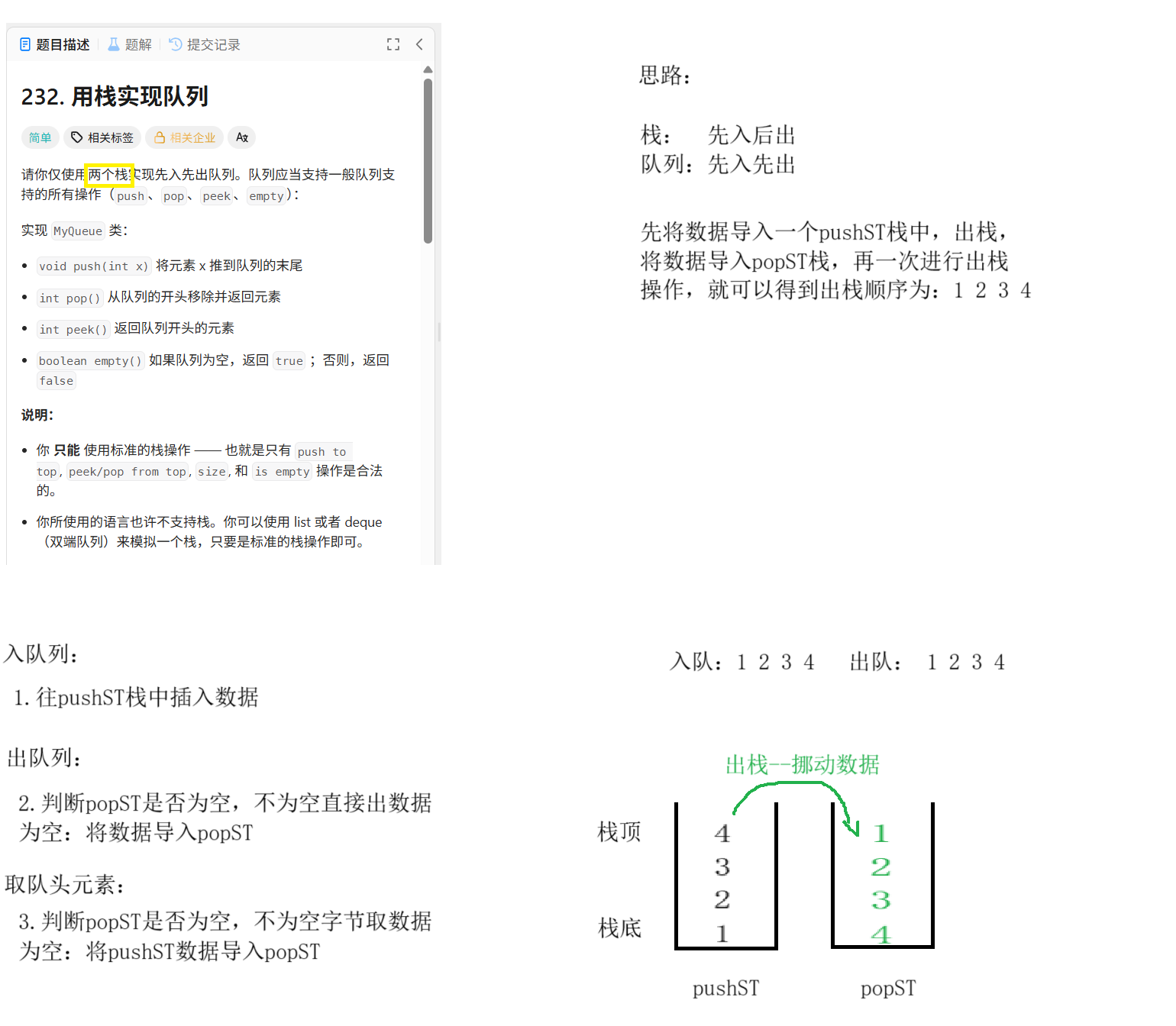
typedef struct {
// 定义
Stack pushST;
Stack popST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
// 初始化
MyQueue* pq=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&pq->pushST);
StackInit(&pq->popST);
return pq;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
//入队
StackPush(&obj->pushST,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
{
//将pushST中的数据全部导入popST
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
int top=StackTop(&obj->popST);
StackPop(&obj->popST);
return top;
}
//取队头
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
{
//将pushST中的数据全部导入popST
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
int top=StackTop(&obj->popST);
return top;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) && StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestroy(&obj->pushST);
StackDestroy(&obj->popST);
free(obj);
obj=NULL;
}
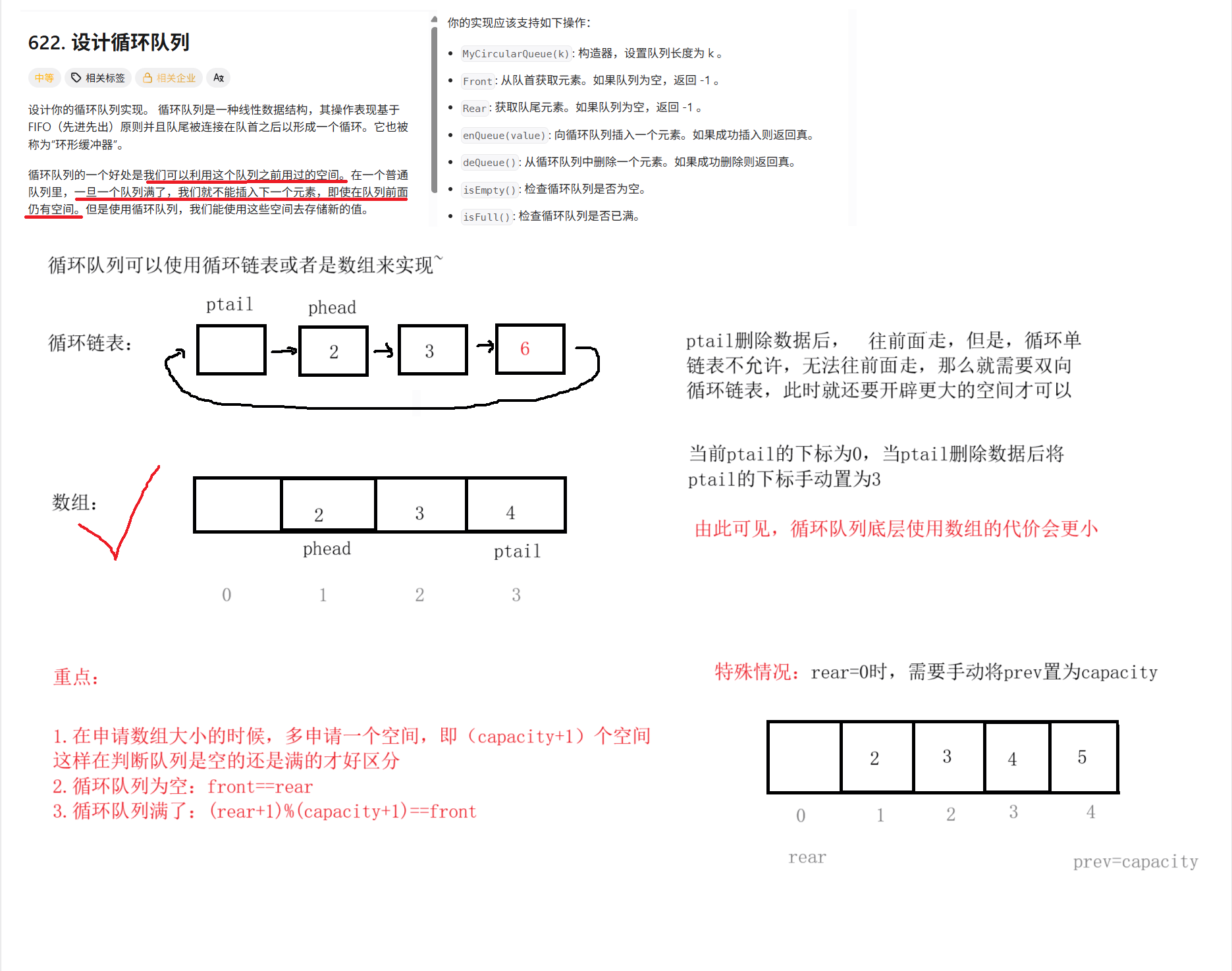
typedef struct {
//底层结构为数组
int* arr;
int front;//队头
int rear;//队尾
int capacity;//循环队列的空间大小
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* pq=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
//申请k+1个空间
pq->arr=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
pq->front=pq->rear=0;
pq->capacity=k;
return pq;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->rear;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->capacity+1)==obj->front;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
//向循环队列中插入数据
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->arr[obj->rear++]=value;
// obj->rear=obj->rear%(obj->capacity+1);
obj->rear %= obj->capacity+1;
return true;
}
//删除数据
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
//队列不为空
++obj->front;
obj->front %= obj->capacity+1;
return true;
}
//取队头
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
//队列不为空
return obj->arr[obj->front];
}
//取队尾
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
int prev=obj->rear-1;
if(obj->rear==0)
{
prev=obj->capacity;
}
return obj->arr[prev];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(obj->arr)
{
free(obj->arr);
}
free(obj);
obj=NULL;
}