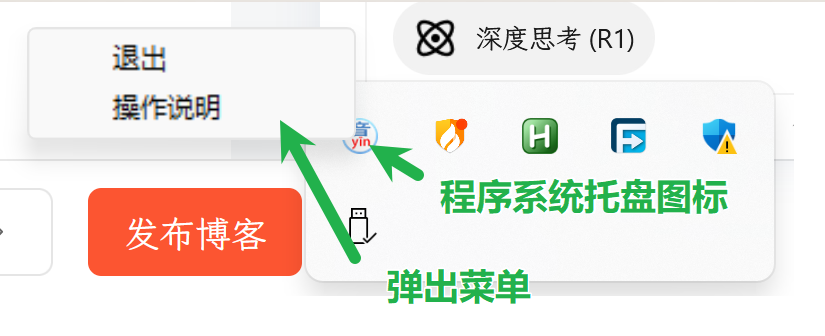
读书或者阅读文档的时候,会碰上一些生字。尽管国学大师网的汉字宝典用来查生字非常好用,而且包含的汉字也特别多,但是如果能够有个可以屏幕取词后提示拼音的工具,无疑更为方便,本文就用python写一个启动后保持在系统托盘的查拼音程序,并打包成exe文件,方便设置为系统启动时自动运行。
屏幕取词可以使用pillow截取鼠标所在位置一定范围的图像再识别文字,但是免费的tesseract识别中文字符的准确率还是不够高,所以不考虑使用这个方式。这个程序要求用户先选择可编辑字符,然后按下热键,再将用户选择的第一个汉字的拼音显示在鼠标上方。可以通过将已选择的字符复制到剪贴板,再读取剪贴板获取用户选择的字符。程序中使用keyboard库模拟按键Ctrl+C实现复制字符,使用pyperclip库操作剪贴板。读取用户选择的字符后,通过pypinyin库查询到相关字符的拼音,用Tinker库将拼音提示框显示在用mouse库获取到的鼠标所在位置上方。
具体代码如下:
import os
import sys
import pyperclip
import pypinyin
import keyboard
import mouse
import threading
import time
from PIL import Image
import pystray
from tkinter import Tk, Label, Toplevel, font, Button
# 全局变量
is_running = True # 程序运行状态标志
hotkey = 'ctrl + \'' # 程序热键,Ctrl+单引号,“引”谐音“音”
# 获取资源文件路径,能够兼容cx_freeze或PyInstaller打包后的exe和直接从源码运行
def resource_path(relative_path):
# 如果是cx_freeze打包后的exe,sys.frozen为True
if getattr(sys, 'frozen', False):
# exe所在目录
return os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sys.executable), relative_path)
# 如果是PyInstaller打包后的exe,sys._MEIPASS存在
elif hasattr(sys, '_MEIPASS'):
return os.path.join(sys._MEIPASS, relative_path)
# 源码运行
return os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), relative_path)
# 显示拼音提示框(在鼠标位置上方)
def show_pinyin_popup(pinyin_text):
root = Tk()
root.withdraw() # 隐藏主窗口
popup = Toplevel(root)
popup.overrideredirect(True) # 去除窗口边框
popup.attributes('-topmost', True) # 置顶
try:
custom_font = font.Font(family='Microsoft YaHei', size=12)
except:
custom_font = font.Font(size=12)
label = Label(
popup,
text=pinyin_text,
bg='lightyellow',
fg='black',
font=custom_font,
padx=8,
pady=4,
relief='solid',
borderwidth=1
)
label.pack()
x, y = mouse.get_position()
popup.update_idletasks()
popup.geometry(f'+{x - popup.winfo_width() // 2}+{y - popup.winfo_height() - 10}')
# 2秒后关闭弹窗和主窗口
def close_all():
popup.destroy()
root.destroy()
# 2000毫秒后异步关闭popup窗体和root窗体,防止下一次显示拼音窗体出错
root.after(2000, close_all)
root.mainloop()
def show_help(icon=None, item=None):
def _show():
help_win = Tk()
help_win.attributes('-topmost', True)
help_win.overrideredirect(True) # 去除窗口边框
# 说明内容
label = Label(
help_win,
text=f"1、选择要查询拼音的汉字后按程序热键“{hotkey}”查询拼音。\n\n"
f"2、对word等写入剪贴板耗时较长的软件,可先选择汉字后使用软件\n"
f"自身功能将文字复制到剪贴板,再按热键查询拼音。",
justify='left',
padx=16,
pady=12
)
label.pack()
# 关闭按钮
close_btn = Button(help_win, text="确定", command=help_win.destroy, width=10)
close_btn.pack(pady=(0, 12))
# 居中显示
help_win.update_idletasks()
w = help_win.winfo_width()
h = help_win.winfo_height()
x = (help_win.winfo_screenwidth() - w) // 2
y = (help_win.winfo_screenheight() - h) // 2
help_win.geometry(f"{w}x{h}+{x}+{y}")
help_win.mainloop()
# 在新线程中显示帮助窗口,防止主线程sleep时帮助窗口不能及时响应关闭事件
threading.Thread(target=_show, daemon=True).start()
# 处理热键事件
def on_hotkey():
if not is_running:
return
# 1. 保存原始剪贴板内容
original_content = pyperclip.paste()
try:
# 2. 模拟 Ctrl+C
keyboard.press_and_release('ctrl+c')
# 等待剪贴板内容变化(成功复制字符),最多等待0.8秒
for _ in range(10):
time.sleep(0.1)
if pyperclip.paste() != original_content:
break
# 3. 读取新剪贴板内容
new_content = pyperclip.paste()
# 4. 查找第一个汉字
first_chinese_char = None
for char in new_content:
if '\u4e00' <= char <= '\u9fff': # 判断是否为汉字
first_chinese_char = char
break
if first_chinese_char:
# 获取所有可能的拼音(多音字)
pinyin_list = pypinyin.pinyin(
first_chinese_char,
style=pypinyin.Style.TONE,
heteronym=True,
errors='ignore'
)
# print(f"找到汉字: {first_chinese_char}, 拼音: {pinyin_list[0]}")
pinyin_str = ', '.join(pinyin_list[0])
# 在鼠标位置显示拼音
show_pinyin_popup(pinyin_str)
finally:
# 5. 恢复原始剪贴板内容
pyperclip.copy(original_content)
# 退出程序
def on_exit(icon, item):
global is_running
is_running = False
icon.stop()
# 主函数
def main():
global is_running
print(f"{resource_path('pinyin.png')=}")
# 加载pinyin.png作为托盘图标
icon_image = Image.open(resource_path('pinyin.png'))
icon = pystray.Icon(
'chinese_pinyin_helper',
icon_image,
'查拼音',
menu=pystray.Menu(
pystray.MenuItem('退出', on_exit),
pystray.MenuItem('操作说明', show_help)
)
)
threading.Thread(target=icon.run, daemon=True).start()
keyboard.add_hotkey(hotkey, on_hotkey, suppress=False)
print(f"程序热键:{hotkey}")
print("对word等写入剪贴板耗时较长的程序,可先将选择的字符复制到剪贴板,再按热键查询拼音。")
print("最小化到系统托盘,点击退出可关闭。")
try:
while is_running:
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("程序退出")
is_running = False
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()为了方便使用,可以将上面的程序使用cx_freeze打包为exe文件,然后设置为开机启动,即可在需要时随时使用。程序中使用了pinyin.png作为图标,使用cx_freeze打包后的exe文件访问资源的路径与直接从python源代码运行时访问资源路径的方式不同,上面的脚本文件中使用resource_path函数做好了访问资源文件的兼容:
# 获取资源文件路径,能够兼容cx_freeze或PyInstaller打包后的exe和直接从源码运行
def resource_path(relative_path):
# 如果是cx_freeze打包后的exe,sys.frozen为True
if getattr(sys, 'frozen', False):
# exe所在目录
return os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sys.executable), relative_path)
# 如果是PyInstaller打包后的exe,sys._MEIPASS存在
elif hasattr(sys, '_MEIPASS'):
return os.path.join(sys._MEIPASS, relative_path)
# 源码运行
return os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), relative_path)
下面是cx_freeze的打包脚本(命名为cxfreeze_setup.py):
# cxfreeze_setup.py
from cx_Freeze import setup, Executable
setup(
name="search_pinyin",
version="1.0",
description="查拼音",
options={
"build_exe": {
"include_files": ["pinyin.png"], # 包含图标文件
"packages": ["tkinter",
"pyperclip",
"pypinyin",
"keyboard",
"mouse",
"pystray",
"PIL",
"os",
"sys",
"threading",
"time"], # 程序所使用的依赖包
"excludes": ["unittest", "email", "html", "http", "xmlrpc", "pydoc"], # 排除不必要的包
"optimize": 2 # 优化级别
}
},
executables=[
Executable(
"show_pinyin.py",
target_name="show_pinyin.exe",
icon="pinyin.png",
base="Win32GUI" # 使用Win32GUI以避免显示控制台窗口
)
]
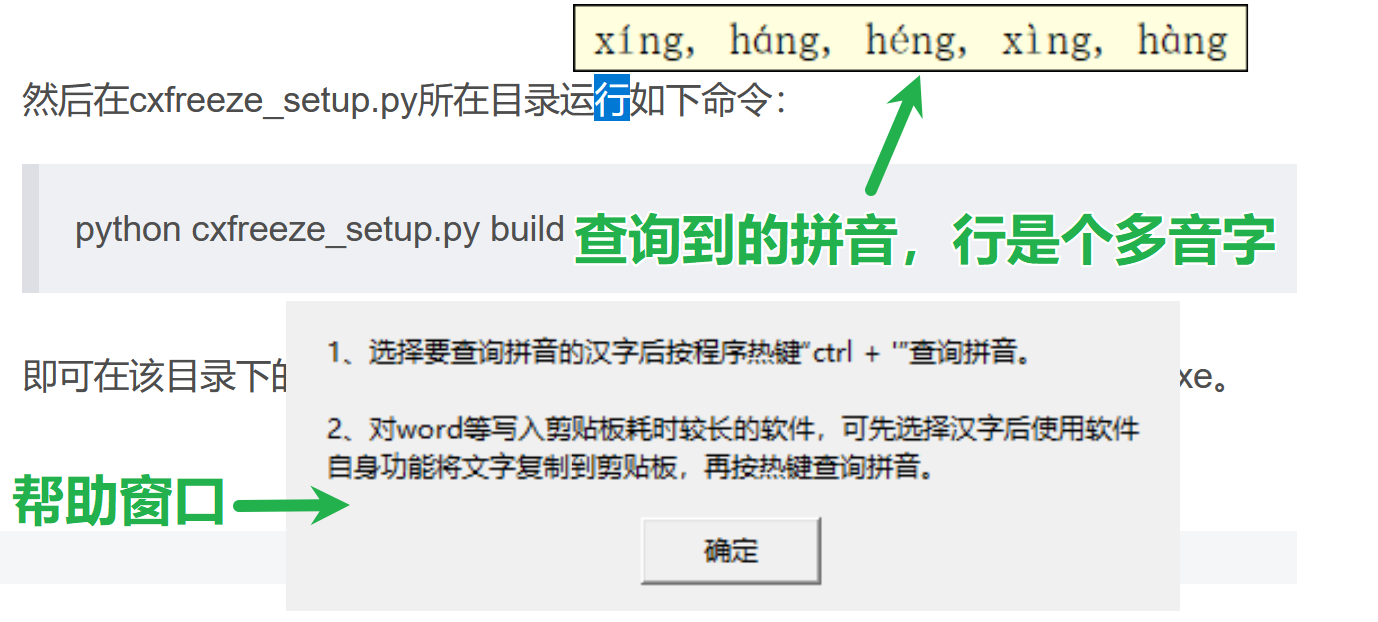
)然后在cxfreeze_setup.py所在目录运行如下命令:
python cxfreeze_setup.py build
即可在该目录下的“build\exe.win-amd64-3.13”文件夹下找到show_pinyin.exe。程序运行截图如下: