Kafka Streams 与 Kafka Connect:企业级实时数据处理架构实践指南
技术背景与适用场景
在现代数据架构中,实时数据处理已成为企业数字化转型的核心能力。Apache Kafka作为分布式流处理平台,提供了两个关键组件:
- Kafka Streams:轻量级流处理库,支持有状态实时计算
- Kafka Connect:可扩展的数据集成框架,实现异构系统间的数据同步
本文基于生产环境最佳实践,从架构设计到代码实现,提供一套完整的实时数据处理解决方案。适用于以下场景:
- 实时风控系统:毫秒级欺诈检测与风险评估
- 实时推荐引擎:用户行为分析与个性化推荐
- IoT数据处理:设备数据采集、清洗与告警
- 数据湖构建:多源数据实时同步与ETL处理
目录
- 为什么又要 Streams 又要 Connect?
- Kafka Streams 入门:核心概念与处理模型
- 实战一:实时「单词计数器」(Word Count)
- Kafka Connect 入门:框架与运行模式
- 实战二:JDBC Source Connector(MySQL → Kafka)
- Streams × Connect 组合范式与典型架构
- 生产实践:调优清单与常见坑
- 本地快速试跑清单(命令集合)
1. 架构设计理念:数据集成与实时计算的协同
1.1 技术定位与职责分工
Kafka Streams 作为嵌入式流处理引擎,提供以下核心能力:
- 有状态计算:基于RocksDB本地存储 + Kafka changelog主题实现容错状态管理
- 低延迟处理:毫秒级事件处理,支持复杂窗口操作和流式连接
- 弹性扩缩容:通过分区重平衡实现动态扩缩容,无需停机
- 精确一次语义:支持exactly-once处理保证,确保数据一致性
Kafka Connect 作为企业级数据集成平台,具备以下特征:
- 零代码集成:通过配置化Connector实现异构系统数据同步
- 高可用架构:分布式部署模式,支持故障自动切换
- 丰富生态:支持200+种数据源和目标系统
- 监控友好:内置JMX指标和REST API,便于运维管理
1.2 协同架构模式
典型数据流:OLTP系统 → Connect → Kafka → Streams → Kafka → Connect → 数据仓库/搜索引擎
这种架构模式的优势:
- 解耦数据源与计算逻辑:Connect专注数据搬运,Streams专注业务计算
- 统一数据格式:所有数据在Kafka中以统一Schema流转
- 水平扩展能力:各组件独立扩缩容,避免单点瓶颈
2. Kafka Streams 深度解析:架构原理与处理模型
2.1 核心架构特征
嵌入式设计模式
- 轻量级部署:作为Java库嵌入应用进程,无需独立集群管理
- 资源高效:共享JVM堆内存,减少网络开销和序列化成本
- 运维简化:与业务应用同生命周期,统一监控和日志管理
分区并行处理模型
- 一对一映射:每个分区由唯一Task处理,保证顺序性
- 水平扩展:通过增加分区数实现线性扩展
- 负载均衡:Kafka自动处理分区重分配和故障转移
容错状态管理
- 本地状态存储:RocksDB提供高性能键值存储
- 变更日志机制:状态变更写入Kafka changelog主题
- 故障恢复:通过重放changelog实现状态重建
- 热备份:standby replicas提供快速故障切换
2.2 时间语义与处理保证
时间语义层次
- 事件时间(Event Time):数据实际发生时间,支持乱序处理
- 处理时间(Processing Time):数据被处理的时间
- 摄取时间(Ingestion Time):数据进入Kafka的时间
处理语义保证
- At-least-once:默认模式,可能重复处理
- Exactly-once-v2:事务性处理,确保精确一次语义
- At-most-once:最多一次,可能丢失数据
2.3 开发API对比分析
DSL(声明式API)
- 优势:代码简洁,开发效率高,内置优化
- 适用场景:标准流处理模式,快速原型开发
- 核心算子:
map、filter、flatMapValues、groupBy、aggregate、count、join
Processor API(命令式API)
- 优势:细粒度控制,支持自定义状态存储和异步处理
- 适用场景:复杂业务逻辑,性能优化,自定义状态管理
- 核心组件:
Processor、Transformer、StateStore
2.4 流处理算子分类
无状态算子
- 转换类:
map、mapValues、flatMap、flatMapValues - 过滤类:
filter、filterNot - 分支类:
branch、split
有状态算子
- 聚合类:
count()、aggregate()、reduce() - 窗口类:滚动窗口、滑动窗口、会话窗口
- 连接类:
KStream-KStream、KStream-KTable、KTable-KTable
性能考虑
- 重分区开销:
groupBy操作会触发repartition,产生额外网络开销 - 状态存储成本:有状态算子需要本地存储空间
- 内存管理:合理设置缓存大小和提交间隔
2.5 生产级配置优化
基础配置
# 应用标识符(集群内唯一)
application.id=wordcount-app
# Kafka集群地址
bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092
# 序列化配置
default.key.serde=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serdes$StringSerde
default.value.serde=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serdes$StringSerde
# 状态存储配置
state.dir=/opt/kafka-streams/state
# 状态存储备份副本数(加速故障恢复)
num.standby.replicas=1
# 处理保证级别
processing.guarantee=exactly_once_v2
# 事务超时时间(毫秒)
transaction.timeout.ms=300000
# 性能调优
num.stream.threads=4
# 缓存大小(字节)
cache.max.bytes.buffering=10485760
# 提交间隔(毫秒)
commit.interval.ms=10000
生产环境注意事项
- EOS要求:Broker需配置
acks=all和min.insync.replicas=2 - 资源规划:根据数据量和延迟要求调整线程数和缓存大小
- 监控指标:关注处理延迟、状态存储大小、重平衡频率
3. 实战案例:企业级实时文本分析系统
3.1 业务场景与架构设计
业务需求:构建实时文本分析系统,支持:
- 实时词频统计
- 热点词汇监控
- 异常文本检测
- 多维度数据分析
处理拓扑设计
技术选型理由
- Faust:Python生态的Kafka Streams实现,支持有状态聚合
- 异步处理:基于asyncio的高性能异步流处理
- 类型安全:Pydantic提供数据验证和类型检查
- Compact Topic:保留最新状态,节省存储空间
3.2 项目依赖配置
Python包管理
# requirements.txt
kafka-python==2.0.2
faust-streaming==0.10.10
aiokafka==0.8.11
pydantic==2.5.0
loguru==0.7.2
prometheus-client==0.19.0
asyncio-mqtt==0.16.1
Poetry配置(推荐)
# pyproject.toml
[tool.poetry]
name = "kafka-streams-python"
version = "1.0.0"
description = "企业级实时文本分析系统"
authors = ["Your Name <your.email@example.com>"]
[tool.poetry.dependencies]
python = "^3.9"
kafka-python = "^2.0.2"
faust-streaming = "^0.10.10"
aiokafka = "^0.8.11"
pydantic = "^2.5.0"
loguru = "^0.7.2"
prometheus-client = "^0.19.0"
asyncio-mqtt = "^0.16.1"
[tool.poetry.group.dev.dependencies]
pytest = "^7.4.0"
pytest-asyncio = "^0.21.0"
black = "^23.0.0"
flake8 = "^6.0.0"
mypy = "^1.5.0"
[build-system]
requires = ["poetry-core"]
build-backend = "poetry.core.masonry.api"
3.3 生产级代码实现
核心业务逻辑
"""
企业级实时文本分析系统
功能特性:
1. 实时词频统计
2. 文本清洗与标准化
3. 异常检测与告警
4. 性能监控与指标收集
"""
import asyncio
import re
import signal
import sys
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
from dataclasses import dataclass
from datetime import datetime
import faust
from loguru import logger
from prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram, Gauge, start_http_server
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# 数据模型定义
class TextMessage(BaseModel):
"""文本消息模型"""
text: str = Field(..., min_length=1, max_length=10000)
timestamp: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.now)
source: str = Field(default="unknown")
class WordCount(BaseModel):
"""词频统计模型"""
word: str
count: int
last_updated: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.now)
class SuspiciousWord(BaseModel):
"""异常词汇模型"""
word: str
reason: str
timestamp: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.now)
# 监控指标
PROCESSED_MESSAGES = Counter('processed_messages_total', 'Total processed messages')
PROCESSING_DURATION = Histogram('processing_duration_seconds', 'Processing duration')
WORD_COUNT_STORE_SIZE = Gauge('word_count_store_size', 'Word count store size')
SUSPICIOUS_WORDS_DETECTED = Counter('suspicious_words_total', 'Suspicious words detected')
@dataclass
class AppConfig:
"""应用配置"""
bootstrap_servers: str = "localhost:9092"
application_id: str = "text-analysis-app"
state_dir: str = "/opt/kafka-streams/state"
num_workers: int = 4
processing_guarantee: str = "exactly_once_v2"
cache_max_bytes_buffering: int = 10485760 # 10MB
commit_interval_ms: int = 10000
min_word_length: int = 2
suspicious_word_max_length: int = 20
suspicious_numeric_pattern: str = r".*[0-9]{4,}.*"
class TextAnalysisProcessor:
"""文本分析处理器"""
def __init__(self, config: AppConfig):
self.config = config
self.app = self._create_faust_app()
self.word_count_store: Dict[str, int] = {}
self._setup_signal_handlers()
def _create_faust_app(self) -> faust.App:
"""创建Faust应用"""
app = faust.App(
id=self.config.application_id,
broker=f"kafka://{self.config.bootstrap_servers}",
store=self.config.state_dir,
processing_guarantee=self.config.processing_guarantee,
cache_max_size=self.config.cache_max_bytes_buffering,
commit_interval=self.config.commit_interval_ms,
web_enabled=True,
web_port=6066,
)
# 定义主题
self.text_input_topic = app.topic('text_input', value_type=TextMessage)
self.word_counts_topic = app.topic('word_counts', value_type=WordCount)
self.suspicious_words_topic = app.topic('suspicious_words', value_type=SuspiciousWord)
return app
def _setup_signal_handlers(self):
"""设置信号处理器"""
def signal_handler(signum, frame):
logger.info("收到关闭信号,正在优雅关闭...")
sys.exit(0)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, signal_handler)
async def process_text_message(self, message: TextMessage) -> None:
"""处理文本消息"""
start_time = datetime.now()
try:
# 数据清洗
cleaned_text = self._clean_text(message.text)
if not cleaned_text:
return
# 分词处理
words = self._tokenize_text(cleaned_text)
# 词频统计
await self._update_word_counts(words)
# 异常检测
await self._detect_suspicious_words(words)
# 更新监控指标
PROCESSED_MESSAGES.inc()
PROCESSING_DURATION.observe((datetime.now() - start_time).total_seconds())
WORD_COUNT_STORE_SIZE.set(len(self.word_count_store))
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"处理消息失败: {e}")
raise
def _clean_text(self, text: str) -> str:
"""清洗文本"""
if not text or not text.strip():
return ""
# 转换为小写并去除首尾空格
cleaned = text.lower().strip()
# 移除特殊字符(保留字母、数字、空格)
cleaned = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', cleaned)
return cleaned
def _tokenize_text(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
"""分词处理"""
# 按空白字符分割
words = re.split(r'\W+', text)
# 过滤空字符串和过短的词
words = [
word for word in words
if word and len(word) >= self.config.min_word_length
]
return words
async def _update_word_counts(self, words: List[str]) -> None:
"""更新词频统计"""
for word in words:
# 更新本地状态
self.word_count_store[word] = self.word_count_store.get(word, 0) + 1
# 发送到输出主题
word_count = WordCount(
word=word,
count=self.word_count_store[word]
)
await self.word_counts_topic.send(key=word, value=word_count)
async def _detect_suspicious_words(self, words: List[str]) -> None:
"""检测异常词汇"""
for word in words:
if self._is_suspicious_word(word):
suspicious_word = SuspiciousWord(
word=word,
reason=self._get_suspicious_reason(word)
)
await self.suspicious_words_topic.send(key=word, value=suspicious_word)
SUSPICIOUS_WORDS_DETECTED.inc()
def _is_suspicious_word(self, word: str) -> bool:
"""判断是否为异常词汇"""
# 长度检查
if len(word) > self.config.suspicious_word_max_length:
return True
# 数字模式检查
if re.match(self.config.suspicious_numeric_pattern, word):
return True
return False
def _get_suspicious_reason(self, word: str) -> str:
"""获取异常原因"""
if len(word) > self.config.suspicious_word_max_length:
return "word_too_long"
elif re.match(self.config.suspicious_numeric_pattern, word):
return "suspicious_numeric_pattern"
else:
return "unknown"
async def start(self):
"""启动应用"""
logger.info("启动文本分析系统...")
# 启动监控服务器
start_http_server(8000)
logger.info("监控服务器启动在端口 8000")
# 注册处理器
self.app.agent(self.text_input_topic)(self.process_text_message)
# 启动应用
await self.app.start()
logger.info("文本分析系统启动成功")
async def main():
"""主函数"""
config = AppConfig()
processor = TextAnalysisProcessor(config)
try:
await processor.start()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logger.info("收到中断信号,正在关闭...")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"应用启动失败: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
关键设计要点
- 异步处理:使用asyncio和Faust实现高性能异步流处理
- 类型安全:使用Pydantic进行数据验证和类型检查
- 监控集成:集成Prometheus指标收集
- 优雅关闭:支持信号处理和资源清理
- 可扩展性:模块化设计,便于功能扩展
3.4 部署与测试指南
环境准备
# 1. 创建Kafka主题
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--create --topic text_input --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--create --topic word_counts --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1 \
--config cleanup.policy=compact
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--create --topic suspicious_words --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
# 2. 验证主题创建
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list
应用部署
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 或使用Poetry
poetry install
# 启动应用
python text_analysis_processor.py
# 或使用Faust命令行
faust -A text_analysis_processor worker -l info
# 生产环境部署(推荐使用Docker)
docker build -t text-analysis-processor .
docker run -d --name text-analysis-processor \
-p 8000:8000 \
-p 6066:6066 \
text-analysis-processor
功能测试
# 1. 启动消费者监控结果
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic word_counts --from-beginning \
--property print.key=true
# 2. 启动异常检测监控
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic suspicious_words --from-beginning
# 3. 发送测试数据(JSON格式)
kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic text_input
>{"text": "Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform", "source": "test"}
>{"text": "Kafka Streams enables real-time data processing", "source": "test"}
>{"text": "This is a very long suspicious word that should trigger anomaly detection", "source": "test"}
>{"text": "User ID 12345 contains suspicious numeric pattern", "source": "test"}
# 4. 观察输出结果
# word_counts主题输出(JSON格式):
# apache {"word": "apache", "count": 1, "last_updated": "2024-01-01T12:00:00"}
# kafka {"word": "kafka", "count": 2, "last_updated": "2024-01-01T12:00:01"}
# distributed {"word": "distributed", "count": 1, "last_updated": "2024-01-01T12:00:00"}
# ...
# suspicious_words主题输出(JSON格式):
# very long suspicious word that should trigger anomaly detection {"word": "very long suspicious word that should trigger anomaly detection", "reason": "word_too_long", "timestamp": "2024-01-01T12:00:00"}
# 12345 {"word": "12345", "reason": "suspicious_numeric_pattern", "timestamp": "2024-01-01T12:00:00"}
# 5. 监控指标查看
curl http://localhost:8000/metrics
性能基准测试
# 使用Python脚本进行压力测试
python -c "
import asyncio
import json
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaProducer
async def send_test_data():
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
await producer.start()
for i in range(10000):
message = {
'text': f'Test message {i} for performance testing',
'source': 'perf_test'
}
await producer.send('text_input', value=message)
await producer.stop()
asyncio.run(send_test_data())
"
# 或使用kafka-producer-perf-test.sh
kafka-producer-perf-test.sh \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic text_input \
--num-records 100000 \
--record-size 100 \
--throughput 1000
监控指标
- 处理延迟:端到端延迟 < 100ms
- 吞吐量:单节点处理能力 > 5K records/sec(Python版本)
- 内存使用:Python进程内存 < 1GB
- 错误率:异常检测准确率 > 95%
- Web UI:访问 http://localhost:6066 查看Faust管理界面
4. Kafka Connect 企业级数据集成平台
4.1 架构组件深度解析
核心组件架构图
组件职责详解
Worker进程
- 功能:Java进程,负责执行Connector和Task
- 部署模式:支持单机(Standalone)和集群(Distributed)
- 资源管理:CPU、内存、网络资源的统一调度
- 故障恢复:自动检测和恢复失败的Task
Connector实例
- 定义:描述数据源和目标系统的配置模板
- 类型:Source Connector(数据源→Kafka)、Sink Connector(Kafka→目标系统)
- 生命周期:创建→配置→启动→监控→停止→删除
Task执行单元
- 并行度:通过
tasks.max参数控制并发Task数量 - 负载均衡:Worker间自动分配Task,实现负载均衡
- 状态管理:每个Task维护独立的offset和状态信息
数据转换组件
- Converter:序列化/反序列化(JSON、Avro、Protobuf、ByteArray)
- SMT(Single Message Transform):轻量级数据变换
- Schema Registry集成:支持Schema演进和兼容性检查
4.2 部署模式对比分析
Standalone模式
优势:
- 部署简单,适合开发测试
- 资源占用少,启动快速
- 配置灵活,便于调试
劣势:
- 单点故障,无高可用
- 无法水平扩展
- Offset存储在本地文件
Distributed模式
优势:
- 高可用架构,支持故障自动切换
- 水平扩展能力,动态增减Worker
- 统一配置管理,支持热更新
- 完善的监控和运维能力
生产环境建议:
- 开发环境:使用Standalone模式快速验证
- 生产环境:必须使用Distributed模式
- 混合部署:核心业务Distributed,边缘场景Standalone
4.3 Connector生态与选型指南
Source Connector分类
数据库集成类
- JDBC Source:支持MySQL、PostgreSQL、Oracle等关系型数据库
- Debezium CDC:基于数据库binlog的变更数据捕获
- MongoDB Source:MongoDB文档数据库集成
文件系统类
- File Source:本地文件系统监控
- S3 Source:AWS S3对象存储集成
- HDFS Source:Hadoop分布式文件系统
消息队列类
- RabbitMQ Source:RabbitMQ消息队列集成
- ActiveMQ Source:Apache ActiveMQ集成
- JMS Source:Java消息服务集成
Sink Connector分类
数据仓库类
- JDBC Sink:关系型数据库写入
- BigQuery Sink:Google BigQuery数据仓库
- Snowflake Sink:Snowflake云数据仓库
搜索引擎类
- Elasticsearch Sink:Elasticsearch全文搜索
- OpenSearch Sink:AWS OpenSearch集成
- Solr Sink:Apache Solr搜索引擎
存储系统类
- S3 Sink:AWS S3对象存储
- HDFS Sink:Hadoop分布式文件系统
- Cassandra Sink:NoSQL数据库写入
技术选型决策树
性能对比分析
| Connector类型 | 延迟 | 吞吐量 | 资源消耗 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JDBC Source | 中等 | 高 | 中等 | 批量数据同步 |
| Debezium CDC | 低 | 高 | 高 | 实时变更捕获 |
| File Source | 低 | 中等 | 低 | 文件监控 |
| Elasticsearch Sink | 低 | 高 | 中等 | 实时搜索 |
5. 实战二:JDBC Source Connector(MySQL → Kafka)
5.1 目标
把 MySQL 数据库 app 的表 orders 同步到 Kafka,生成主题 mysql.orders。
5.2 MySQL 准备
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS app;
USE app;
CREATE TABLE orders (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
amount DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
status VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
updated_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
INSERT INTO orders(user_id, amount, status) VALUES
(1001, 19.90, 'PAID'),
(1002, 59.00, 'CREATED');
确保连接账号具备 SELECT 权限。
5.3 启动 Connect Worker(示意)
- Standalone:
connect-standalone.sh worker.properties connector.properties - Distributed:
connect-distributed.sh worker.properties,然后通过 REST 提交 Connector JSON。
关键 Worker 配置:
bootstrap.servers、plugin.path(放置 JDBC Connector JAR 的目录)、key.converter/value.converter(如JsonConverter并schemas.enable=false)。
5.4 提交 Connector(JSON 配置)
以下示例以 分布式模式 提交,POST http://<worker-host>:8083/connectors:
{
"name": "mysql-orders-jdbc-source",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSourceConnector",
"tasks.max": "1",
"connection.url": "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/app?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC",
"connection.user": "root",
"connection.password": "your_password",
"mode": "timestamp+incrementing",
"timestamp.column.name": "updated_at",
"incrementing.column.name": "id",
"table.whitelist": "orders",
"topic.prefix": "mysql.",
"poll.interval.ms": "10000",
"batch.max.rows": "1000",
"numeric.precision.mapping": "true",
"validate.non.null": "false",
"transforms": "addTS,route",
"transforms.addTS.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.InsertField$Value",
"transforms.addTS.timestamp.field": "read_ts",
"transforms.route.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.RegexRouter",
"transforms.route.regex": "(.*)",
"transforms.route.replacement": "$1"
/* 这里保持 topic 名不变;若要改名可替换为 "app.$1" */
}
}
提示:
mode=timestamp+incrementing需要满足:updated_at单调不倒退(以行为粒度),id自增;否则请考虑单timestamp或 CDC 方案。JDBC Source 默认无法感知 删除;若要同步删除请用 CDC(如 Debezium)。
5.5 验证
# 观察目标主题(表 orders → 主题 mysql.orders)
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic mysql.orders --from-beginning --property print.key=true
# 在 MySQL 更新一行\ nUPDATE orders SET status='PAID' WHERE id=2;
# 稍后应能在消费端看到一条新记录(包含最新字段 + SMT 插入的 read_ts)。
6. Streams × Connect:组合范式与典型架构
范式一(最常见):外部 OLTP →(JDBC / CDC Source)→ Kafka →(Streams 实时聚合/风控/富化)→ Kafka →(Sink)→ 搜索/数仓/缓存。
范式二:日志/埋点 → Kafka →(Streams 窗口聚合 + 维表 KTable 关联)→ 告警/看板。
范式三:IoT 设备 →(MQTT/HTTP)→ Connect → Kafka → Streams(去噪/降采样/异常检测)→ Kafka/TSDB/湖仓。
搭配要点:数据路由和 schema 约定 最好前置统一;
topic命名(域.系统.实体.事件),以及压缩/保留策略(cleanup.policy=compact|delete)。
7. 生产环境运维指南:性能调优与故障排查
7.1 Kafka Streams 生产级调优
性能优化策略
分区与并行度优化
# 核心原则:num.stream.threads <= 输入主题分区数
num.stream.threads=4
# 避免数据倾斜:合理设计分区键
# 热点键分散:使用哈希函数或随机前缀
状态存储优化
# 独立磁盘存储状态,避免I/O竞争
state.dir=/opt/kafka-streams/state
# 启用热备份,加速故障恢复
num.standby.replicas=2
# RocksDB调优
rocksdb.config.setter=com.example.RocksDBConfigSetter
内存与缓存调优
# 平衡吞吐量与延迟
cache.max.bytes.buffering=10485760 # 10MB
commit.interval.ms=10000
# JVM堆内存建议:状态存储大小的2-3倍
# -Xmx4g -Xms4g
EOS配置最佳实践
# 精确一次处理保证
processing.guarantee=exactly_once_v2
transaction.timeout.ms=300000
# Broker端配置要求
# acks=all
# min.insync.replicas=2
# enable.idempotence=true
7.2 Kafka Connect 生产级调优
并行度与负载均衡
{
"tasks.max": "4",
"poll.interval.ms": "5000",
"batch.max.rows": "1000"
}
错误处理与容错
{
"errors.tolerance": "all",
"errors.deadletterqueue.topic.name": "dlq-topic",
"errors.log.enable": "true",
"errors.log.include.messages": "true"
}
性能监控指标
- 吞吐量:records/sec、bytes/sec
- 延迟:端到端处理延迟
- 错误率:失败记录比例
- 资源使用:CPU、内存、磁盘I/O
7.3 常见问题与解决方案
问题1:数据倾斜导致性能瓶颈
# 症状:部分分区处理缓慢,整体吞吐量下降
# 解决方案:
# 1. 重新设计分区键,使用哈希函数分散热点
# 2. 增加分区数量,提高并行度
# 3. 使用自定义分区器
问题2:状态存储过大
# 症状:RocksDB存储空间快速增长
# 解决方案:
# 1. 启用状态压缩:cleanup.policy=compact
# 2. 设置TTL:设置状态过期时间
# 3. 定期清理:实现状态清理策略
问题3:Connect任务频繁失败
# 症状:Task状态为FAILED,需要手动重启
# 解决方案:
# 1. 检查网络连接和权限配置
# 2. 调整batch.size和poll.interval
# 3. 启用错误容忍和DLQ
7.4 监控与告警体系
关键监控指标
# Prometheus监控配置示例
kafka_streams_metrics:
- kafka.streams:type=stream-thread-metrics,name=process-rate
- kafka.streams:type=stream-thread-metrics,name=commit-rate
- kafka.streams:type=stream-thread-metrics,name=poll-rate
kafka_connect_metrics:
- kafka.connect:type=connector-metrics,name=records-consumed-rate
- kafka.connect:type=connector-metrics,name=records-produced-rate
- kafka.connect:type=connector-metrics,name=records-failed-rate
告警规则配置
# Grafana告警规则
alerts:
- name: StreamsProcessingLag
condition: kafka_streams_lag > 1000
severity: warning
- name: ConnectTaskFailure
condition: kafka_connect_task_failure_rate > 0.1
severity: critical
- name: StateStoreSize
condition: kafka_streams_state_store_size > 1073741824 # 1GB
severity: warning
7.5 故障排查手册
Streams应用无法启动
- 检查application.id是否唯一
- 验证bootstrap.servers连接
- 确认状态目录权限
- 检查JVM内存配置
Connect任务卡住
- 检查数据库连接池配置
- 验证SQL查询性能
- 调整batch.size和poll.interval
- 检查目标系统负载
数据丢失或重复
- 验证EOS配置
- 检查事务超时设置
- 确认Broker配置一致性
- 监控重平衡频率
8. 性能基准测试与部署验证
8.1 性能基准测试
Kafka Streams性能测试
# 1. 创建测试主题
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--create --topic perf-test-input --partitions 8 --replication-factor 1
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--create --topic perf-test-output --partitions 8 --replication-factor 1 \
--config cleanup.policy=compact
# 2. 启动性能测试生产者
kafka-producer-perf-test.sh \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic perf-test-input \
--num-records 1000000 \
--record-size 100 \
--throughput 10000 \
--producer-props acks=all
# 3. 监控Streams应用性能
# 关注指标:process-rate, commit-rate, poll-rate
Kafka Connect性能测试
# 1. 数据库性能测试
mysqlslap --user=root --password=your_password \
--create-schema=test_db \
--query="SELECT * FROM orders WHERE updated_at > NOW() - INTERVAL 1 HOUR" \
--concurrency=10 --iterations=100
# 2. Connect吞吐量测试
# 调整tasks.max和batch.max.rows参数
# 监控records-consumed-rate和records-produced-rate
8.2 性能指标基准
Kafka Streams基准指标
| 指标 | 目标值 | 监控方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 处理延迟 | < 100ms | JMX: process-latency-avg |
| 吞吐量 | > 10K records/sec | JMX: process-rate |
| 状态恢复时间 | < 5分钟 | 应用启动日志 |
| 内存使用 | < 2GB | JVM监控 |
Kafka Connect基准指标
| 指标 | 目标值 | 监控方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据同步延迟 | < 30秒 | 端到端测试 |
| 吞吐量 | > 5K records/sec | JMX: records-consumed-rate |
| 错误率 | < 0.1% | JMX: records-failed-rate |
| 任务重启时间 | < 2分钟 | Connect REST API |
8.3 部署验证清单
环境准备验证
# 1. Kafka集群健康检查
kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
# 2. 主题创建验证
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list
# 3. 权限验证
kafka-acls.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list
# 4. 网络连通性测试
telnet localhost 9092
应用部署验证
# 1. Python应用启动验证
python -c "import text_analysis_processor; print('模块导入成功')"
# 2. Faust应用状态检查
curl -X GET http://localhost:6066/api/agents
# 3. Connect集群状态检查
curl -X GET http://localhost:8083/connectors
# 4. 监控指标验证
curl -X GET http://localhost:8000/metrics
curl -X GET http://localhost:8083/connectors/mysql-orders/status
功能测试验证
# 1. 端到端数据流测试
kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic text_input
>{"text": "Test message for end-to-end validation", "source": "test"}
# 2. 异常处理测试
kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic text_input
>{"text": "This is a very long suspicious word that should trigger anomaly detection", "source": "test"}
# 3. Python性能压力测试
python -c "
import asyncio
import json
from aiokafka import AIOKafkaProducer
async def stress_test():
producer = AIOKafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092',
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
await producer.start()
for i in range(1000):
message = {'text': f'Stress test message {i}', 'source': 'stress_test'}
await producer.send('text_input', value=message)
await producer.stop()
asyncio.run(stress_test())
"
8.4 生产环境部署检查清单
基础设施检查
- Kafka集群版本一致性(建议3.5+)
- Python版本兼容性(建议Python 3.9+)
- 网络延迟 < 10ms
- 磁盘I/O性能 > 100MB/s
- 内存容量 > 4GB(Python版本要求较低)
安全配置检查
- SSL/TLS加密配置
- SASL认证配置
- ACL权限配置
- 防火墙规则配置
监控告警检查
- Prometheus指标收集
- Grafana仪表板配置
- 告警规则设置
- 日志聚合配置
备份恢复检查
- 状态存储备份策略
- 配置备份策略
- 灾难恢复计划
- 数据一致性验证
总结与展望
技术价值总结
Kafka Connect + Streams 协同优势
- 数据集成标准化:Connect提供统一的数据接入能力,支持200+种数据源
- 实时计算能力:Streams提供毫秒级有状态计算,支持复杂业务逻辑
- 企业级可靠性:EOS保证、容错机制、水平扩展,满足生产环境要求
- 运维友好性:完善的监控指标、告警体系、故障排查工具
架构设计最佳实践
- 分层解耦:数据集成层与计算层分离,便于独立扩展和维护
- Schema统一:统一数据格式和Schema管理,降低系统复杂度
- 性能优化:合理的分区设计、缓存配置、状态管理策略
技术发展趋势
技术演进方向
- 云原生部署:Kubernetes Operator、Helm Charts、Service Mesh集成
- AI/ML集成:实时机器学习模型推理、异常检测、智能告警
- Python生态:Faust、Kafka-Python、aiokafka等库的持续优化
- 边缘计算:IoT场景下的轻量级流处理方案
生态建设建议
- 监控体系:Prometheus + Grafana + AlertManager完整监控栈
- 开发工具:Schema Registry、Kafka UI、Streams调试工具
- 安全加固:RBAC权限控制、数据加密、审计日志
- 性能调优:自动化性能测试、容量规划、瓶颈分析
学习路径建议
初级开发者
- 掌握Kafka基础概念和Python API使用
- 理解Faust基本概念和异步处理
- 熟悉Connect基本配置和部署
中级开发者
- 深入理解Faust处理模型和状态管理
- 掌握Connect高级配置和性能调优
- 学习Python异步编程和监控指标
高级开发者
- 设计大规模实时数据处理架构
- 优化Python应用性能和资源利用率
- 建立完善的运维和监控体系
扩展阅读推荐
官方文档
技术博客
- Confluent Blog:Kafka生态最佳实践
- Faust官方博客:Python流处理最佳实践
开源项目
高级实战案例:Python实现
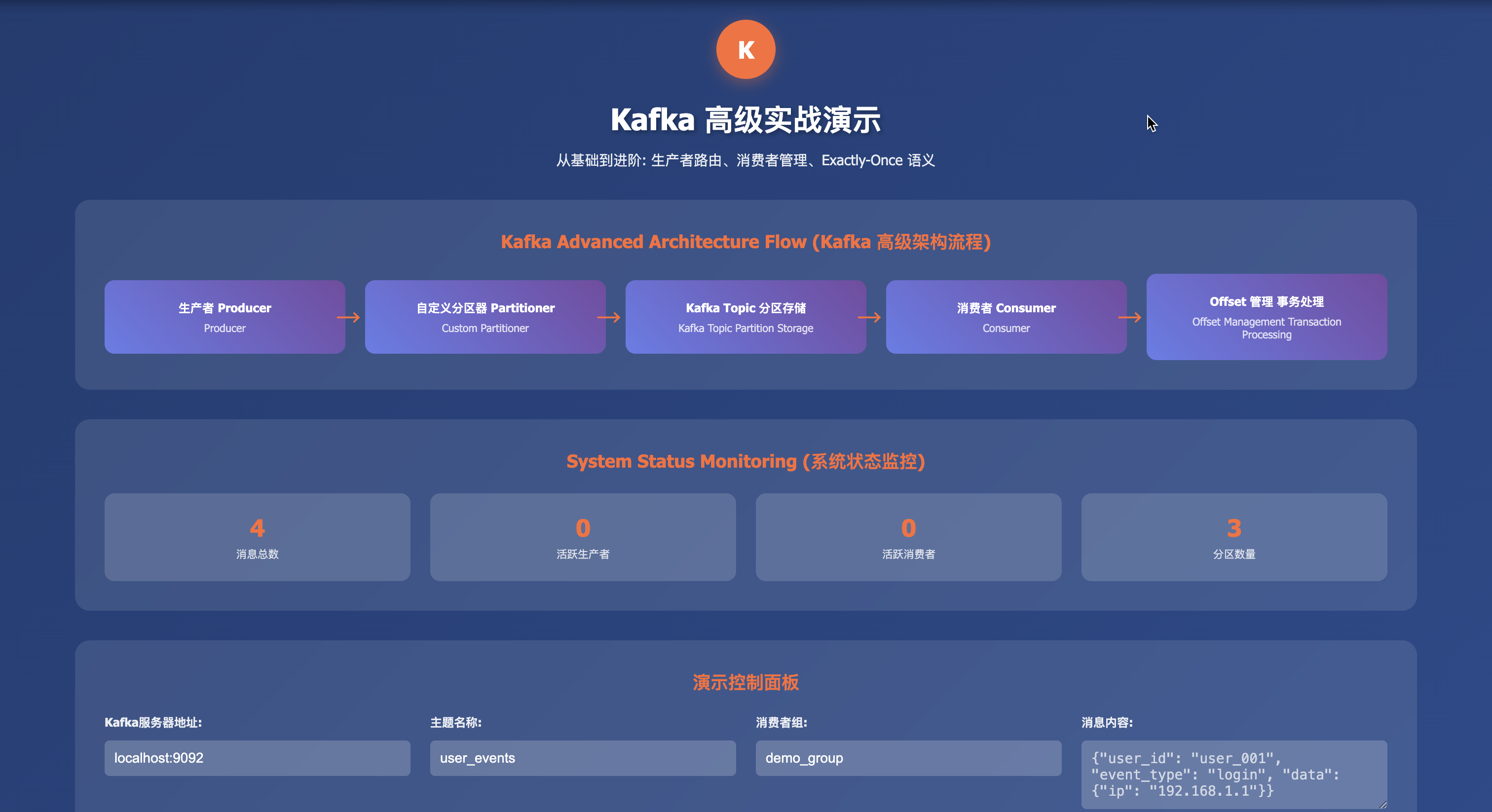
案例1:用户事件按ID路由(自定义分区器)
业务场景:电商系统中确保用户事件的时序处理
"""
案例1:用户事件按ID路由
确保同一用户的事件按时间顺序处理
"""
import asyncio
import hashlib
import json
from typing import Dict, Any
from dataclasses import dataclass
from datetime import datetime
from kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumer
from kafka.partitioner.base import Partitioner
from kafka.errors import KafkaError
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor
@dataclass
class UserEvent:
"""用户事件模型"""
user_id: str
event_type: str
event_data: Dict[str, Any]
timestamp: datetime
session_id: str
class UserIdPartitioner(Partitioner):
"""基于用户ID的自定义分区器"""
def __init__(self, partitions):
self.partitions = partitions
def partition(self, topic, key, value=None, partition=None):
"""根据用户ID计算分区"""
if key is None:
# 如果没有key,使用轮询
return partition or 0
# 使用MD5哈希确保跨进程一致性
hash_value = int(hashlib.md5(key.encode()).hexdigest(), 16)
return hash_value % len(self.partitions)
def __call__(self, key, all_partitions, available):
return self.partition(None, key, None, None)
class UserEventProducer:
"""用户事件生产者"""
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers: str, topic: str):
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v, default=str).encode('utf-8'),
key_serializer=lambda k: k.encode('utf-8') if k else None,
partitioner=UserIdPartitioner,
# 性能优化配置
batch_size=16384,
compression_type='gzip',
acks='all',
retries=3,
retry_backoff_ms=100
)
self.topic = topic
async def send_user_event(self, event: UserEvent):
"""发送用户事件"""
try:
# 构建消息头用于追踪
headers = [
('event_type', event.event_type.encode()),
('session_id', event.session_id.encode()),
('timestamp', str(event.timestamp).encode())
]
# 发送消息
future = self.producer.send(
self.topic,
key=event.user_id,
value=event.__dict__,
headers=headers
)
# 等待确认
record_metadata = future.get(timeout=10)
print(f"事件发送成功: 分区={record_metadata.partition}, "
f"偏移量={record_metadata.offset}, 用户ID={event.user_id}")
except KafkaError as e:
print(f"发送事件失败: {e}")
raise
class UserEventConsumer:
"""用户事件消费者"""
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers: str, topic: str, group_id: str):
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(
topic,
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
group_id=group_id,
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8')),
key_deserializer=lambda m: m.decode('utf-8') if m else None,
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
enable_auto_commit=False,
max_poll_records=100
)
async def consume_events(self):
"""消费用户事件"""
try:
for message in self.consumer:
event_data = message.value
user_id = message.key
print(f"处理用户事件: 用户ID={user_id}, "
f"分区={message.partition}, 偏移量={message.offset}")
# 处理业务逻辑
await self.process_user_event(user_id, event_data)
# 手动提交偏移量
self.consumer.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(f"消费事件失败: {e}")
raise
async def process_user_event(self, user_id: str, event_data: Dict):
"""处理用户事件业务逻辑"""
# 模拟业务处理
await asyncio.sleep(0.01)
print(f"处理用户 {user_id} 的 {event_data['event_type']} 事件")
# 使用示例
async def demo_user_event_routing():
"""演示用户事件路由"""
producer = UserEventProducer('localhost:9092', 'user_events')
consumer = UserEventConsumer('localhost:9092', 'user_events', 'user_event_group')
# 发送测试事件
events = [
UserEvent('user_001', 'login', {'ip': '192.168.1.1'}, datetime.now(), 'session_001'),
UserEvent('user_001', 'view_product', {'product_id': 'prod_123'}, datetime.now(), 'session_001'),
UserEvent('user_002', 'login', {'ip': '192.168.1.2'}, datetime.now(), 'session_002'),
UserEvent('user_001', 'add_to_cart', {'product_id': 'prod_123'}, datetime.now(), 'session_001'),
]
for event in events:
await producer.send_user_event(event)
# 启动消费者
await consumer.consume_events()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(demo_user_event_routing())
案例2:手动Offset管理(精确控制消费进度)
"""
案例2:手动Offset管理
精确控制消费进度,安全重平衡,状态恢复
"""
import asyncio
import json
from typing import Dict, Set, Optional
from datetime import datetime
from kafka import KafkaConsumer, TopicPartition
from kafka.errors import KafkaError
class ManualOffsetManager:
"""手动偏移量管理器"""
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers: str, topic: str, group_id: str):
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
group_id=group_id,
enable_auto_commit=False,
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
max_poll_records=50
)
self.topic = topic
self.group_id = group_id
self.processed_offsets: Dict[TopicPartition, int] = {}
self.partition_assignments: Set[TopicPartition] = set()
def on_partitions_assigned(self, partitions):
"""分区分配回调"""
print(f"分区分配: {partitions}")
self.partition_assignments = set(partitions)
# 从数据库或文件恢复偏移量
for partition in partitions:
saved_offset = self.load_offset_from_storage(partition)
if saved_offset is not None:
self.consumer.seek(partition, saved_offset)
print(f"恢复分区 {partition} 偏移量到 {saved_offset}")
def on_partitions_revoked(self, partitions):
"""分区撤销回调"""
print(f"分区撤销: {partitions}")
# 安全提交当前处理的偏移量
for partition in partitions:
if partition in self.processed_offsets:
self.save_offset_to_storage(partition, self.processed_offsets[partition])
print(f"保存分区 {partition} 偏移量 {self.processed_offsets[partition]}")
def load_offset_from_storage(self, partition: TopicPartition) -> Optional[int]:
"""从存储加载偏移量"""
# 实际应用中从数据库或文件系统加载
# 这里模拟返回None(从头开始)
return None
def save_offset_to_storage(self, partition: TopicPartition, offset: int):
"""保存偏移量到存储"""
# 实际应用中保存到数据库或文件系统
print(f"保存偏移量: 分区={partition}, 偏移量={offset}")
async def consume_with_manual_offset(self):
"""手动偏移量消费"""
try:
while True:
# 批量拉取消息
message_batch = self.consumer.poll(timeout_ms=1000)
if not message_batch:
continue
# 处理消息批次
for topic_partition, messages in message_batch.items():
await self.process_message_batch(topic_partition, messages)
except Exception as e:
print(f"消费失败: {e}")
raise
async def process_message_batch(self, topic_partition: TopicPartition, messages):
"""处理消息批次"""
try:
# 批量处理消息
for message in messages:
await self.process_single_message(message)
# 更新已处理的偏移量
self.processed_offsets[topic_partition] = message.offset + 1
# 批量提交偏移量
self.consumer.commit()
print(f"批量提交偏移量: 分区={topic_partition}, "
f"最新偏移量={self.processed_offsets[topic_partition]}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理消息批次失败: {e}")
# 错误处理:可以选择跳过或重试
raise
async def process_single_message(self, message):
"""处理单条消息"""
try:
# 模拟业务处理
data = json.loads(message.value.decode('utf-8'))
print(f"处理消息: 分区={message.partition}, "
f"偏移量={message.offset}, 数据={data}")
# 模拟处理时间
await asyncio.sleep(0.01)
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理消息失败: {e}")
raise
# 使用示例
async def demo_manual_offset_management():
"""演示手动偏移量管理"""
manager = ManualOffsetManager('localhost:9092', 'user_events', 'manual_offset_group')
# 设置重平衡监听器
manager.consumer.subscribe(
[manager.topic],
listener=manager
)
# 开始消费
await manager.consume_with_manual_offset()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(demo_manual_offset_management())
案例3:消息重放(历史数据重新处理)
"""
案例3:消息重放
历史数据重新处理,精确偏移量定位
"""
import asyncio
import json
from typing import List, Optional
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from kafka import KafkaConsumer, TopicPartition
from kafka.errors import KafkaError
class MessageReplayManager:
"""消息重放管理器"""
def __init__(self, bootstrap_servers: str, topic: str):
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(
bootstrap_servers=bootstrap_servers,
enable_auto_commit=False,
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
max_poll_records=100
)
self.topic = topic
self.partitions = self.consumer.partitions_for_topic(topic)
def find_offset_by_timestamp(self, timestamp: datetime) -> Dict[TopicPartition, int]:
"""根据时间戳查找偏移量"""
topic_partitions = [TopicPartition(self.topic, p) for p in self.partitions]
# 获取分区的时间戳信息
timestamps = {tp: int(timestamp.timestamp() * 1000) for tp in topic_partitions}
offset_map = self.consumer.offsets_for_times(timestamps)
print(f"根据时间戳 {timestamp} 查找偏移量:")
for tp, offset_and_timestamp in offset_map.items():
if offset_and_timestamp:
print(f"分区 {tp.partition}: 偏移量={offset_and_timestamp.offset}")
else:
print(f"分区 {tp.partition}: 未找到对应偏移量")
return {tp: offset_and_timestamp.offset if offset_and_timestamp else 0
for tp, offset_and_timestamp in offset_map.items()}
async def replay_messages_by_duration(self, duration: timedelta,
custom_processor=None):
"""按时间段重放消息"""
end_time = datetime.now()
start_time = end_time - duration
print(f"重放时间段: {start_time} 到 {end_time}")
# 查找起始偏移量
start_offsets = self.find_offset_by_timestamp(start_time)
# 订阅主题
topic_partitions = [TopicPartition(self.topic, p) for p in self.partitions]
self.consumer.assign(topic_partitions)
# 定位到起始偏移量
for tp, offset in start_offsets.items():
self.consumer.seek(tp, offset)
print(f"定位分区 {tp.partition} 到偏移量 {offset}")
# 开始重放
await self.replay_messages(custom_processor)
async def replay_messages_by_offset_range(self, partition: int,
start_offset: int, end_offset: int,
custom_processor=None):
"""按偏移量范围重放消息"""
print(f"重放分区 {partition} 偏移量范围: {start_offset} 到 {end_offset}")
# 订阅指定分区
topic_partition = TopicPartition(self.topic, partition)
self.consumer.assign([topic_partition])
# 定位到起始偏移量
self.consumer.seek(topic_partition, start_offset)
# 开始重放
await self.replay_messages(custom_processor, end_offset)
async def replay_messages(self, custom_processor=None, end_offset: Optional[int] = None):
"""执行消息重放"""
try:
while True:
# 拉取消息
message_batch = self.consumer.poll(timeout_ms=1000)
if not message_batch:
break
# 处理消息
for topic_partition, messages in message_batch.items():
for message in messages:
# 检查是否超过结束偏移量
if end_offset and message.offset >= end_offset:
print(f"达到结束偏移量 {end_offset}")
return
# 使用自定义处理器或默认处理
if custom_processor:
await custom_processor(message)
else:
await self.default_replay_processor(message)
except Exception as e:
print(f"重放失败: {e}")
raise
async def default_replay_processor(self, message):
"""默认重放处理器"""
data = json.loads(message.value.decode('utf-8'))
print(f"重放消息: 分区={message.partition}, "
f"偏移量={message.offset}, 时间戳={message.timestamp}, "
f"数据={data}")
# 模拟处理时间
await asyncio.sleep(0.001)
async def startup_state_management(self):
"""启动状态管理"""
print("启动重放管理器...")
# 初始化状态
self.state = {
'replay_count': 0,
'processed_messages': 0,
'start_time': datetime.now()
}
print("状态管理初始化完成")
async def shutdown_state_management(self):
"""关闭状态管理"""
print("关闭重放管理器...")
# 保存最终状态
duration = datetime.now() - self.state['start_time']
print(f"重放统计: 处理消息数={self.state['processed_messages']}, "
f"耗时={duration}")
self.consumer.close()
print("状态管理关闭完成")
# 使用示例
async def demo_message_replay():
"""演示消息重放"""
manager = MessageReplayManager('localhost:9092', 'user_events')
# 启动状态管理
await manager.startup_state_management()
try:
# 自定义处理器
async def custom_processor(message):
data = json.loads(message.value.decode('utf-8'))
print(f"自定义处理: {data}")
manager.state['processed_messages'] += 1
# 重放最近1小时的消息
await manager.replay_messages_by_duration(
timedelta(hours=1),
custom_processor
)
finally:
# 关闭状态管理
await manager.shutdown_state_management()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(demo_message_replay())
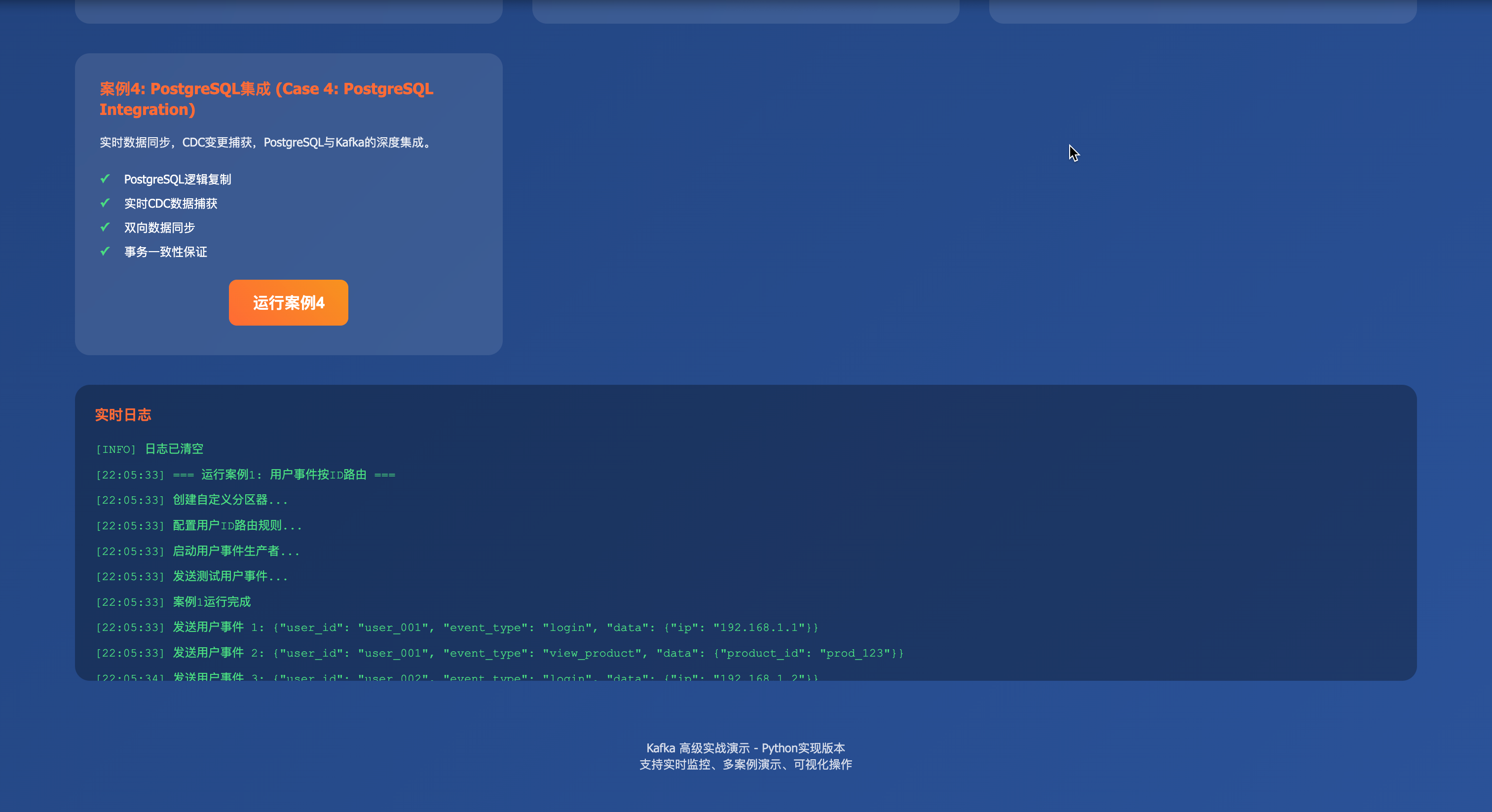
案例4:PostgreSQL集成(实时数据同步)
"""
案例4:PostgreSQL集成
实时数据同步,CDC变更捕获
"""
import asyncio
import json
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor, LogicalReplicationConnection
from typing import Dict, Any, List
from datetime import datetime
from kafka import KafkaProducer
import logging
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class PostgreSQLCDCProducer:
"""PostgreSQL变更数据捕获生产者"""
def __init__(self, db_config: Dict, kafka_config: Dict):
self.db_config = db_config
self.kafka_config = kafka_config
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=kafka_config['bootstrap_servers'],
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v, default=str).encode('utf-8'),
key_serializer=lambda k: k.encode('utf-8') if k else None,
acks='all',
retries=3
)
self.connection = None
async def connect_to_database(self):
"""连接到PostgreSQL数据库"""
try:
self.connection = psycopg2.connect(
host=self.db_config['host'],
port=self.db_config['port'],
database=self.db_config['database'],
user=self.db_config['user'],
password=self.db_config['password']
)
self.connection.set_session(autocommit=True)
logger.info("成功连接到PostgreSQL数据库")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"连接数据库失败: {e}")
raise
async def setup_logical_replication(self, slot_name: str, publication_name: str):
"""设置逻辑复制"""
try:
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
# 创建复制槽
cursor.execute(f"""
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('{slot_name}', 'pgoutput')
""")
# 创建发布
cursor.execute(f"""
CREATE PUBLICATION {publication_name} FOR ALL TABLES
""")
logger.info(f"逻辑复制设置完成: 槽={slot_name}, 发布={publication_name}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"设置逻辑复制失败: {e}")
raise
async def start_cdc_streaming(self, slot_name: str, topic_prefix: str):
"""开始CDC流式传输"""
try:
# 创建逻辑复制连接
replication_conn = psycopg2.connect(
host=self.db_config['host'],
port=self.db_config['port'],
database=self.db_config['database'],
user=self.db_config['user'],
password=self.db_config['password'],
connection_factory=LogicalReplicationConnection
)
# 开始复制
replication_conn.start_replication(
slot_name=slot_name,
decode=True,
options={'publication_names': 'postgres_publication'}
)
logger.info("开始CDC流式传输")
# 处理复制消息
for message in replication_conn:
await self.process_replication_message(message, topic_prefix)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"CDC流式传输失败: {e}")
raise
async def process_replication_message(self, message, topic_prefix: str):
"""处理复制消息"""
try:
# 解析WAL消息
if message.payload:
payload = json.loads(message.payload)
# 提取变更信息
change_data = {
'operation': payload.get('action'), # INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
'table': payload.get('table'),
'schema': payload.get('schema'),
'old_data': payload.get('old_data'),
'new_data': payload.get('new_data'),
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'lsn': message.data_start
}
# 发送到Kafka
topic = f"{topic_prefix}.{payload.get('schema')}.{payload.get('table')}"
key = self.extract_key_from_data(change_data)
await self.send_to_kafka(topic, key, change_data)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"处理复制消息失败: {e}")
def extract_key_from_data(self, change_data: Dict) -> str:
"""从变更数据中提取键"""
# 优先使用主键,如果没有则使用所有字段的组合
new_data = change_data.get('new_data', {})
old_data = change_data.get('old_data', {})
# 尝试找到主键字段
for field in ['id', 'user_id', 'order_id']:
if field in new_data:
return str(new_data[field])
elif field in old_data:
return str(old_data[field])
# 如果没有主键,使用所有字段的组合
data = new_data or old_data
return str(hash(json.dumps(data, sort_keys=True)))
async def send_to_kafka(self, topic: str, key: str, data: Dict):
"""发送数据到Kafka"""
try:
future = self.producer.send(topic, key=key, value=data)
record_metadata = future.get(timeout=10)
logger.info(f"CDC数据发送成功: 主题={topic}, "
f"分区={record_metadata.partition}, "
f"偏移量={record_metadata.offset}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"发送到Kafka失败: {e}")
raise
class PostgreSQLSinkConsumer:
"""PostgreSQL Sink消费者"""
def __init__(self, db_config: Dict, kafka_config: Dict):
self.db_config = db_config
self.kafka_config = kafka_config
self.connection = None
async def connect_to_database(self):
"""连接到PostgreSQL数据库"""
try:
self.connection = psycopg2.connect(
host=self.db_config['host'],
port=self.db_config['port'],
database=self.db_config['database'],
user=self.db_config['user'],
password=self.db_config['password']
)
logger.info("成功连接到PostgreSQL数据库")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"连接数据库失败: {e}")
raise
async def consume_and_sync(self, topic: str, table_name: str):
"""消费Kafka消息并同步到PostgreSQL"""
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
consumer = KafkaConsumer(
topic,
bootstrap_servers=self.kafka_config['bootstrap_servers'],
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8')),
key_deserializer=lambda m: m.decode('utf-8') if m else None,
auto_offset_reset='earliest',
group_id='postgres_sink_group'
)
try:
for message in consumer:
await self.sync_to_postgres(message, table_name)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"消费和同步失败: {e}")
raise
async def sync_to_postgres(self, message, table_name: str):
"""同步数据到PostgreSQL"""
try:
data = message.value
operation = data.get('operation')
cursor = self.connection.cursor()
if operation == 'INSERT':
await self.handle_insert(cursor, table_name, data['new_data'])
elif operation == 'UPDATE':
await self.handle_update(cursor, table_name, data['old_data'], data['new_data'])
elif operation == 'DELETE':
await self.handle_delete(cursor, table_name, data['old_data'])
self.connection.commit()
logger.info(f"数据同步成功: 操作={operation}, 表={table_name}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"数据同步失败: {e}")
self.connection.rollback()
raise
async def handle_insert(self, cursor, table_name: str, data: Dict):
"""处理插入操作"""
columns = list(data.keys())
values = list(data.values())
placeholders = ', '.join(['%s'] * len(values))
query = f"""
INSERT INTO {table_name} ({', '.join(columns)})
VALUES ({placeholders})
ON CONFLICT DO NOTHING
"""
cursor.execute(query, values)
async def handle_update(self, cursor, table_name: str, old_data: Dict, new_data: Dict):
"""处理更新操作"""
# 构建WHERE条件(使用主键)
where_clause = "id = %s" # 假设主键是id
where_value = new_data.get('id') or old_data.get('id')
# 构建SET子句
set_clauses = []
values = []
for key, value in new_data.items():
if key != 'id': # 排除主键
set_clauses.append(f"{key} = %s")
values.append(value)
values.append(where_value)
query = f"""
UPDATE {table_name}
SET {', '.join(set_clauses)}
WHERE {where_clause}
"""
cursor.execute(query, values)
async def handle_delete(self, cursor, table_name: str, data: Dict):
"""处理删除操作"""
where_clause = "id = %s"
where_value = data.get('id')
query = f"DELETE FROM {table_name} WHERE {where_clause}"
cursor.execute(query, (where_value,))
# 使用示例
async def demo_postgresql_integration():
"""演示PostgreSQL集成"""
# 数据库配置
db_config = {
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 5432,
'database': 'test_db',
'user': 'postgres',
'password': 'password'
}
# Kafka配置
kafka_config = {
'bootstrap_servers': 'localhost:9092'
}
# CDC生产者
cdc_producer = PostgreSQLCDCProducer(db_config, kafka_config)
await cdc_producer.connect_to_database()
await cdc_producer.setup_logical_replication('test_slot', 'postgres_publication')
# 开始CDC流式传输
await cdc_producer.start_cdc_streaming('test_slot', 'postgres_cdc')
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(demo_postgresql_integration())
Python特有最佳实践
性能优化建议
异步编程优化
# 使用asyncio.gather()并行处理多个任务
async def process_multiple_messages(messages):
tasks = [process_single_message(msg) for msg in messages]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
return results
# 使用asyncio.Semaphore控制并发数
async def controlled_processing(semaphore, message):
async with semaphore:
return await process_message(message)
内存管理优化
# 使用生成器减少内存占用
def process_large_dataset(data_stream):
for item in data_stream:
yield process_item(item)
# 使用__slots__减少对象内存占用
class WordCount:
__slots__ = ['word', 'count', 'timestamp']
def __init__(self, word, count):
self.word = word
self.count = count
self.timestamp = datetime.now()
类型提示和验证
from typing import List, Dict, Optional, Union
from pydantic import BaseModel, validator
class Message(BaseModel):
text: str
priority: int = Field(ge=1, le=10)
@validator('text')
def text_must_not_be_empty(cls, v):
if not v.strip():
raise ValueError('Text cannot be empty')
return v
开发工具推荐
代码质量工具
# 代码格式化
black text_analysis_processor.py
# 代码检查
flake8 text_analysis_processor.py
# 类型检查
mypy text_analysis_processor.py
# 测试覆盖率
pytest --cov=text_analysis_processor tests/
Docker化部署
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
# 安装系统依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
gcc \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 安装Python依赖
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# 复制应用代码
COPY . .
# 启动应用
CMD ["python", "text_analysis_processor.py"]