1、BL2跳转BL31
在上一页在bl2_main函数中的最后一句是:
smc(BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE, (unsigned long)next_bl_ep_info, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
这个是触发smc操作。这个smc的handle在bl1的阶段就被制定了。
这个handle smc id是BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE。对应的handle函数是smc_handler64,对应在bl1/aarch64/bl1_exception.S文件中:
func smc_handler64
/* ----------------------------------------------
* Detect if this is a RUN_IMAGE or other SMC.
* ----------------------------------------------
*/
/* 判定触发smc操作时带入的参数是否是跳转执行image的操作 */
mov x30, #BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE //将BL1_SMC_RUN_IMAGE的值保存到x30
cmp x30, x0 //比较x30与x0的值
b.ne smc_handler //如果x30与x0不同则认为是普通类型的异常,进入到smc_handler进行处理
/* ------------------------------------------------
* Make sure only Secure world reaches here.
* ------------------------------------------------
*/
mrs x30, scr_el3 //获取scr寄存器的值
tst x30, #SCR_NS_BIT //比较scr寄存器中的NS位与SCR_NS_BIT是否相等
b.ne unexpected_sync_exception //如果当前NS位为非安全位,则证明不合法,产生异常
/* ----------------------------------------------
* Handling RUN_IMAGE SMC. First switch back to
* SP_EL0 for the C runtime stack.
* ----------------------------------------------
*/
ldr x30, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_RUNTIME_SP] /获取offset和sp的值
msr spsel, #0 //清空spsel中的值
mov sp, x30 //保存x30的值到sp寄存器,用于返回
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Pass EL3 control to next BL image.
* Here it expects X1 with the address of a entry_point_info_t
* structure describing the next BL image entrypoint.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mov x20, x1 //将x1中的数据保存到x20中
mov x0, x20 //将x20的数据保存到x0中
bl bl1_print_next_bl_ep_info //打印出bl3x镜像文件信息
ldp x0, x1, [x20, #ENTRY_POINT_INFO_PC_OFFSET] //将传入的参数和bl3x入口函数PC指针
msr elr_el3, x0
msr spsr_el3, x1
ubfx x0, x1, #MODE_EL_SHIFT, #2 //设定cortex模式
cmp x0, #MODE_EL3 //比较x0寄存器中的值是否为MODE_EL3
b.ne unexpected_sync_exception //如果x0中不是MODE_EL3则产生异常
bl disable_mmu_icache_el3 //禁止MMU的指令cache
tlbi alle3
#if SPIN_ON_BL1_EXIT
bl print_debug_loop_message
debug_loop:
b debug_loop
#endif
mov x0, x20
bl bl1_plat_prepare_exit/
* 设定返回参数 */
ldp x6, x7, [x20, #(ENTRY_POINT_INFO_ARGS_OFFSET + 0x30)]
ldp x4, x5, [x20, #(ENTRY_POINT_INFO_ARGS_OFFSET + 0x20)]
ldp x2, x3, [x20, #(ENTRY_POINT_INFO_ARGS_OFFSET + 0x10)]
ldp x0, x1, [x20, #(ENTRY_POINT_INFO_ARGS_OFFSET + 0x0)]
eret //跳转到bl3x执行
endfunc smc_handler64
为什么要使用smc的方式呢,因为在atf中这种底安全等级到高安全等级的切换就必须使用smc的方式。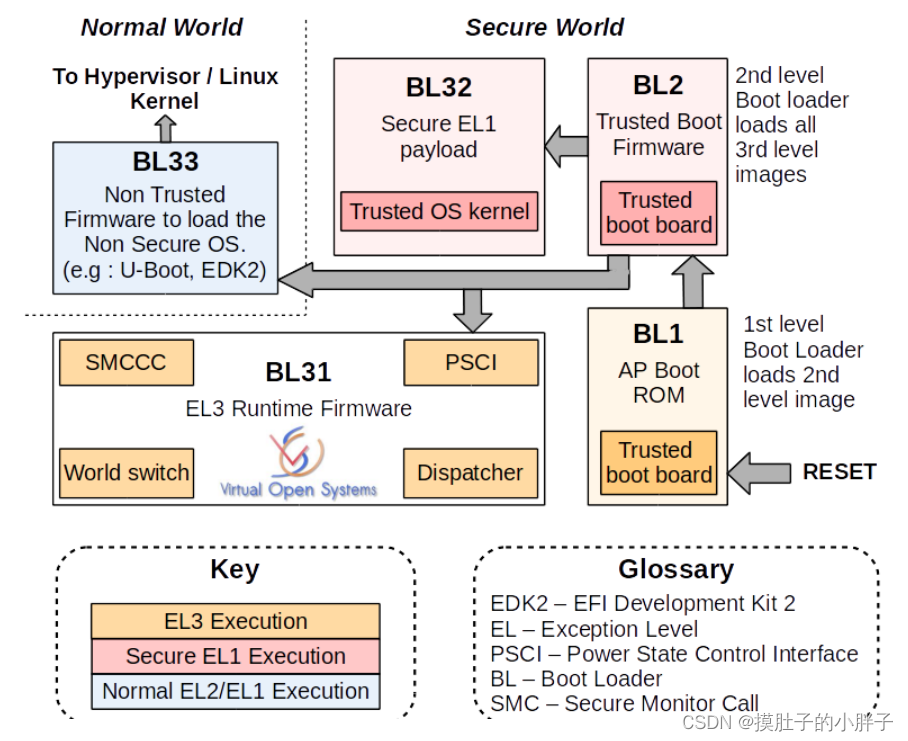
2、BL31
BL31位于SRAM中,EL3模式。除了做架构初始化和平台初始化外,还做了如下工作:
- PSCI服务初始化,后续提供CPU功耗管理操作。
- BL32镜像运行初始化,处于Secure EL1模式。
- 初始化非安全EL2或EL1,跳转到BL33执行。
- 负责安全非安全世界切换。
- 进行安全服务请求的分发。(这个就是推出了atf,但是会有个线程在那里一直跑着,检测有没smc指令下来)
通过bl31.ld.S文件可知, bl31的入口函数是:bl31_entrypoint函数,该函数的内容如下:
其实真正意义上的来说应该是TFA启动,然后bl31就是那个所谓的atf:(个人浅薄认识)
进入了bl31:
1、bl31_entrypoint()是冷启动的入口,只会被cpu0执行,初始化+必要的服务操作:bl31_entrypoint–>
2、bl31_main是ATF主体,必要初始化,配置EL3中的各种smc操作,以便在后续顺利响应在CA和TA中产生的smc操作。至此可以提供psci、smc等服务。然后再为进入BL33做好准备工作:bl31_main–>
3、
2.1、bl31_entrypoint
bl31_entrypoint()是冷启动的入口,只会被cpu0执行。
func bl31_entrypoint
#if !RESET_TO_BL31
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------
* Preceding bootloader has populated x0 with a pointer to a
* 'bl31_params' structure & x1 with a pointer to platform
* specific structure
* ---------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mov x20, x0
mov x21, x1
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* For !RESET_TO_BL31 systems, only the primary CPU ever reaches
* bl31_entrypoint() during the cold boot flow, so the cold/warm boot
* and primary/secondary CPU logic should not be executed in this case.
*
* Also, assume that the previous bootloader has already set up the CPU
* endianness and has initialised the memory.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
/* el3初始化操作,该el3_entrypoint_common函数在上面已经介绍过,其中runtime_exceptions为el3 runtime software的异常向量表,内容定义在bl31/aarch64/runtime_exceptions.S文件中 */
el3_entrypoint_common \
_set_endian=0 \
_warm_boot_mailbox=0 \
_secondary_cold_boot=0 \
_init_memory=0 \
_init_c_runtime=1 \
_exception_vectors=runtime_exceptions----------------------------runtime_exceptions是ATF的异常向量表。
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* Relay the previous bootloader's arguments to the platform layer
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mov x0, x20
mov x1, x21
#else
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* For RESET_TO_BL31 systems which have a programmable reset address,
* bl31_entrypoint() is executed only on the cold boot path so we can
* skip the warm boot mailbox mechanism.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
el3_entrypoint_common \
_set_endian=1 \
_warm_boot_mailbox=!PROGRAMMABLE_RESET_ADDRESS \
_secondary_cold_boot=!COLD_BOOT_SINGLE_CPU \
_init_memory=1 \
_init_c_runtime=1 \
_exception_vectors=runtime_exceptions
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* For RESET_TO_BL31 systems, BL31 is the first bootloader to run so
* there's no argument to relay from a previous bootloader. Zero the
* arguments passed to the platform layer to reflect that.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
mov x0, 0
mov x1, 0
#endif /* RESET_TO_BL31 */
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Perform platform specific early arch. setup
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
/* 平台架构相关的初始化设置 */
bl bl31_early_platform_setup-------------------------------------初始化UART,以及获取BL32、BL33的entrypoint。
bl bl31_plat_arch_setup------------------------------------------MMU内存初始化。
/* ---------------------------------------------
* Jump to main function.
* ---------------------------------------------
*/
bl bl31_main //跳转到bl31_main函数,执行该阶段需要的主要操作
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
* Clean the .data & .bss sections to main memory. This ensures
* that any global data which was initialised by the primary CPU
* is visible to secondary CPUs before they enable their data
* caches and participate in coherency.
* -------------------------------------------------------------
*/
adr x0, __DATA_START__
adr x1, __DATA_END__
sub x1, x1, x0
bl clean_dcache_range
adr x0, __BSS_START__
adr x1, __BSS_END__
sub x1, x1, x0
bl clean_dcache_range--------------------------------------------刷data和bss段到内存中
b el3_exit //执行完成将跳转到bl33中执行,即执行bootloader
endfunc bl31_entrypoint
//执行完成将跳转到bl33中执行,即执行bootloader
endfunc bl31_entrypoint
2.2、bl31_main
该函数主要完成必要初始化操作,配置EL3中的各种smc操作,以便在后续顺利响应在CA和TA中产生的smc操作。
bl31_main()是ATF主体,初始化好ATF服务、启动optee os,至此可以提供psci、TOS等服务。然后再为进入BL33做好准备工作。(启动了连两个系统镜像)
void bl31_main(void)
{
NOTICE("BL31: %s\n", version_string);
NOTICE("BL31: %s\n", build_message);
/* Perform platform setup in BL31 */
bl31_platform_setup(); //初始化相关驱动,时钟等
/* Initialise helper libraries */
bl31_lib_init(); //用于执行bl31软件中相关全局变量的初始化
/* Initialize the runtime services e.g. psci. */
INFO("BL31: Initializing runtime services\n");
runtime_svc_init(); //初始化el3中的service,通过在编译时指定特定的section来确定哪些service会被作为el3 service
/*
* All the cold boot actions on the primary cpu are done. We now need to
* decide which is the next image (BL32 or BL33) and how to execute it.
* If the SPD runtime service is present, it would want to pass control
* to BL32 first in S-EL1. In that case, SPD would have registered a
* function to intialize bl32 where it takes responsibility of entering
* S-EL1 and returning control back to bl31_main. Once this is done we
* can prepare entry into BL33 as normal.
*/
/*
* If SPD had registerd an init hook, invoke it.
*/
/* 如果注册了TEE OS支持,在调用完成run_service_init之后会使用TEE OS的入口函数初始化bl32_init变量,然后执行对应的Init函数,以OP-TEE为例,bl32_init将会被初始化成opteed_init,到此将会执行 opteed_init函数来进入OP-TEE OS的Image,当OP-TEE image OS执行完了image后,将会产生一个TEESMC_OPTEED_RETURN_ENTRY_DONE的smc来通过bl31已经完成了OP-TEE的初始化*/
if (bl32_init) {
INFO("BL31: Initializing BL32\n");
(*bl32_init)();
}
/*
* We are ready to enter the next EL. Prepare entry into the image
* corresponding to the desired security state after the next ERET.
*/
bl31_prepare_next_image_entry(); //准备跳转到bl33,在执行runtime_service的时候会存在一个spd service,该在service的init函数中将会去执行bl32的image完成TEE OS初始化
console_flush();
/*
* Perform any platform specific runtime setup prior to cold boot exit
* from BL31
*/
bl31_plat_runtime_setup();
}
2.3、runtime_svc_init
runtime_svc_init()作为BL31初始化一部分,初始化了运行在主CPU上的运行服务框架。这必须在TOS和普通世界软件启动之前执行,因为安全和非安全软件可能需要使用这部分内容。
runtime_svc_init()主要对注册的服务进行有限性验证,调用各自服务的初始化函数init(),以及将不同SMC OEN转换到注册服务ID。
在实际使用中,注册一个服务可能对应一系列SMC调用。
该函数主要用来建立smc索引表并执行EL3中提供的service的初始化操作。
后面在ATF服务注册里面好好详细讲一下这个怎么在ATF中注册咱们自定义的服务调用。
void runtime_svc_init(void)
{
int rc = 0, index, start_idx, end_idx;
/* Assert the number of descriptors detected are less than maximum indices */
/*判定rt_svc_descs段中的是否超出MAX_RT_SVCS条*/
assert((RT_SVC_DESCS_END >= RT_SVC_DESCS_START) &&
(RT_SVC_DECS_NUM < MAX_RT_SVCS));
/* If no runtime services are implemented then simply bail out */
if (RT_SVC_DECS_NUM == 0)
return;
/* Initialise internal variables to invalid state */
/* 初始化 t_svc_descs_indices数组中的数据成-1,表示当前所有的service无效*/
memset(rt_svc_descs_indices, -1, sizeof(rt_svc_descs_indices));
/* 获取第一条EL3 service在RAM中的起始地址,通过获取RT_SVC_DESCS_START的值来确定,该值在链接文件中有定义 */
rt_svc_descs = (rt_svc_desc_t *) RT_SVC_DESCS_START;
/* 遍历整个rt_svc_des段,将其call type与rt_svc_descs_indices中的index建立对应关系 */
for (index = 0; index < RT_SVC_DECS_NUM; index++) {
rt_svc_desc_t *service = &rt_svc_descs[index];
/*
* An invalid descriptor is an error condition since it is
* difficult to predict the system behaviour in the absence
* of this service.
*/
/* 判定在编译的时候注册的service是否有效 */
rc = validate_rt_svc_desc(service);
if (rc) {
ERROR("Invalid runtime service descriptor %p\n",
(void *) service);
panic();
}
/*
* The runtime service may have separate rt_svc_desc_t
* for its fast smc and standard smc. Since the service itself
* need to be initialized only once, only one of them will have
* an initialisation routine defined. Call the initialisation
* routine for this runtime service, if it is defined.
*/
/* 执行当前service的init的操作 */
if (service->init) {
rc = service->init();
if (rc) {
ERROR("Error initializing runtime service %s\n",
service->name);
continue;
}
}
/*
* Fill the indices corresponding to the start and end
* owning entity numbers with the index of the
* descriptor which will handle the SMCs for this owning
* entity range.
*/
/* 根据该service的call type以及start oen来确定一个唯一的index,并且将该service中支持的所有的call type生成的唯一表示映射到同一个index中 */
start_idx = get_unique_oen(rt_svc_descs[index].start_oen,
service->call_type);
assert(start_idx < MAX_RT_SVCS);
end_idx = get_unique_oen(rt_svc_descs[index].end_oen,
service->call_type);
assert(end_idx < MAX_RT_SVCS);
for (; start_idx <= end_idx; start_idx++)
rt_svc_descs_indices[start_idx] = index;
}
}
2.4、 el3_exit()
el3_exit()退出当前ATF执行下一阶段的镜像。
/* -----------------------------------------------------
* This routine assumes that the SP_EL3 is pointing to
* a valid context structure from where the gp regs and
* other special registers can be retrieved.
* -----------------------------------------------------
*/
func el3_exit
/* -----------------------------------------------------
* Save the current SP_EL0 i.e. the EL3 runtime stack
* which will be used for handling the next SMC. Then
* switch to SP_EL3
* -----------------------------------------------------
*/
mov x17, sp
msr spsel, #1
str x17, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_RUNTIME_SP]
/* -----------------------------------------------------
* Restore SPSR_EL3, ELR_EL3 and SCR_EL3 prior to ERET
* -----------------------------------------------------
*/
ldr x18, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_SCR_EL3]
ldp x16, x17, [sp, #CTX_EL3STATE_OFFSET + CTX_SPSR_EL3]
msr scr_el3, x18
msr spsr_el3, x16
msr elr_el3, x17
/* Restore saved general purpose registers and return */
b restore_gp_registers_eret
endfunc el3_exit
到这里就到OS里面去执行了。不过在这之前先讲讲这个SMC,atf的服务注册。