建立文件
temp.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:textSize="50dp" />
</LinearLayout>activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>MainActivity
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyTextView.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}MyTextView
package com.example.myapplication;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MyTextView extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.temp);
}
}
"ALT+ENTER"点击"Add activity to manifest"
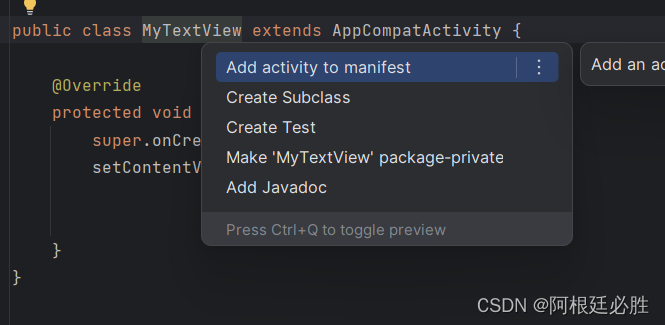
然后点击按钮就可以切换页面了
原理
Intent用于Android程序中各组件(Activity、BroadcastReceive、Service)的交互,并且可以在组件之间传递数据,分为显式Intent和隐式Intent。
Intent的中文意思为“意图”,在Android中可以理解为想要做什么,What do want to do? 所以什么时候要用到Intent就很好理解了。
通过Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls)构造函数创建Intent实例,第一个参数为当前Context,第二个参数为要启动的目标类。如当需要启动OtherActivity时:
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,OtherActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);二.公共构造函数:
1、Intent() 空构造函数
2、Intent(Intent o) 拷贝构造函数
3、Intent(String action) 指定action类型的构造函数
4、Intent(String action, Uri uri) 指定Action类型和Uri的构造函数,URI主要是结合程序之间的数据共享ContentProvider
5、Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 传入组件的构造函数,也就是上文提到的
6、Intent(String action, Uri uri, Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 前两种结合体
多种构造函数本文用的是第5种
/**
* Create an intent for a specific component. All other fields (action, data,
* type, class) are null, though they can be modified later with explicit
* calls. This provides a convenient way to create an intent that is
* intended to execute a hard-coded class name, rather than relying on the
* system to find an appropriate class for you; see {@link #setComponent}
* for more information on the repercussions of this.
*
* @param packageContext A Context of the application package implementing
* this class.
* @param cls The component class that is to be used for the intent.
*
* @see #setClass
* @see #setComponent
* @see #Intent(String, android.net.Uri , Context, Class)
*/
public Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) {
mComponent = new ComponentName(packageContext, cls);
}为特定组件创建 Intent 。所有其他字段(操作、数据、类型、类)均为 null,但稍后可以使用显式调用对其进行修改
packageContext – 实现此类的应用程序包的上下文。 cls – 要用于目的的组件类。
其中context含义
Context,字面意思:语境、环境、上下文,在 Android 系统中,可以理解为当前对象在应用程序中所处的工作环境
内部定义很多访问应用程序环境中全局信息的接口,通过它可以访问到应用程序的资源有关的类,如:Resources、AssetManager、Package 及权限相关信息等。还可以通过它调用应用程序级的操作,如:启动 Activity 和 Service、发送广播等。
/**
* Interface to global information about an application environment. This is
* an abstract class whose implementation is provided by
* the Android system. It
* allows access to application-specific resources and classes, as well as
* up-calls for application-level operations such as launching activities,
* broadcasting and receiving intents, etc.
*/
public abstract class Context {...}
与应用程序环境的全局信息的接口。 这是一个抽象类,其实现由 Android 系统提供。 它
允许访问特定于应用程序的资源和类,以及
对应用程序级操作(如启动活动)的上行调用,
广播和接收意图等