在智能对话系统的世界里,我们常常追求完全自动化的解决方案。但现实情况是,有些时候机器并不能完美地理解人类的需求,这就需要人工干预来弥补机器的不足。LangGraph通过引入“人工干预”机制,让智能对话系统在自动化的同时,也能灵活地融入人工的智慧。今天,我们就来聊聊这个有趣的话题。
人工干预可以让智能系统在执行任务时,根据用户的反馈进行调整,从而更好地满足用户的需求。这种人机协作的方式,既利用了机器的高效性,又弥补了机器可能存在的不足。
LangGraph的人工干预机制
LangGraph通过一个特殊的工具interrupt来实现人工干预。可以在智能系统执行任务的过程中,暂停任务的执行,等待用户的输入。用户可以根据自己的需求,对任务的参数进行修改,或者直接接受系统的建议。
1.一个简单的例子:预订酒店
假设你正在开发一个智能酒店预订系统,你希望在用户预订酒店时,能够让他们手动修改酒店的名称。
你可以使用LangGraph的interrupt工具来实现这个功能。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_community.chat_models.tongyi import ChatTongyi
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.types import interrupt
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
#模型初始化
llm = ChatTongyi(
model="qwen-turbo",#qwen-max-latest qwen-plus
temperature=0,
verbose=True,
)
#定义一个工具函数,有interrupt 封装一个工具支持人工参与的循环审查
def book_hotel(hotel_name: str):
"""预订酒店"""
response = interrupt(
f"尝试调用book_hotel酒店的名称{{'hotel_name': {hotel_name}}}. "
"请编辑后点击确认."
)
if response["type"] == "accept":
pass
elif response["type"] == "edit":
hotel_name = response["args"]["hotel_name"]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown response type: {response['type']}")
return f"成功的预订到酒店,名称为 {hotel_name}."
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
agent = create_react_agent(
model=llm,
tools=[book_hotel],
checkpointer=checkpointer,
)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
for chunk in agent.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "预订附近的桔子酒店"}]},
config
):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
运行结果截图

在这个例子中,当用户请求预订酒店时,系统会调用book_hotel函数。函数会通过interrupt工具暂停任务的执行,等待用户的输入。用户可以选择接受系统的建议,或者修改酒店的名称。无论用户如何选择,系统都会根据用户的选择继续执行任务。
2.下面示例dome是用户的确认:
from langgraph.types import Command
for chunk in agent.stream(
Command(resume={"type": "accept"}),
# Command(resume={"type": "edit", "args": {"hotel_name": "如家酒店"}}),
config
):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
运行结果截图

再工具执行到interrupt时,会根据配置thread_id=1,循环等待用户的确认。
集成人工干预
封装工具add_human_in_the_loop,这样就可以将人工干预的功能集成到任何现有的工具中。
这意味着,你可以轻松地将人工干预的功能添加到你的智能对话系统中,而不需要重新编写整个系统。
1.工具方法add_human_in_the_loop
from typing import Callable
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool, tool as create_tool
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langgraph.types import interrupt
from langgraph.prebuilt.interrupt import HumanInterruptConfig, HumanInterrupt
def add_human_in_the_loop(
tool: Callable | BaseTool,
*,
interrupt_config: HumanInterruptConfig = None,
) -> BaseTool:
"""封装一个工具以支持人工参与的循环审查"""
if not isinstance(tool, BaseTool):
tool = create_tool(tool)
if interrupt_config is None:
interrupt_config = {
"allow_accept": True,
"allow_edit": True,
"allow_respond": True,
}
@create_tool(
tool.name,
description=tool.description,
args_schema=tool.args_schema
)
def call_tool_with_interrupt(config: RunnableConfig, **tool_input):
request: HumanInterrupt = {
"action_request": {
"action": tool.name,
"args": tool_input
},
"config": interrupt_config,
"description": "请审查工具调用。"
}
print(2222)
response = interrupt([request])[0]
print(4444)
# approve the tool call
if response["type"] == "accept":
tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config)
# update tool call args
elif response["type"] == "edit":
tool_input = response["args"]["args"]
tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config)
# respond to the LLM with user feedback
elif response["type"] == "response":
user_feedback = response["args"]
tool_response = user_feedback
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的中断响应类型: {response['type']}")
return tool_response
return call_tool_with_interrupt
2.tools中调用封装
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_community.chat_models.tongyi import ChatTongyi
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.types import interrupt
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
#模型初始化
llm = ChatTongyi(
model="qwen-turbo",#qwen-max-latest qwen-plus
temperature=0,
verbose=True,
)
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
def book_hotel(hotel_name: str):
"""预订酒店"""
return f"已成功预订了酒店 {hotel_name}."
print(1111)
agent = create_react_agent(
model=llm,
tools=[
add_human_in_the_loop(book_hotel),
],
checkpointer=checkpointer,
)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
# 运行代理
for chunk in agent.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "预订附近的桔子酒店"}]},
config
):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
运行结果截图

当用户请求预订酒店时,系统会自动调用book_hotel函数,并在执行过程中等待用户的输入。
3.人工干预反馈
print(3333)
from langgraph.types import Command
for chunk in agent.stream(
# Command(resume=[{"type": "accept"}]),
Command(resume=[{"type": "edit", "args": {"args": {"hotel_name": "如家酒店"}}}]),
config
):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
#结果:抱歉,附近没有桔子酒店可供预订。已为您成功预订了附近的如家酒店。如果您需要其他帮助,请随时告诉我。
运行结果截图
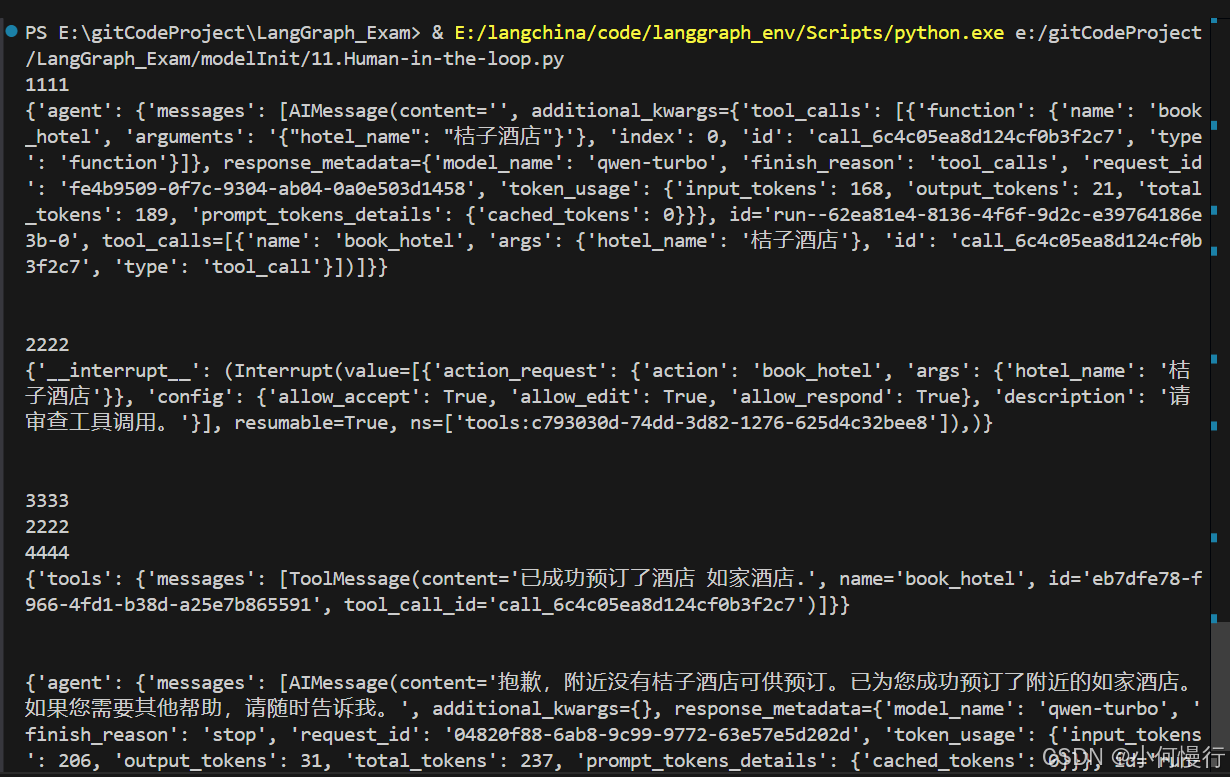
在这个例子中,我们使用add_human_in_the_loop工具将人工干预的功能添加到了book_hotel函数中。这样,当用户请求预订酒店时,系统会自动调用book_hotel函数,并在执行过程中等待用户的输入。
人工干预的实际应用
人工干预不仅适用于酒店预订,还可以应用于各种需要用户参与的场景。
比如,智能客服系统可以在处理用户投诉时,让用户手动修改投诉的内容;智能写作助手可以在生成文章时,让用户手动修改文章的标题或内容。
这种人机协作的方式,可以让智能系统更好地满足用户的需求。