🌟 什么是 MCP?
模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。
MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。
可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它们的应用程序之间的通用翻译器。就像 HTTP 帮助 Web 浏览器与 Web 服务器通信一样,MCP 帮助应用程序与 AI 模型通信!

模型上下文协议架构
🚀 为什么选择 MCP?
模型的好坏取决于提供给它们的上下文。我们可以拥有一个近在咫尺的强大模型,但如果它没有能力连接外部世界并检索必要的数据和上下文,那么它就不会像它可能的那样有用。
我们将要用 MCP 做的所有事情,没有 MCP 也能实现。但是,想想要让 LLM 更具推理能力,我们需要连接的每一个工具。假设我们必须使用不同的 API 来满足不同的服务需求。但每个服务提供商构建其 API 的方式可能不同,甚至使用不同的语言。
在这里,我们希望确保我们使用同一种语言与所有必需的 API 进行通信。这就是 MCP 发挥作用的地方。它标准化了我们的 AI 应用程序与外部系统的交互方式。它有助于我们一次性构建所需的功能并重复使用,而不是根据不同的数据源一次又一次地为它们构建相同的集成。
💪 MCP 的主要优势
🔌 即插即用集成
- 连接任何 AI 模型到任何应用程序
- 切换模型时无需重写代码
- 标准化的通信协议
🛠️ 工具优先方法
- 模型将其能力作为工具暴露出来
- 应用程序可以动态发现和使用工具
- 非常适合智能体和自治系统
🌐 语言无关
- 可以用任何编程语言编写客户端
- 模型可以用任何框架实现
- 实现整个 AI 生态系统的真正互操作性
⚡ 实时通信
- 支持服务器发送事件 (SSE)
- 结果可用时流式传输
- 非常适合聊天应用程序和交互式系统
🏗️ 架构深入探讨
🖥️ 服务端 (server.py)
@mcp.tool()
def add_data(query: str) -> bool:
"""Add new data to the people table""" // 使用 SQL INSERT 查询向 people 表添加新数据
# Tool implementation // 工具实现
服务端:
- 📝 将工具定义为简单的 Python 函数
- 🎯 通过 MCP 装饰器暴露工具
- 🔄 处理请求并返回响应
- 📚 维护工具文档和模式 (schema)
📡 服务端 (server.py) 组件
- FastMCP 服务器
- MCP 工具
- 数据库管理
- 错误处理
👥 客户端 (langchain_client.py)
class LangchainMCPClient:
async def initialize_agent(self):
"""Initialize the agent with tools""" // 使用工具初始化智能体
# Client implementation // 客户端实现
客户端:
- 🤝 连接到 MCP 服务器
- 🔍 发现可用工具
- 🤖 创建一个 AI 智能体来使用工具
- 💬 处理用户交互
👥 客户端组件 (langchain_client.py)
- LangChain 集成
- 智能体系统
- 工具管理
- 对话历史
🔗 MCP 层
- 工具注册
- 请求处理
- 响应处理
- 事件流
🔄 工作流
🚀 服务器启动
- 服务器初始化并加载工具
- 工具注册其能力
- 服务器开始监听连接
🤝 客户端连接
- 客户端发现服务器
- 获取可用工具
- 创建具有工具访问权限的智能体
💬 用户交互
- 用户发送请求
- 智能体处理请求
- 工具在服务器上执行
- 结果返回给用户
📊 数据流
添加记录:
用户: "add John 30 Engineer" // 添加 John 30 岁 工程师 ↓ 智能体: Formats SQL query // 格式化 SQL 查询 ↓ MCP 工具: INSERT INTO people VALUES ('John', 30, 'Engineer') ↓ 服务器: Executes SQL // 执行 SQL ↓ 数据库: Stores data // 存储数据 ↓ 响应: "Successfully added John (age: 30, profession: Engineer)" // 成功添加 John(年龄:30,职业:工程师)读取记录:
用户: "show all records" // 显示所有记录 ↓ 智能体: Formats SELECT query // 格式化 SELECT 查询 ↓ MCP 工具: SELECT * FROM people ↓ 服务器: Fetches data // 获取数据 ↓ 客户端: Formats table // 格式化表格 ↓ 响应: Displays formatted table // 显示格式化表格
🎯 真实世界示例
我们经常使用 Cursor IDE 或 Claude Desktop 作为 MCP 主机,其中客户端依赖于外部 LLM(Claude Sonnet, GPT-4 等)。虽然这些工具非常出色,但在某些情况下——尤其是在处理敏感数据时——完全安全和私密的 MCP 客户端至关重要。在我们的实现中,我们创建了一个由本地 LLM 驱动的 MCP 客户端,该客户端可以向 SQLite 数据库添加行并从 SQLite(数据库管理系统)中选择行,其中:
- 📥 添加数据
- 用户请求添加人员
- 智能体格式化 SQL 查询
- MCP 工具执行查询
- 确认信息返回给用户
- 📤 读取数据
- 用户请求查看记录
- 智能体创建 SELECT 查询
- MCP 工具获取数据
- 结果格式化为漂亮的表格
🛠️ MCP 实现的技术栈
1. 🐍 Python 框架和库
- Python 3.x — 核心编程语言
- FastMCP — MCP 服务器实现
- LangChain — AI/LLM 框架集成
- SQLite3 — 数据库管理
- asyncio — 异步 I/O 操作
- nest_asyncio — 嵌套事件循环支持
2. 🤖 AI/LLM 集成
- Ollama — 本地 LLM 模型托管(“llama3.2”)
3. 🗃️ 数据库层
- SQLite — 轻量级数据库
def init_db():
conn = sqlite3.connect('demo.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Schema creation... // 模式创建...
4. 🔌 通信协议
- SSE (服务器发送事件) — 实时更新
- MCP 协议 — 工具通信
server_config = {
"default": {
"url": f"{mcp_server_url}/sse",
"transport": "sse",
"options": {...}
}
}
代码实现
- 安装所需库
# 🔄 核心 MCP 和 LangChain 包
pip install langchain # LangChain 框架
pip install langchain-core # 核心 LangChain 功能
pip install langchain-community # 社区工具和集成
pip install langchain-mcp-adapters # 用于 LangChain 的 MCP 适配器
pip install fastmcp # FastMCP 服务器实现
# 🤖 LLM 集成
pip install langchain-ollama # LangChain 的 Ollama 集成
# 🔌 网络和异步
pip install httpx # 异步 HTTP 客户端
pip install nest-asyncio # 嵌套异步支持
- server.py
import sqlite3
import argparse
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP('sqlite-demo') // 初始化 FastMCP 实例
def init_db():
conn = sqlite3.connect('demo.db') // 连接数据库
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people ( // 如果 people 表不存在则创建
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
age INTEGER NOT NULL,
profession TEXT NOT NULL
)
''')
conn.commit()
return conn, cursor
@mcp.tool() // 定义为 MCP 工具
def add_data(query: str) -> bool:
"""使用 SQL INSERT 查询向 people 表添加新数据。
Args:
query (str): SQL INSERT 查询,遵循以下格式:
INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession)
VALUES ('John Doe', 30, 'Engineer')
Schema (模式):
- name: 文本字段 (必需)
- age: 整数字段 (必需)
- profession: 文本字段 (必需)
注意:'id' 字段是自动生成的
Returns:
bool: 如果数据添加成功则返回 True,否则返回 False
Example (示例):
>>> query = '''
... INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession)
... VALUES ('Alice Smith', 25, 'Developer')
... '''
>>> add_data(query)
True
"""
conn, cursor = init_db()
try:
print(f"\n\n正在使用查询执行 add_data:{query}")
cursor.execute(query)
conn.commit()
return True
except sqlite3.Error as e:
print(f"添加数据时出错:{e}")
return False
finally:
conn.close()
@mcp.tool() // 定义为 MCP 工具
def read_data(query: str = "SELECT * FROM people") -> list:
"""使用 SQL SELECT 查询从 people 表读取数据。
Args:
query (str, optional): SQL SELECT 查询。默认为 "SELECT * FROM people"。
示例:
- "SELECT * FROM people"
- "SELECT name, age FROM people WHERE age > 25"
- "SELECT * FROM people ORDER BY age DESC"
Returns:
list: 包含查询结果的元组列表。
对于默认查询,元组格式为 (id, name, age, profession)
Example (示例):
>>> # 读取所有记录
>>> read_data()
[(1, 'John Doe', 30, 'Engineer'), (2, 'Alice Smith', 25, 'Developer')]
>>> # 使用自定义查询读取
>>> read_data("SELECT name, profession FROM people WHERE age < 30")
[('Alice Smith', 'Developer')]
"""
conn, cursor = init_db()
try:
print(f"\n\n正在使用查询执行 read_data:{query}")
cursor.execute(query)
return cursor.fetchall()
except sqlite3.Error as e:
print(f"读取数据时出错:{e}")
return []
finally:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Start the server // 启动服务器
print("🚀正在启动服务器... ")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--server_type", type=str, default="sse", choices=["sse", "stdio"],
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# Only pass server_type to run() // 只将 server_type 传递给 run()
mcp.run(args.server_type)
- langchain_client.py
import asyncio
import nest_asyncio
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
from langchain_mcp_adapters.tools import MCPTool
from langchain.agents.format_scratchpad import format_log_to_str
from langchain.agents.output_parsers import ReActSingleInputOutputParser, ReActJsonSingleInputOutputParser
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage, SystemMessage
import httpx
from langchain.tools import Tool
from typing import Optional, Any, Callable, Awaitable
# Enable nested asyncio for Jupyter-like environments // 为类似 Jupyter 的环境启用嵌套 asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
REACT_TEMPLATE = """尽力回答以下问题。你可以使用以下工具:
{tools}
使用以下格式:
Question: 你必须回答的输入问题
Thought: 你应该总是思考该做什么
Action: {tool_names}
Action Input: 要执行的 SQL 查询
Observation: 操作的结果
Thought: 我现在知道最终答案了
Final Answer: [用于 read_data 的格式化表格或用于 add_data 的成功消息]
例如:
Question: add John Doe 30 year old Engineer
Thought: 我需要向数据库添加一个新人员
Action: add_data
Action Input: INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('John Doe', 30, 'Engineer')
Observation: 数据添加成功
Thought: 我已成功添加该人员
Final Answer: 成功将 John Doe (年龄: 30, 职业: Engineer) 添加到数据库
Question: show all records
Thought: 我需要从数据库检索所有记录
Action: read_data
Action Input: SELECT * FROM people
Observation: [包含记录的格式化表格]
Thought: 我已检索所有记录
Final Answer: [显示所有记录的格式化表格]
开始!
Question: {input}
{agent_scratchpad}"""
class LangchainMCPClient:
def __init__(self, mcp_server_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000"):
print("正在初始化 LangchainMCPClient...")
self.llm = ChatOllama(
model="llama3.2",
temperature=0.6,
streaming=False # Disable streaming for better compatibility // 禁用流式传输以获得更好的兼容性
)
# Updated server configuration with shorter timeouts // 更新了服务器配置,使用更短的超时时间
server_config = {
"default": {
"url": f"{mcp_server_url}/sse",
"transport": "sse",
"options": {
"timeout": 10.0, // 连接超时
"retry_connect": True, // 重试连接
"max_retries": 2, // 最大重试次数
"read_timeout": 5.0, // 读取超时
"write_timeout": 5.0 // 写入超时
}
}
}
print(f"正在连接到 MCP 服务器于 {mcp_server_url}...")
self.mcp_client = MultiServerMCPClient(server_config)
self.chat_history = []
# System prompt for the agent // 智能体的系统提示
self.SYSTEM_PROMPT = """你是一个 AI 助手,帮助用户与数据库交互。
你可以使用可用工具从数据库中添加和读取数据。
添加数据时:
1. 正确格式化 SQL 查询:INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('Name', Age, 'Profession')
2. 确保在文本值周围使用单引号
3. 不要在数值周围使用引号
读取数据时:
1. 使用 SELECT * FROM people 获取所有记录
2. 使用 WHERE 子句进行过滤:SELECT * FROM people WHERE condition
3. 以清晰、格式化的方式呈现结果
始终:
1. 仔细思考每一步
2. 验证操作是否成功
3. 提供清晰的操作摘要"""
async def check_server_connection(self):
"""Check if the MCP server is accessible""" // 检查 MCP 服务器是否可访问
base_url = self.mcp_client.connections["default"]["url"].replace("/sse", "")
try:
print(f"正在测试连接到 {base_url}...")
async with httpx.AsyncClient(timeout=5.0) as client: # Shorter timeout // 更短的超时时间
# Try the SSE endpoint directly // 直接尝试 SSE 端点
sse_url = f"{base_url}/sse"
print(f"正在检查 SSE 端点于 {sse_url}...")
response = await client.get(sse_url, timeout=5.0)
print(f"获取到响应:{response.status_code}")
if response.status_code == 200:
print("SSE 端点可访问!")
return True
print(f"服务器响应状态码:{response.status_code}")
return False
except httpx.ConnectError:
print(f"无法连接到服务器于 {base_url}")
print("请确保服务器正在运行且端口正确")
return False
except httpx.ReadTimeout:
print("连接已建立但在读取时超时")
print("这对于 SSE 连接是正常的 - 继续...")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"连接 MCP 服务器时出错:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
return False
async def initialize_agent(self):
"""Initialize the agent with tools and prompt template""" // 使用工具和提示模板初始化智能体
print("\n正在初始化智能体...")
if not await self.check_server_connection():
raise ConnectionError("无法连接到 MCP 服务器。请确保服务器正在运行。")
try:
print("正在获取可用工具...")
mcp_tools = await self.mcp_client.get_tools()
# Verify tools are properly initialized // 验证工具是否正确初始化
print("正在验证工具...")
for i, tool in enumerate(mcp_tools):
print(f"\n工具 {i}:")
print(f" 名称: {tool.name if hasattr(tool, 'name') else '无名称'}")
print(f" 描述: {tool.description if hasattr(tool, 'description') else '无描述'}")
print(f" 类型: {type(tool)}")
print(f" 可调用: {callable(tool)}")
# 省略调试输出的翻译
print(f" 方法: {[method for method in dir(tool) if not method.startswith('_')]}")
print(f" 完整工具: {tool.__dict__}")
# Test call // 测试调用
try:
print(" 正在测试工具调用...")
if i == 0:
test_query = "INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('Test', 30, 'Test')"
else:
test_query = "SELECT * FROM people"
result = await tool.ainvoke({"query": test_query})
print(f" 测试结果: {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f" 测试错误: {type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
if len(mcp_tools) < 2:
raise ValueError(f"期望 2 个工具,得到 {len(mcp_tools)}")
# Create async wrapper functions with better error handling // 创建具有更好错误处理的异步包装函数
async def add_data_wrapper(query: str):
try:
tool = mcp_tools[0] # add_data tool // add_data 工具
if not tool:
print("工具 0 (add_data) 未正确初始化")
return "错误:添加数据工具未正确初始化"
print(f"正在使用查询执行 add_data:{query}")
# Clean up the query // 清理查询
query = query.strip().replace('\\n', ' ').replace(' ', ' ')
# Fix common formatting issues // 修复常见的格式问题
if "VALUES" in query:
parts = query.split("VALUES")
if len(parts) == 2:
values = parts[1].strip()
if values.startswith("(") and values.endswith(")"):
values = values[1:-1].split(",")
if len(values) == 3:
name = values[0].strip().strip("'")
age = values[1].strip()
profession = values[2].strip().strip("'")
query = f"INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('{name}', {age}, '{profession}')"
# Call the tool using the async method // 使用异步方法调用工具
result = await tool.ainvoke({"query": query})
print(f"添加数据结果: {result}")
if result:
return "数据添加成功" # Clear success message // 清晰的成功消息
return "未能添加数据" # Clear failure message // 清晰的失败消息
except Exception as e:
print(f"add_data_wrapper 中出错:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
return f"添加数据时出错:{str(e)}"
async def read_data_wrapper(query: str = "SELECT * FROM people"):
try:
tool = mcp_tools[1] # read_data tool // read_data 工具
if not tool:
print("工具 1 (read_data) 未正确初始化")
return "错误:读取数据工具未正确初始化"
print(f"正在使用查询执行 read_data:{query}")
# Clean up the query // 清理查询
query = query.strip().replace('\\n', ' ').replace(' ', ' ')
# Call the tool using the async method // 使用异步方法调用工具
result = await tool.ainvoke({"query": query})
print(f"读取数据结果: {result}")
if not result:
return "未找到记录"
# Format results in a table // 将结果格式化为表格
records = []
for i in range(0, len(result), 4):
records.append({
'name': result[i+1],
'age': result[i+2],
'profession': result[i+3]
})
# Create table header // 创建表头
output = [
f"显示 {len(records)} 条记录:",
"",
"| Name | Age | Profession |",
"|---------------|-----|------------------|"
]
# Add each record // 添加每条记录
for record in records:
name = record['name'].ljust(13)
age = str(record['age']).ljust(5)
profession = record['profession'].ljust(16)
output.append(f"| {name} | {age} | {profession} |")
return "\n".join(output)
except Exception as e:
print(f"read_data_wrapper 中出错:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
return f"读取数据时出错:{str(e)}"
# Create Langchain tools with async functions // 使用异步函数创建 Langchain 工具
self.tools = [
Tool(
name="add_data",
description="向数据库添加人员。示例:INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('John Doe', 30, 'Engineer')",
func=lambda x: "使用异步版本",
coroutine=add_data_wrapper
),
Tool(
name="read_data",
description="从数据库读取。示例:SELECT * FROM people",
func=lambda x: "使用异步版本",
coroutine=read_data_wrapper
)
]
print(f"找到 {len(self.tools)} 个工具")
# Create the prompt template with system message // 创建带有系统消息的提示模板
system_message = SystemMessage(content=self.SYSTEM_PROMPT)
human_message = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(REACT_TEMPLATE)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
system_message,
human_message
]).partial(tool_names="add_data or read_data")
# Create the agent with simpler configuration // 使用更简单的配置创建智能体
self.agent = create_react_agent(
llm=self.llm,
tools=self.tools,
prompt=prompt
)
# Create the executor with better configuration // 使用更好的配置创建执行器
self.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=self.agent,
tools=self.tools,
verbose=True, // 详细输出
handle_parsing_errors=True, // 处理解析错误
max_iterations=1, # Only try once // 只尝试一次
early_stopping_method="force", # Stop after max_iterations // 在 max_iterations 后停止
return_intermediate_steps=True # Ensure we get the steps // 确保我们得到步骤
)
print("\n可用工具:")
for tool in self.tools:
print(f"- {tool.name}: {tool.description}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n初始化智能体时出错:{e}")
raise
async def process_message(self, user_input: str) -> str:
"""Process a single user message and return the agent's response""" // 处理单个用户消息并返回智能体的响应
try:
print("\n正在处理消息:", user_input)
# Execute the agent // 执行智能体
response = await self.agent_executor.ainvoke({
"input": user_input,
"chat_history": self.chat_history
})
print("\n原始响应:", response)
final_result = None
# Get the result from intermediate steps // 从中间步骤获取结果
if isinstance(response, dict) and "intermediate_steps" in response:
steps = response["intermediate_steps"]
if steps and isinstance(steps[-1], tuple):
action, observation = steps[-1]
# Handle add_data response // 处理 add_data 响应
if "add_data" in str(action):
query = str(action.tool_input)
if "VALUES" in query:
values = query[query.find("VALUES")+7:].strip("() ")
name, age, profession = [v.strip().strip("'") for v in values.split(",")]
final_result = f"成功将 {name} (年龄: {age}, 职业: {profession}) 添加到数据库"
# Handle read_data response // 处理 read_data 响应
elif "read_data" in str(action):
if isinstance(observation, str) and "Showing" in observation:
final_result = observation # Use the formatted table // 使用格式化的表格
else:
final_result = str(observation) # Use any other read response // 使用任何其他读取响应
# Use raw observation if no specific handling // 如果没有特定处理,则使用原始观察结果
if final_result is None:
final_result = str(observation)
# Update response output and chat history // 更新响应输出和聊天历史
response["output"] = final_result
self.chat_history.extend([
HumanMessage(content=user_input),
AIMessage(content=final_result)
])
print("\n最终结果:", final_result)
return final_result
return "无法处理请求。请重试。"
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"处理消息时出错:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}\n请尝试重新表述您的请求。"
print(f"\n处理消息时出错:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
print(f"完整错误:{e.__dict__}")
return error_msg
async def interactive_chat(self):
"""Start an interactive chat session""" // 开始交互式聊天会话
print("聊天会话已开始。输入 'exit' 退出。")
while True:
user_input = input("\n您:")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
print("正在结束聊天会话...")
break
response = await self.process_message(user_input)
print("\n智能体:", response)
async def main():
try:
print("正在启动 Langchain MCP 客户端...")
client = LangchainMCPClient()
print("\n正在初始化智能体...")
await client.initialize_agent()
print("\n正在启动交互式聊天...")
await client.interactive_chat()
except ConnectionError as e:
print(f"\n连接错误:{e}")
print("请检查:")
print("1. MCP 服务器正在运行 (python server.py --server_type=sse)")
print("2. 服务器 URL 正确 (http://127.0.0.1:8000)")
print("3. 服务器可以从您的机器访问")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n意外错误:{type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Run the async main function // 运行异步 main 函数
asyncio.run(main())
⚠️ 重要说明:
系统要求:
- Python 3.8 或更高版本
- SQLite3 (Python 自带)
- 足够的磁盘空间用于 LLM 模型
Ollama 设置:
- 单独从以下地址安装 Ollama:Ollama
- 拉取所需模型:
ollama run llama3.2
🚀 开始使用
# Start the MCP server // 启动 MCP 服务器
python server.py --server_type=sse
# Run the client // 运行客户端
python langchain_client.py
1. 🚀 初始化阶段
- 服务器启动并注册工具
- 客户端连接到服务器
- 客户端发现可用工具
- 智能体使用工具进行初始化
2. 💬 用户交互阶段
当用户输入:“add Panama 55 year old as the SME” (添加 Panama 55 岁作为 SME)
- 输入传递给智能体
- 智能体格式化 SQL 查询
- 查询传递给 MCP 工具
- 工具在服务器上执行
- 结果返回给用户
响应日志
server.py 日志


langchain_client.py 响应日志
(注意:日志中的大部分内容保持英文原文以反映程序输出,仅翻译关键启动信息、用户输入和最终智能体回复)
(.venv) C:\Users\PLNAYAK\Documents\local_mcp_server>python langchain_client.py
Starting Langchain MCP Client... // 正在启动 Langchain MCP 客户端...
Initializing LangchainMCPClient... // 正在初始化 LangchainMCPClient...
Connecting to MCP server at http://127.0.0.1:8000... // 正在连接到 MCP 服务器于 http://127.0.0.1:8000...
Initializing agent... // 正在初始化智能体...
Testing connection to http://127.0.0.1:8000... // 正在测试连接到 http://127.0.0.1:8000...
Checking SSE endpoint at http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse... // 正在检查 SSE 端点于 http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse...
Connection established but timed out while reading // 连接已建立但在读取时超时
This is normal for SSE connections - proceeding... // 这对于 SSE 连接是正常的 - 继续...
Getting available tools... // 正在获取可用工具...
Verifying tools... // 正在验证工具...
(工具验证细节省略)
Found 2 tools // 找到 2 个工具
Available tools: // 可用工具:
- add_data: Add a person to the database... (向数据库添加人员...)
- read_data: Read from the database... (从数据库读取...)
Starting interactive chat... // 正在启动交互式聊天...
Chat session started. Type 'exit' to quit. // 聊天会话已开始。输入 'exit' 退出。
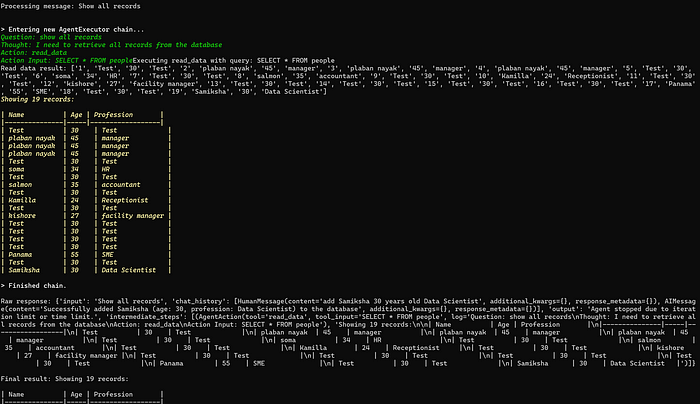
您:add Samiksha 30 years old Data Scientist
Processing message: add Samiksha 30 years old Data Scientist // 正在处理消息...
> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
Question: add Samiksha 30 years old Data Scientist
Thought: I need to add a new person to the database
Action: add_data
Action Input: INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('Samiksha', 30, 'Data Scientist')Executing add_data with query: INSERT INTO people (name, age, profession) VALUES ('Samiksha', 30, 'Data Scientist')
Add data result: true
Data added successfully
> Finished chain.
Raw response: ... (原始响应省略)
Final result: Successfully added Samiksha (age: 30, profession: Data Scientist) to the database // 最终结果: 成功将 Samiksha (年龄: 30, 职业: Data Scientist) 添加到数据库
智能体:Successfully added Samiksha (age: 30, profession: Data Scientist) to the database
您:Show all records
Processing message: Show all records // 正在处理消息: Show all records
> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
Question: show all records
Thought: I need to retrieve all records from the database
Action: read_data
Action Input: SELECT * FROM peopleExecuting read_data with query: SELECT * FROM people
Read data result: ... (读取数据结果省略)
Showing 19 records:
... (表格内容省略)
> Finished chain.
Raw response: ... (原始响应省略)
Final result: Showing 19 records:\n\n| Name | Age | Profession |\n|---------------|-----|------------------|\n| Test | 30 | Test |\n... (其他记录省略) ...\n| Samiksha | 30 | Data Scientist | // 最终结果: 显示 19 条记录: ...
智能体:Showing 19 records: // 显示 19 条记录:
| Name | Age | Profession |
|---------------|-----|------------------|
| Test | 30 | Test |
| plaban nayak | 45 | manager |
| plaban nayak | 45 | manager |
| plaban nayak | 45 | manager |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| soma | 34 | HR |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| salmon | 35 | accountant |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Kamilla | 24 | Receptionist |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| kishore | 27 | facility manager |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Panama | 55 | SME |
| Test | 30 | Test |
| Samiksha | 30 | Data Scientist |
您:
🎯 此工作流的优势
- 🔌 模块化
- 易于添加新工具
- 易于修改现有工具
- 清晰的关注点分离
- 🚀 可扩展性
- 异步操作
- 连接池
- 资源管理
- 👥 用户体验
- 自然语言输入
- 格式化输出
- 错误处理
- 🛠️ 可维护性
- 清晰的代码结构
- 分离的组件
- 易于调试
这个工作流通过自然语言命令创建了一个健壮、可扩展且用户友好的数据库操作系统! 🎉
🔮 未来可能性
- 🎨 创意应用
- AI 艺术生成
- 自然语言处理
- 自治智能体
- 🏢 企业用例
- 数据库管理
- 客户服务
- 流程自动化
- 🔬 研究应用
- 模型比较
- 工具组合
- 智能体开发
🎉 结论
MCP 代表了 AI 集成方面向前迈出的重要一步,使得连接模型与应用程序比以往任何时候都更容易。无论我们是在构建聊天界面、数据库管理器还是自治智能体,MCP 都为您提供了所需的基础!