1 基本概念
在网络编程中,字节数据的处理是核心环节之一。无论是客户端与服务器之间的通信,还是数据的编解码操作,都离不开对字节缓冲区的高效管理。Java 原生的 ByteBuffer 虽然提供了基础功能,但在灵活性、性能和易用性上存在诸多局限。而 Netty 框架提供的 ByteBuf 则彻底解决了这些问题,成为处理网络字节数据的首选工具。
2 为什么需要 Bytebuf
Java 原生的 ByteBuffer 存在以下明显短板:
- 单指针设计:仅有一个
position指针,读写操作需频繁调用flip()切换模式,容易出错; - 固定容量:创建后容量不可动态调整,超出容量时需手动扩容,操作繁琐;
- 内存管理复杂:堆外内存(直接内存)的释放依赖 GC,可能导致内存泄漏;
- API 设计不友好:缺乏直接读写基本类型、字符串的便捷方法。
相比之下,ByteBuf 针对网络编程场景进行了全面优化:
- 采用双指针设计,读写无需切换模式;
- 支持自动扩容,无需手动处理容量不足问题;
- 内置引用计数机制,精准控制内存生命周期;
- 提供丰富的 API,简化字节数据操作。
3 Bytebuf数据结构
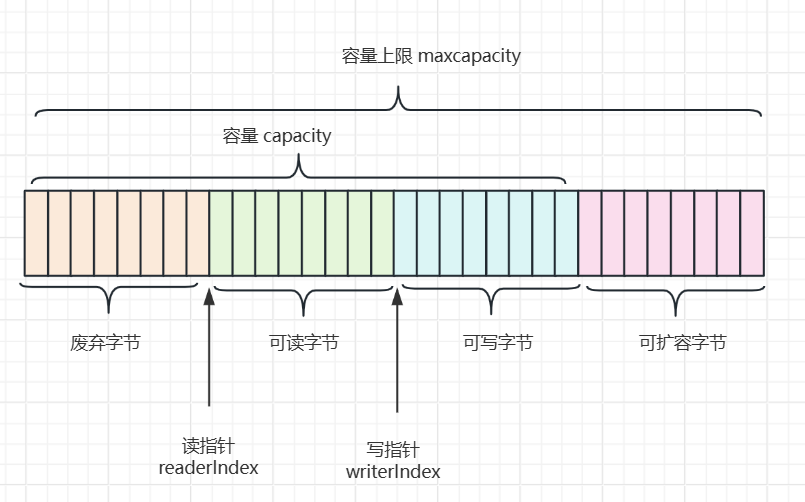
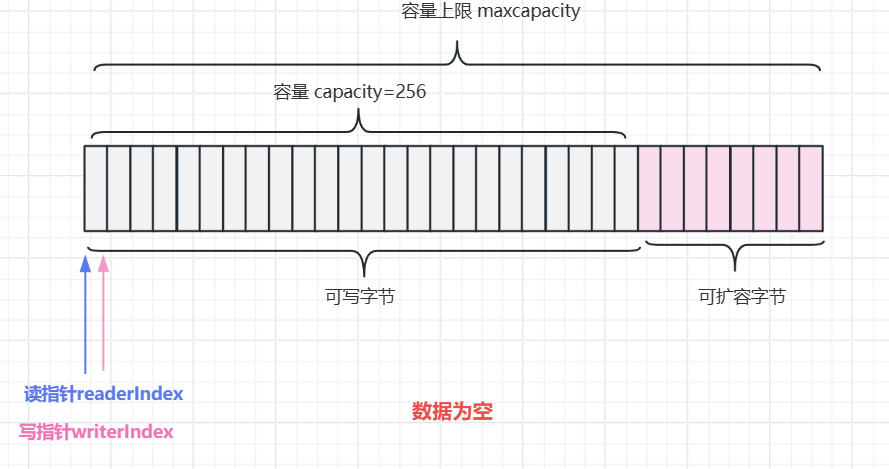
3.1 创建一个空Bytebuf
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 空ByteBuf
emptyByteBuf();
}
private static void emptyByteBuf() {
// byteBuf 分配一块内存,自动判断是否分配堆内存或者堆外内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}输出
read index:0
write index:0
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
数据为空时bytebuf的内存结构
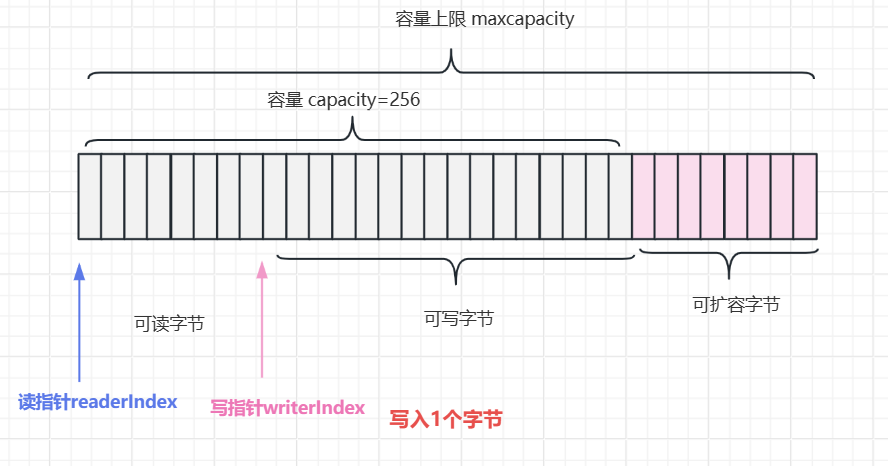
3.2 往Bytebuf中写入数据
private static void writeByte() {
// byteBuf 分配一块内存,自动判断是否分配堆内存或者堆外内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// 写入1个字节
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[]{(byte)1});
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}read index:0
write index:1
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 |. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
写入1个字节内存结构
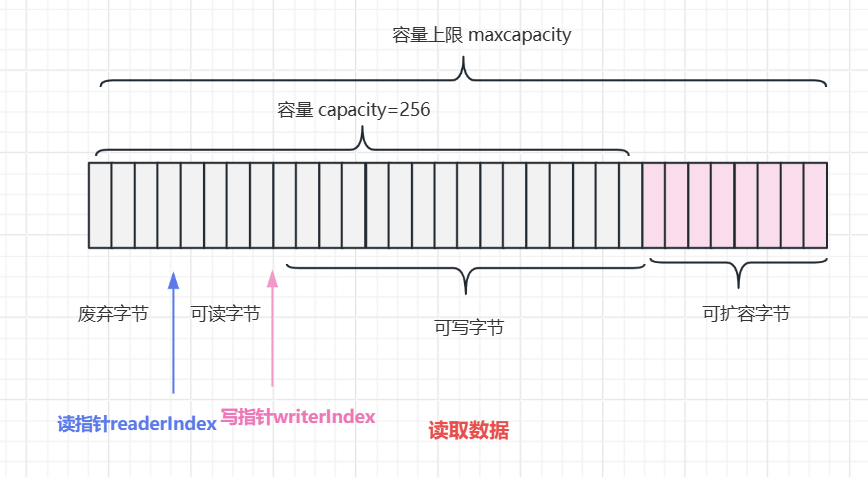
 3.3 Bytebuf中读取数据
3.3 Bytebuf中读取数据
private static void readByte() {
// byteBuf 分配一块内存,自动判断是否分配堆内存或者堆外内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// 写入1个字节
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[]{(byte)1, (byte)2});
printMsg(byteBuf);
// 读取1个字节
byte b = byteBuf.readByte();
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}read index:0
write index:2
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 |.. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:1
write index:2
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 02 |. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
3.4 Bytebuf读取后重复读取
public static void main(String[] args) {
// jvm堆内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// 写数据
byteBuf.maxWritableBytes();
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {1, 2, 3, 4});
printMsg(byteBuf);
// 重置,写指针复位到起始位置重新写入,覆盖写
byteBuf.resetWriterIndex();
byteBuf.writeInt(6);
printMsg(byteBuf);
// 读
byteBuf.markReaderIndex();
byte a = byteBuf.readByte();
byte b = byteBuf.readByte();
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}read index:0
write index:4
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0
write index:8
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 01 02 03 04 |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0
write index:4
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 00 00 06 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
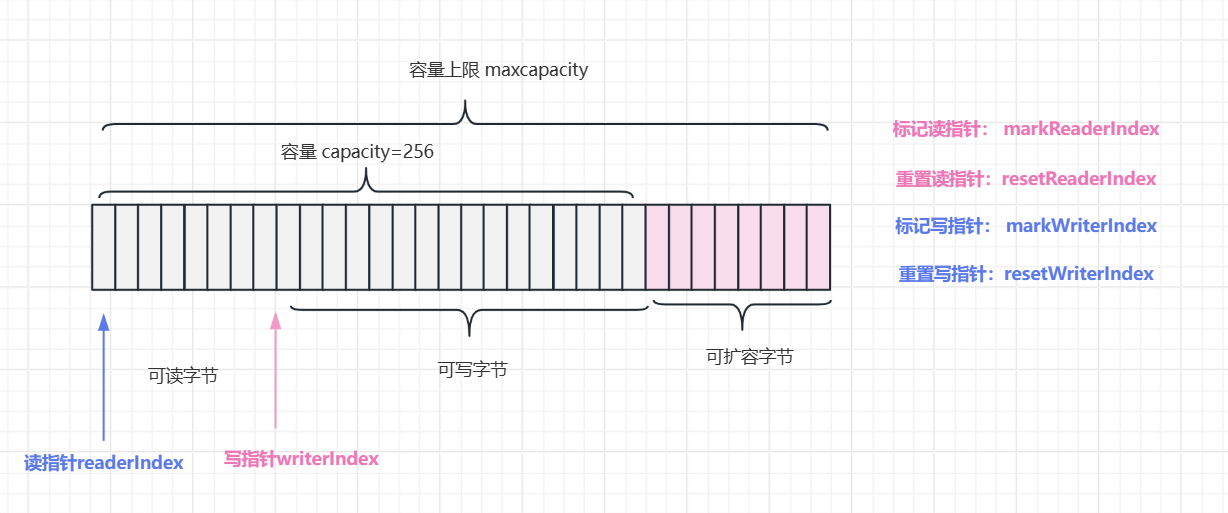
备注:markWriterIndex、resetWriterIndex一般是配套使用,如果未标记写指针的位置默认从起始位置开始;markReaderIndex、resetReaderIndex一般也是配套使用,如果未标记读取的位置,则从起始位置重新读取
4 Bytebuf扩容
- 初始尝试:如果
minNewCapacity小于等于 4MB(4194304字节),新容量为大于等于minNewCapacity的最小 2 的幂; - 超过 4MB 时:如果
minNewCapacity大于 4MB,新容量为大于等于minNewCapacity且为 4MB 整数倍的值; - 上限控制:新容量不能超过
ByteBuf的最大容量。
案例: 未超过4M,成倍增长
public class ByteBufCapacity {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// jvm堆内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
for (int i=0; i<256; i++) {
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {(byte) i});
}
printMsg(byteBuf);
for (int i=0; i<256; i++) {
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {(byte) i});
}
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
// ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}read index:0
write index:256
capacity:256
maxCapacity:2147483647read index:0
write index:512
capacity:512
maxCapacity:2147483647
大于4M,每次增加4M扩容
package com.bonnie.netty.bytebuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
public class ByteBufCapacity {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// jvm堆内存
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
// 4M
for (int i=0; i<4194304; i++) {
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {(byte) i});
}
printMsg(byteBuf);
// 扩容+4M
for (int i=0; i<4194304; i++) {
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {(byte) i});
}
printMsg(byteBuf);
// 扩容+4M
for (int i=0; i<4194304; i++) {
byteBuf.writeBytes(new byte[] {(byte) i});
}
printMsg(byteBuf);
}
private static void printMsg(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("read index:").append(byteBuf.readerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("write index:").append(byteBuf.writerIndex()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("capacity:").append(byteBuf.capacity()).append("\n");
stringBuilder.append("maxCapacity:").append(byteBuf.maxCapacity()).append("\n");
// ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump(stringBuilder, byteBuf);
System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
read index:0
write index:4194304
capacity:4194304
maxCapacity:2147483647read index:0
write index:8388608
capacity:8388608
maxCapacity:2147483647read index:0
write index:12582912
capacity:12582912
maxCapacity:2147483647
5 堆内存和堆外内存
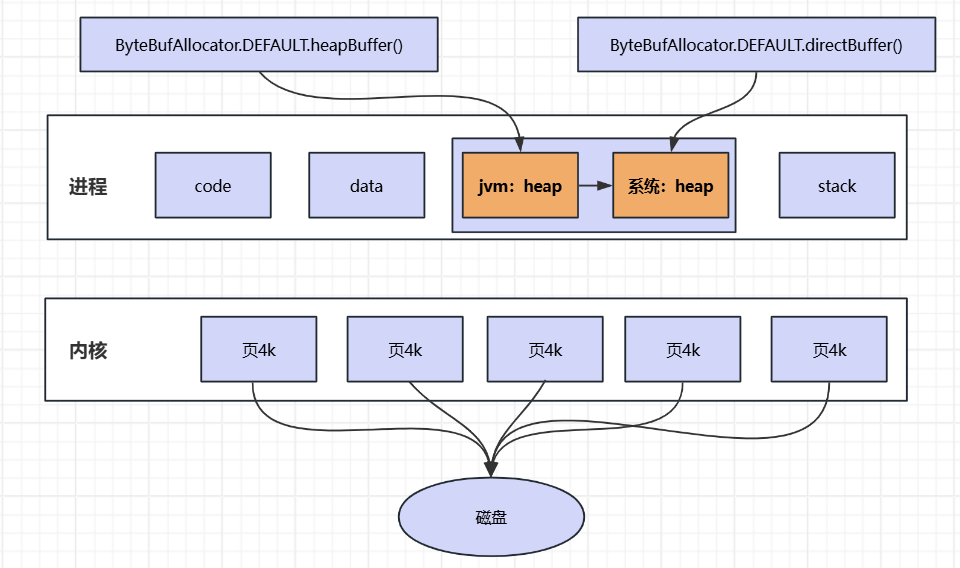 实堆内的意思就是java虚拟机里面的堆空间,而堆外的意思是java进程中系统 为它分配的堆空间,jvm堆中的数据如果想要写入磁盘,就会进行write系统调用,调用过程为:jvm堆->系统 堆->PageCache->磁盘,如果数据是放在系统heap中,调用过程为:系统堆->PageCache->磁盘。 我们可以看到,使用堆内内存写入数据会少一次的拷贝次数
实堆内的意思就是java虚拟机里面的堆空间,而堆外的意思是java进程中系统 为它分配的堆空间,jvm堆中的数据如果想要写入磁盘,就会进行write系统调用,调用过程为:jvm堆->系统 堆->PageCache->磁盘,如果数据是放在系统heap中,调用过程为:系统堆->PageCache->磁盘。 我们可以看到,使用堆内内存写入数据会少一次的拷贝次数