一、Variables
1.String
①.双引号
s1 = "eagsh" ;s2 = "fers"
s3 = [s1 s2]: 1×2 string 数组
s3 = [s1;s2] : 2×1 string 数组
②.单引号
s1 = ' eagsh ' ;s2 = ' fers '
s3 = [s1 s2]: ' eagshfers '
s3(3) = 'g'
'e' == s3 : 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 (每个位置分别与e做逻辑运算)
s3(s3 == ' e ')= 'a' : s3中找到所有 'e'的位置,全部用 'a' 替换
strcmp(str1,str2):比较str1与str2是否完全一样,一样:1;不一样:0.
s3 = [s1;s2]报错,两个字符串长度不匹配
反转: s1 = 'I like the letter E' ; s2 = s1(length(s1) : -1 : 1)
2.Structure
student(1).name = 'sdfsd';
student(1).id = '456';
student(1).grade =[123 13 4523 25; 3252 532 325 325;35 253 35 242];
student(2).name = 'adxkjs';
student(2).id = '4385';
student(2).grade =[123 13 4523 25; 3252 532 325 325;35 253 35 242];
student
student(1).grade(1,1) % 第1行第1列的元素
student(1).grade(1) %第1个元素
fieldnames(student): structure 下的所有field
rmfield(student,'id'):删除structure 下 名叫 'id' 的field
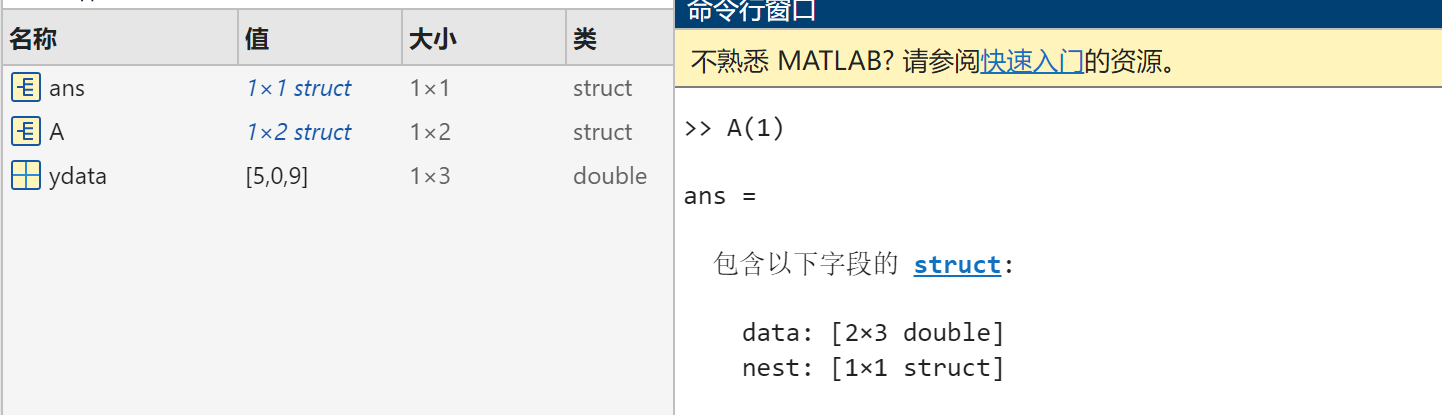
3.Nesting Structures
A = struct('data',[3 4 7;8 0 1],'nest',...
struct('testnum','Test 1',...
'xdata',[4 2 8],'ydata',[7 1 6]));
A(2).data = [9 3 2;7 6 5];
A(2).nest.testnum = 'Test 2';
A(2).nest.xdata = [3 4 2];
A(2).nest,ydata = [5 0 9];
A.nest;A有两个 field ,一个 ’data‘,一个 ' nest ' ,nest 有三个 field ,分别是 ' testnum '、' xdata'、'ydata'
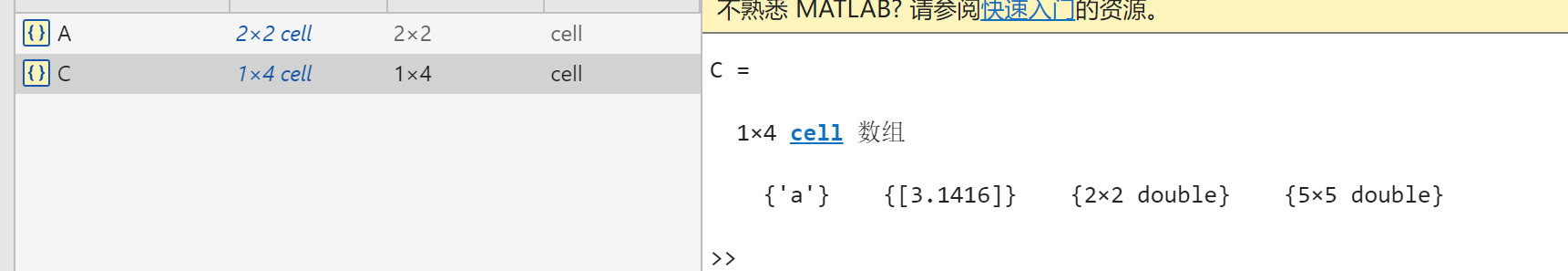
4.Cell Array
① .1 Declare Cell Array
A(1,1) = {[1 4 3;0 5 8;7 2 9]};
A(1,2) = {'matlab'};
A(2,1) = {3+7i};
A(2,2) = {-pi:pi:pi};
A;① . 2 Declare Cell Array
clc;clear;
A{1,1} = [1 4 3;0 5 8;7 2 9];
A{1,2} = 'matlab';
A{2,1} = 3+7i;
A{2,2} = -pi:pi:pi;
A;② Accessing Cell Array
C = A{1,1}:数据类型是矩阵的话,大括号返回cell中矩阵的数据
A{2,1}(1,1):数据类型是矩阵的话,取出矩阵第1行第1列的数据
D = A(1,1):数据类型是矩阵的话,小括号返回cell中矩阵大小
③ Cell ArrayFunctions
cell2struct():将 cell 转化成 struct 类型的函数
num2cell() & mat2cell():
clc;clear;
a = magic(3);
b = num2cell(a);函数magic()会生成一个 3×3 的幻方矩阵。幻方矩阵是一种特殊的方阵,其每一行、每一列以及两条对角线上的元素之和都相等。
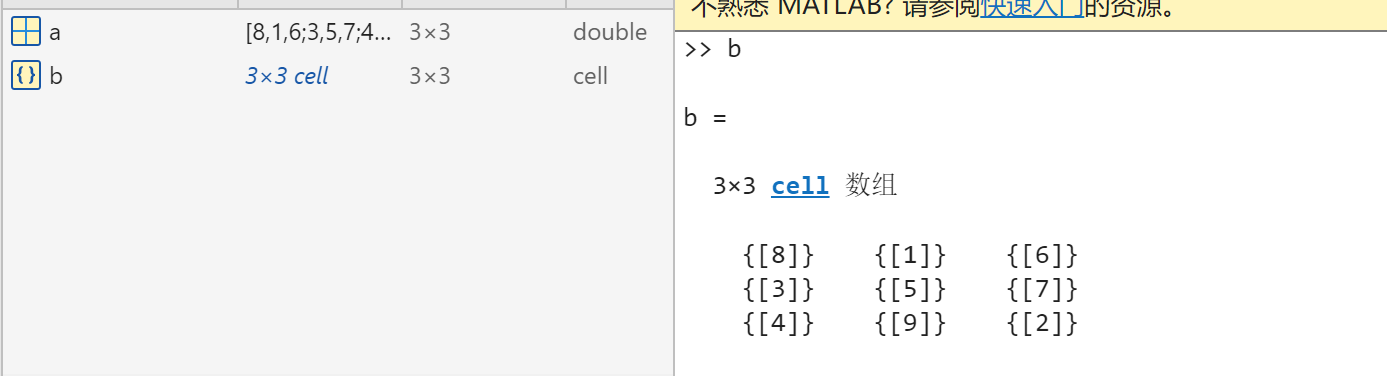
num2cell() :将矩阵的每个元素数值都转化成一个cell,
clc;clear;
a = magic(3);
c = mat2cell(a,[1,2],[2,1]);mat2cell():将矩阵 a,行数按照1:2分,列数按照2:1分.
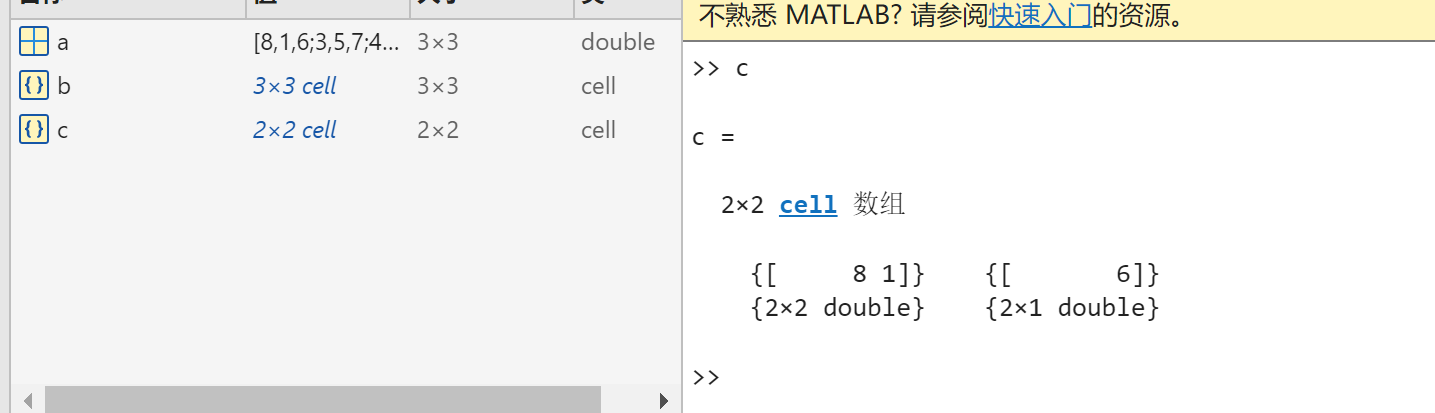
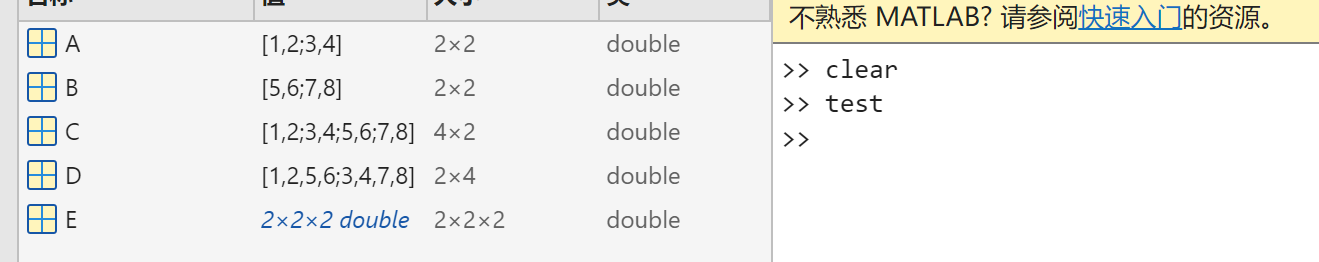
5.Mutidimensional Array
方法1:
A{1,1,1} = [1 2;4 5];
A{1,2,1} = 'name';
A{2,1,1} = 2-4i;
A{2,1,2} = 7;
A{1,1,2} = 'name2';
A{1,2,2} = 3;
A{2,1,2} = 0:1:3;
A{2,2,2} = [4 5]';方法2:
1表示竖着接,2表示横着接,3表示在深度方向接
A = [1 2;3 4];
B = [5 6; 7 8];
C = cat(1,A,B);
D = cat(2,A,B);
E = cat(3,A,B);reshape()
转换前与转换后所有元素个数元素相同,则可以使用reshape函数,改变矩阵形状,将原来2*2的矩阵转化成 1*4的矩阵
A = { 'a',[1 2; 3 4];pi,magic(5)};
C = reshape(A,1,4);6.Checking Variable And Variable Status
isinteger、islogical、isnan、isnumeric、isreal、iscell、ischar、isempty
| 函数 | 作用 | 示例(返回 true 的情况) |
|---|---|---|
| isinteger | 判断是否为整数类型 | int32(5) |
| islogical | 判断是否为逻辑类型(true/false) |
true |
| isnan | 判断是否为 NaN |
0/0 |
| isnumeric | 判断是否为数值类型 | 3.14,int8(5) |
| isreal | 判断是否为实数(无虚部) | 5 |
| iscell | 判断是否为元胞数组 | { ' a ' , [ 1 2 ] } |
| ischar | 判断是否为字符数组 | ' hello ' |
| isempty | 判断是否为空数组 | [],' ',{} |
7.File Access
① save() and load()
a = magic(4)
save my2.mat -ascii
load('my2.mat','-ascii')
save(filename,varivables),仅保存variable指定的结构体数组的变量或字段。
② Excel File Reading()
xlsread():
Score = xlsread(filename );
Score = xlsread(filename ,' B2:D4 ');把文件名为 ' filename ’的文件中的数据读取出来,数据包括以B2和D4连线的矩形内的所有数据
且第一行与第二行的运行结果一样
xlswrite():
M = mean(Score')';
xlswrite('1.xlsx',M,1,'E2:E4');
xlswrite('1.xlsx',{'Mean'},1,'E1');
转置再存入,然后表上平均
在第F行加入计算过后的标准差
M = std(Score')';
xlswrite('Score.xlsx',M,1,'F2:F4');
xlswrite('Score.xlsx',{'standard deviation'},1,'F1');
[Score header]= xlsread("Score.xlsx"),使用两个变量分别接收excel中两种数据类型:数值和字符(cell类型)
将Score和header写入另一个表格
xlswrite("Score1.xlsx",header)
xlswrite("Score1.xlsx",Score,1,'B2:F4')
③ Low-level File Input / Output
fid = fopen( ' [filename] ',' [ permission] ');%打开文件
% permission:' r ' ,' r+ ' ,' w ' ,' w+ ' ,' a ' ,' a+ '
status = fclose(fid)
clc;clear;
x = 0:pi/10:pi;
y = sin(x);
fid = fopen('sinx.txt','w');
for i = 1:11
fprintf(fid,'%5.3f %8.4f\n',x(i),y(i));
end
fclose(fid);
type sinx.txt
%5.3f ,写入是数据整数部分加小数部分一共5位,小数部分占3位
④ Reading from Files
clc;clear;
fid = fopen('Score3.xlsx','r');
i = 1;
while ~feof(fid)
name(i,:) = fscanf(fid,'%5c',1);
year(i) = fscanf(fid,'%d',1);
no1(i) = fscanf(fid,'%d',1);
no2(i) = fscanf(fid,'%d',1);
no3(i) = fscanf(fid,'%g',1);
no4(i) = fscanf(fid,'%g\n',1);
i = i+1;
end
fclose(fid);每次调用 fscanf 后,文件指针会向后移动,下次读取从新的位置开始。
name(i,:) = fscanf(fid,'%5c',1); % i 代表第 i 行,1代表每次只读取一次 ' %5c ' 格式的数据