P1271 【深基9.例1】选举学生会
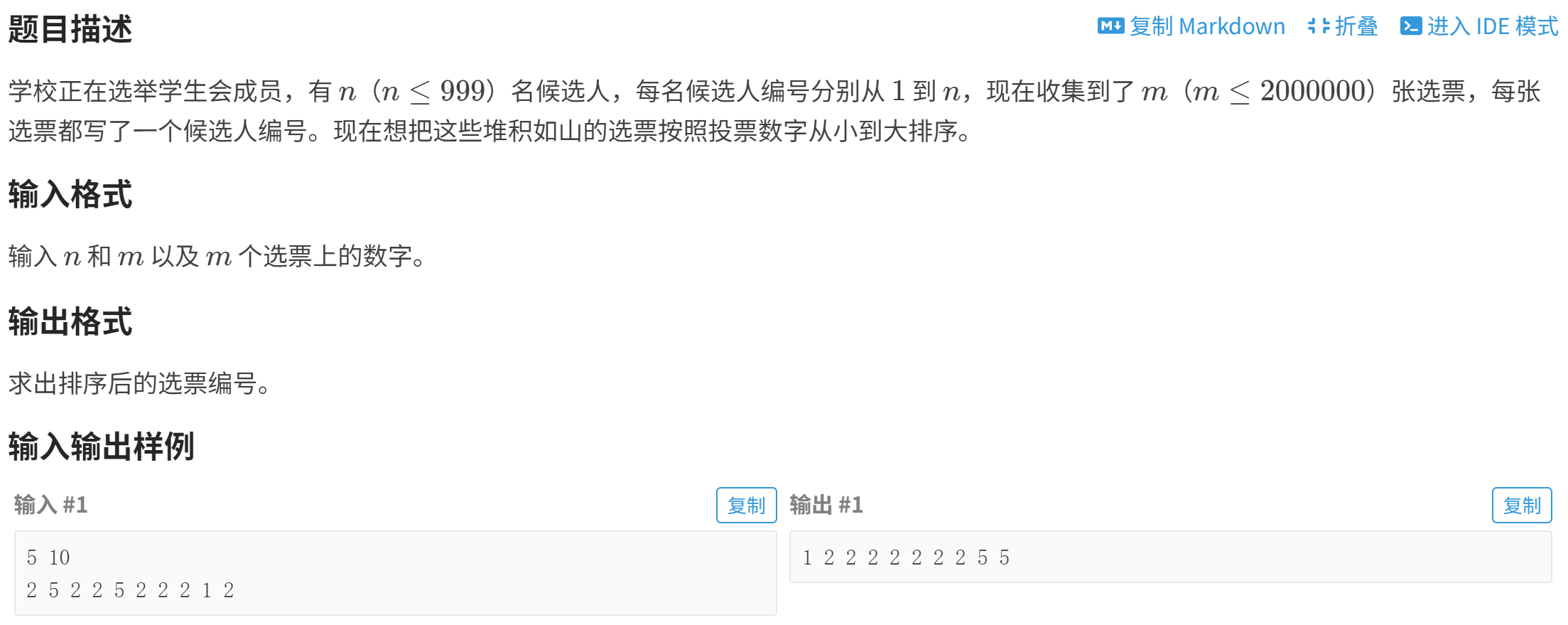
【方法一】快速排序
使用sort(),注意数组的范围!!!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[2000000],n,m;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a,a+m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}【方法二】桶排序
桶排序(Bucket Sort)是一种基于分配策略的排序算法,其工作原理是将数组分到有限数量的桶子里,然后对每个桶内的元素进行排序(可能再使用其他排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序),最后合并所有已排序的桶,从而完成整个数据集的排序。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m,p;
cin>>n>>m;
int a[1000]={0}; // 以候选人作为“桶”
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>p;
a[p]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<a[i];j++)
{
cout<<i<<' ';
}
}
return 0;
}P1923 【深基9.例4】求第 k 小的数
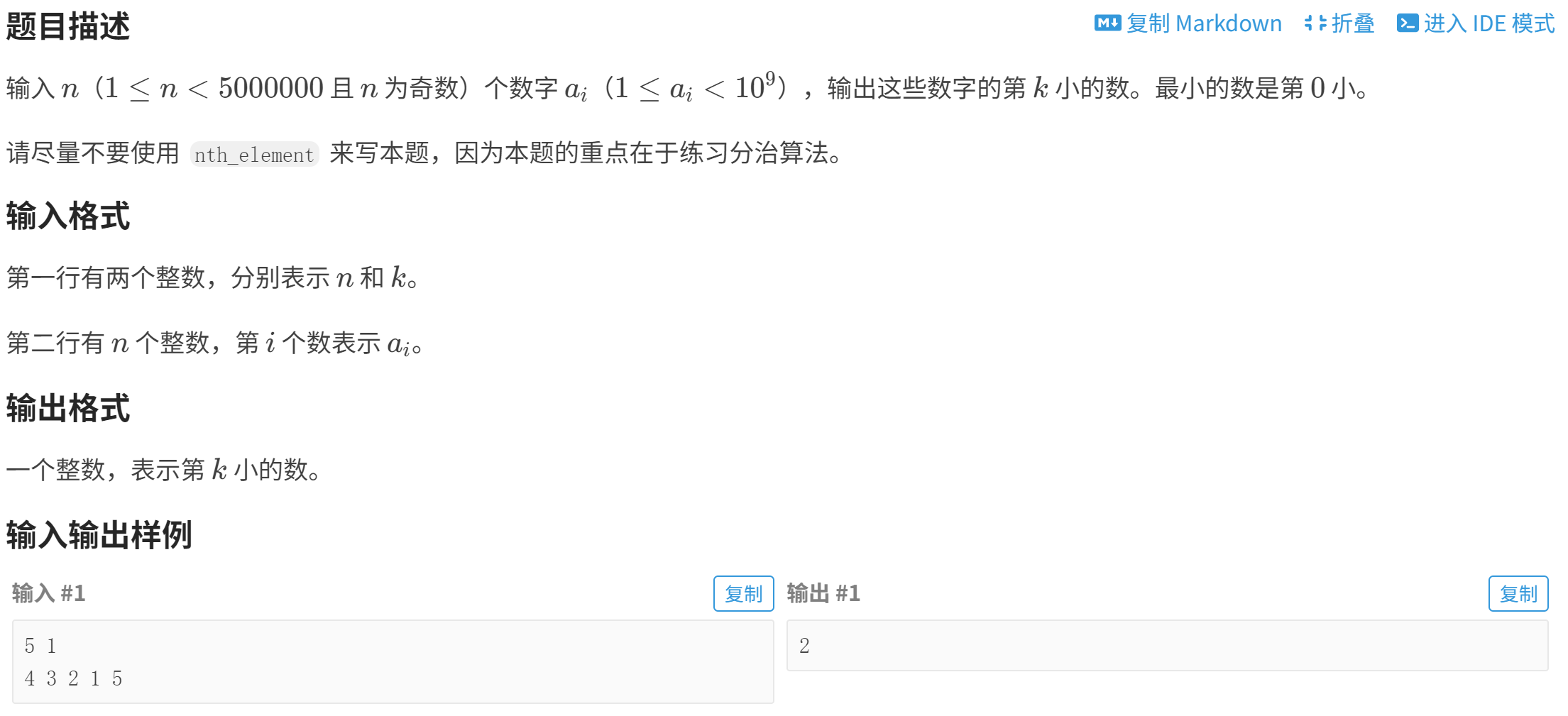
【方法一】快速排序,直接输出
但是无法通过所有的测试点!!!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
int a[5000001]={0};
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a,a+n);
cout<<a[k];
return 0;
}【方法二】根据快排的思想进行二分
在原二分的基础上可以进行修改:因为每次递归都会将数组划分为三部分,而答案只会在这三部分中的一个,不需要再对其他部分进行搜索,从而达到优化时间复杂度的效果。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int x[5000005],k;
void qsort(int l,int r)
{
int i=l,j=r,mid=x[(l+r)/2];
do
{
while(x[j]>mid)
{
j--;
}
while(x[i]<mid)
{
i++;
}
if(i<=j)
{
swap(x[i],x[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}while(i<=j);
//快排后数组被划分为三块: l<=j<=i<=r
if(k<=j)
{
qsort(l,j); //在左区间只需要搜左区间
}
else if(i<=k)
{
qsort(i,r); //在右区间只需要搜右区间
}
else //如果在中间区间直接输出
{
printf("%d",x[j+1]);
exit(0);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x[i]);
}
qsort(0,n-1);
}【方法三】利用
nth_element在 STL 里有
nth_element 函数。它的用法是nth_element(a+x,a+x+y,a+x+len)。执行之后数组 a 下标 x 到 x+y−1 的元素都小于 a[x+y],下标 x+y+1 到 x+len−1 的元素 都大于 a[x+y],但不保证数组有序。此时 a[x+y] 就是数组区间 x 到 x+len−1 中第 y 小的数,当然也可以自己定义 cmp 函数。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int x[5000005],k;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x[i]);
}
nth_element(x,x+k,x+n);
printf("%d",x[k]);
}P1781 宇宙总统
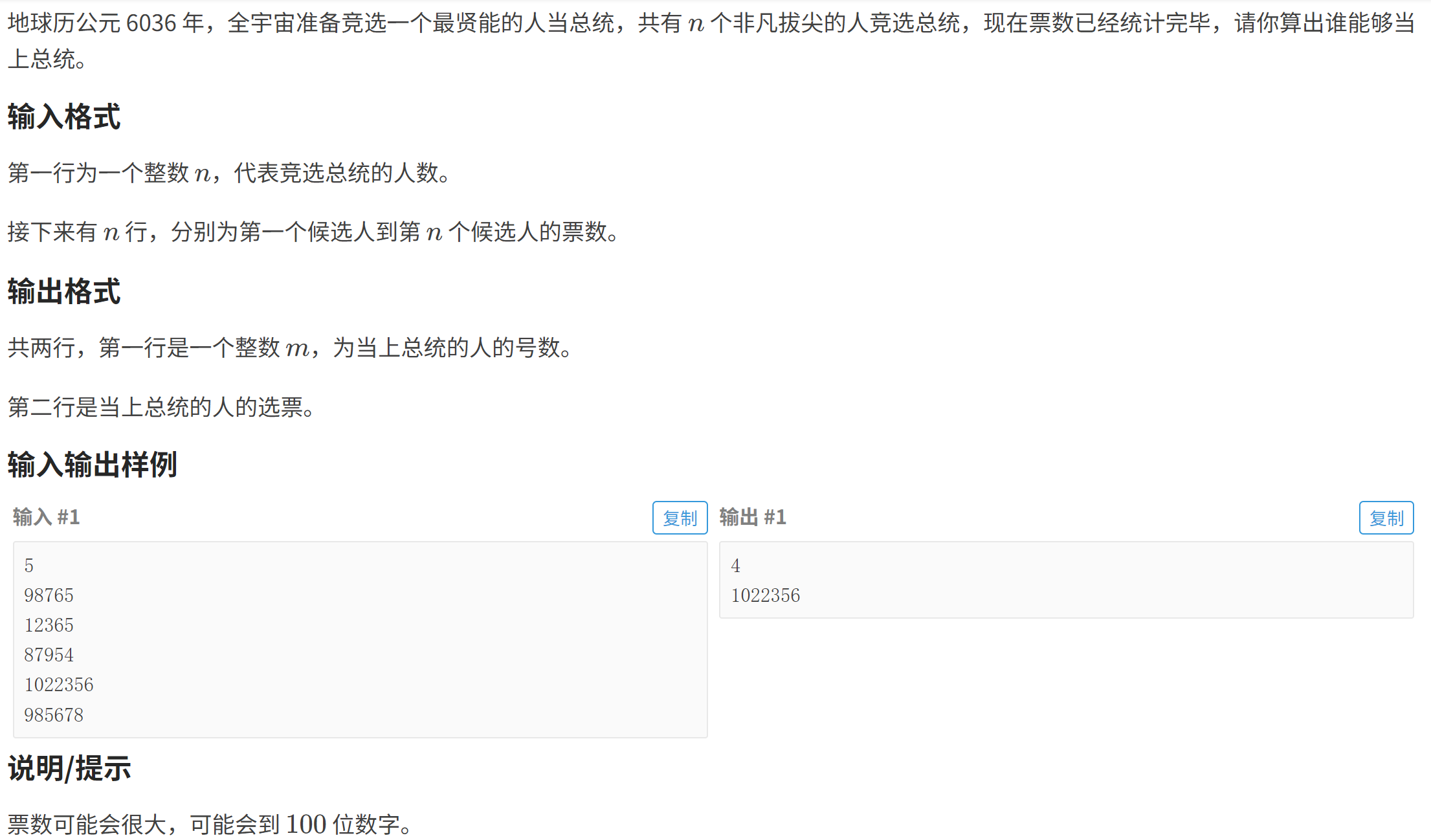
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int num;
string a[21];
string max;
cin>>max;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
if((a[i].length()>max.length()) || (a[i].length()==max.length() && a[i]>max))
{
max=a[i];
num=i+1;
}
}
cout<<num<<endl;
cout<<max<<endl;
return 0;
}P2676 [USACO07DEC] Bookshelf B

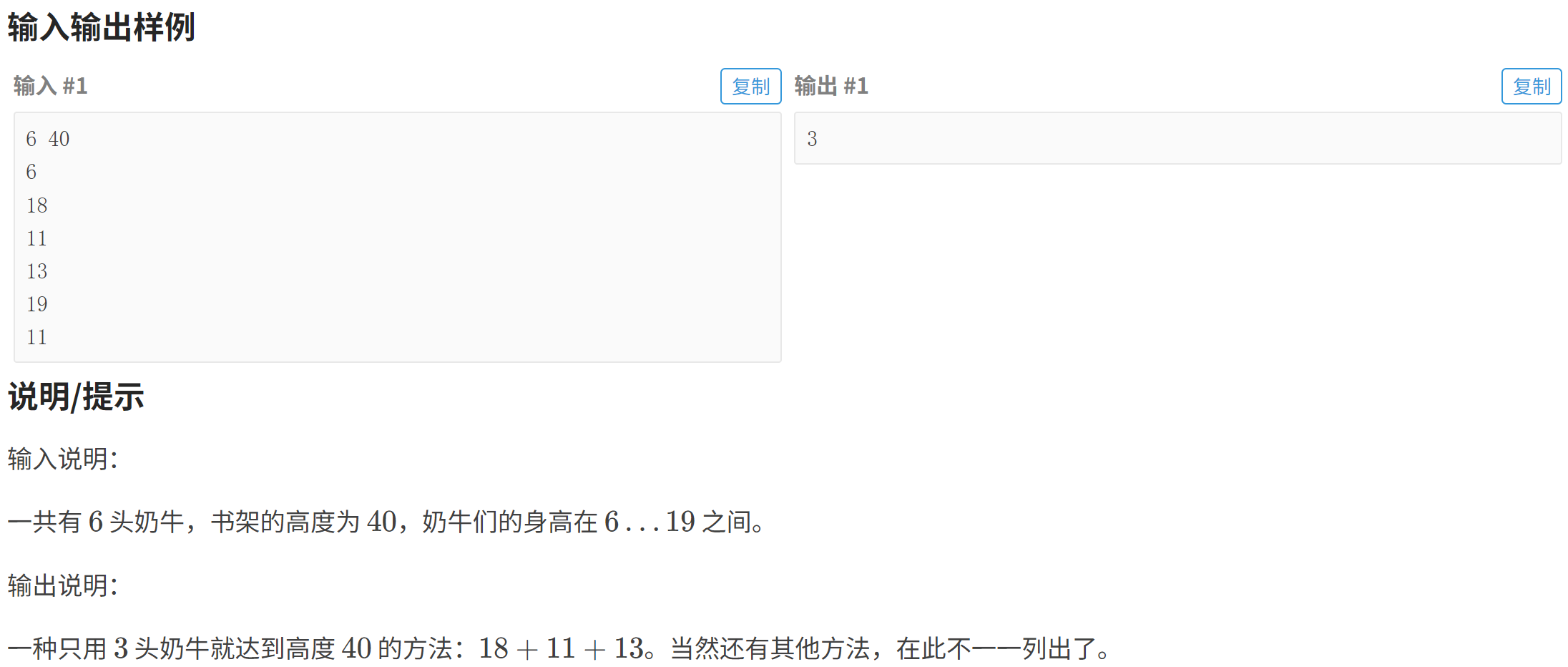
贪心算法
先选最大的数(即最高的奶牛),一定能使取的数的数目(即奶牛数)最小
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long S[200005];
long N,B,sum=0;
cin>>N>>B;
int num=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
cin>>S[i];
}
sort(S,S+N);
for(int i=N-1;i>=0;i--)
{
sum+=S[i];
num++;
if(sum>=B)
{
break;
}
}
cout<<num;
return 0;
}P1116 车厢重组
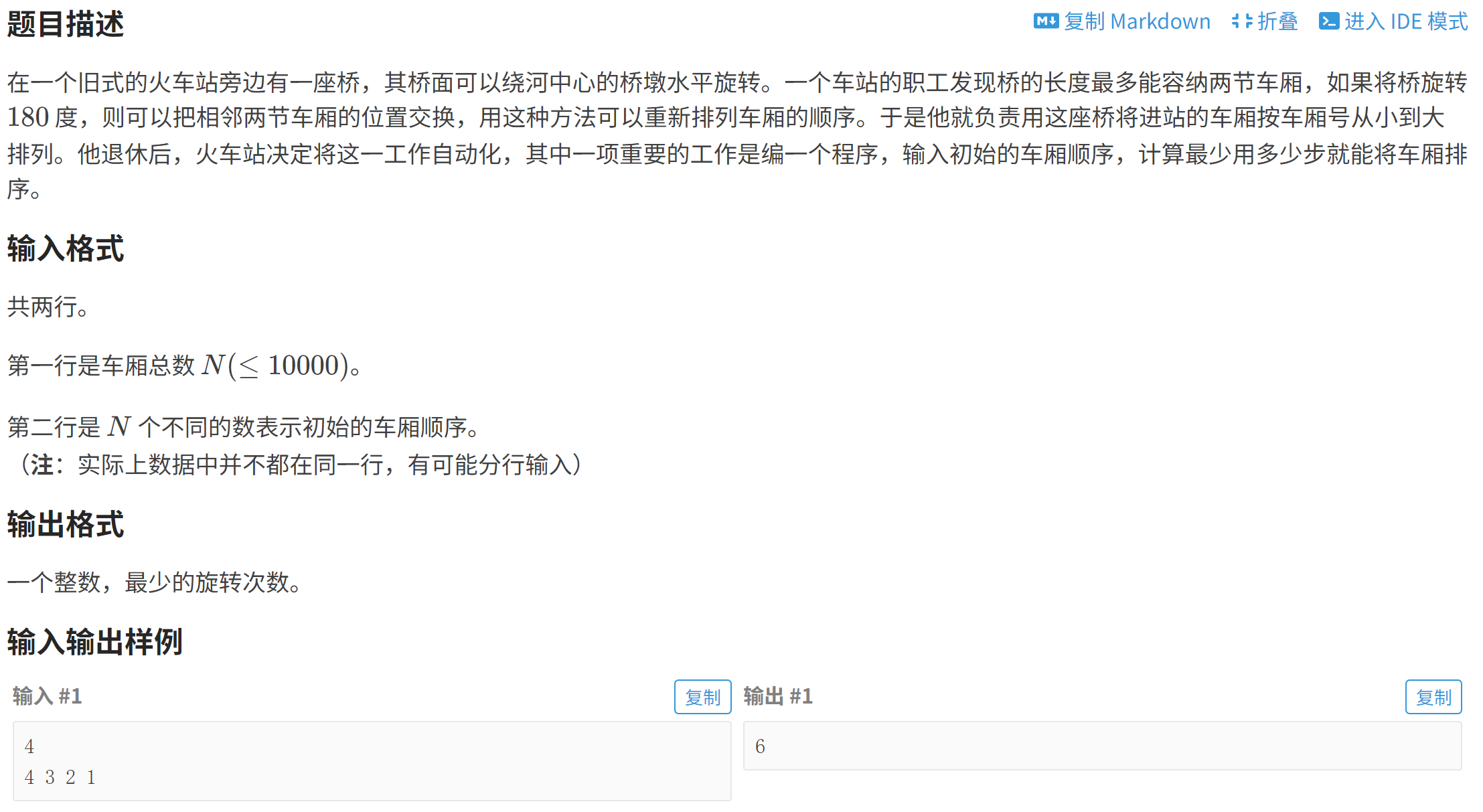
计算每个数字后面有几个数字比它小,再相加,就可以计算出需要的最少次数。
相对于冒泡排序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
int a[10010];
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
int num=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i]>a[j])
{
num++;
}
}
}
cout<<num;
return 0;
}P1068 [NOIP 2009 普及组] 分数线划定

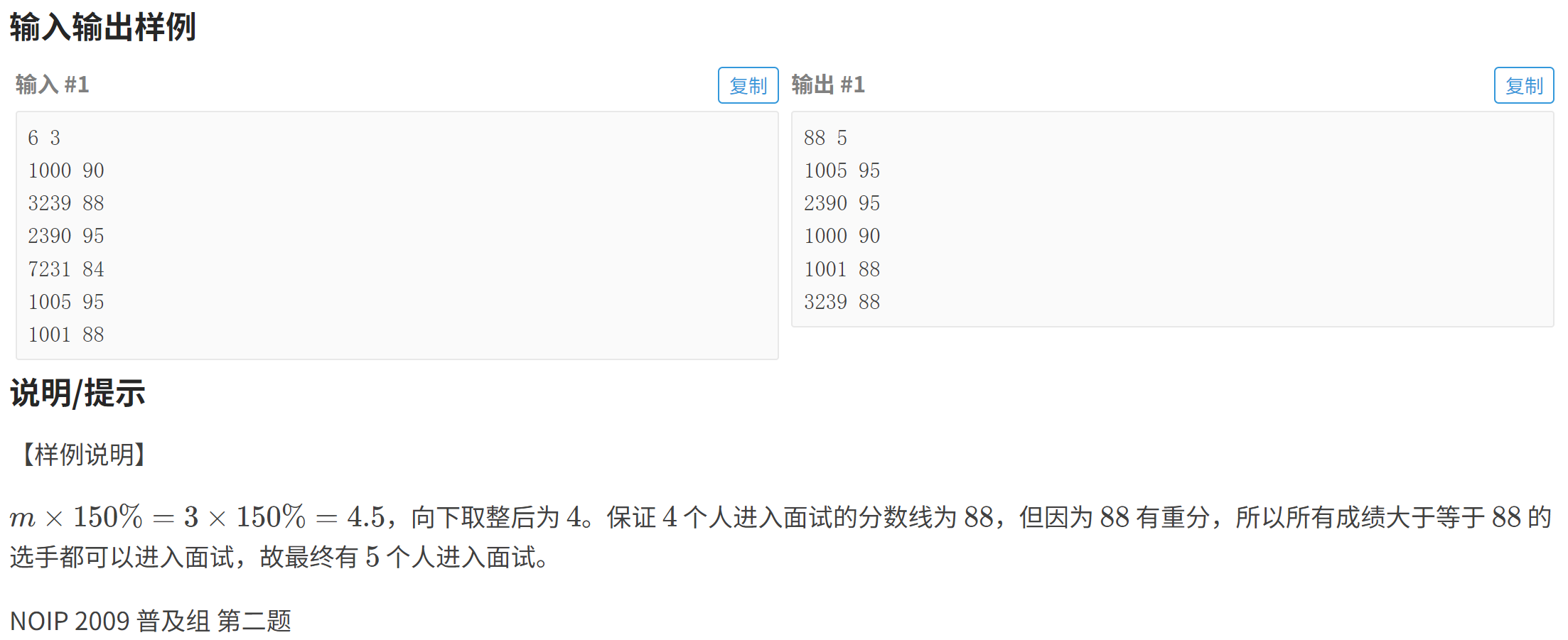
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct people
{
int k;
int s;
}per[5001];
bool cmp(people a,people b)
{
if(a.s!=b.s)
{
return a.s>b.s;
}
else
{
return a.k<b.k;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>per[i].k>>per[i].s;
}
int num=m*1.5;
sort(per,per+n,cmp);
for(int i=num;i<n;i++)
{
if(per[i].s==per[num-1].s)
{
num++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
cout<<per[num-1].s<<" "<<num<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
cout<<per[i].k<<" "<<per[i].s<<endl;
}
return 0;
}P5143 攀爬者

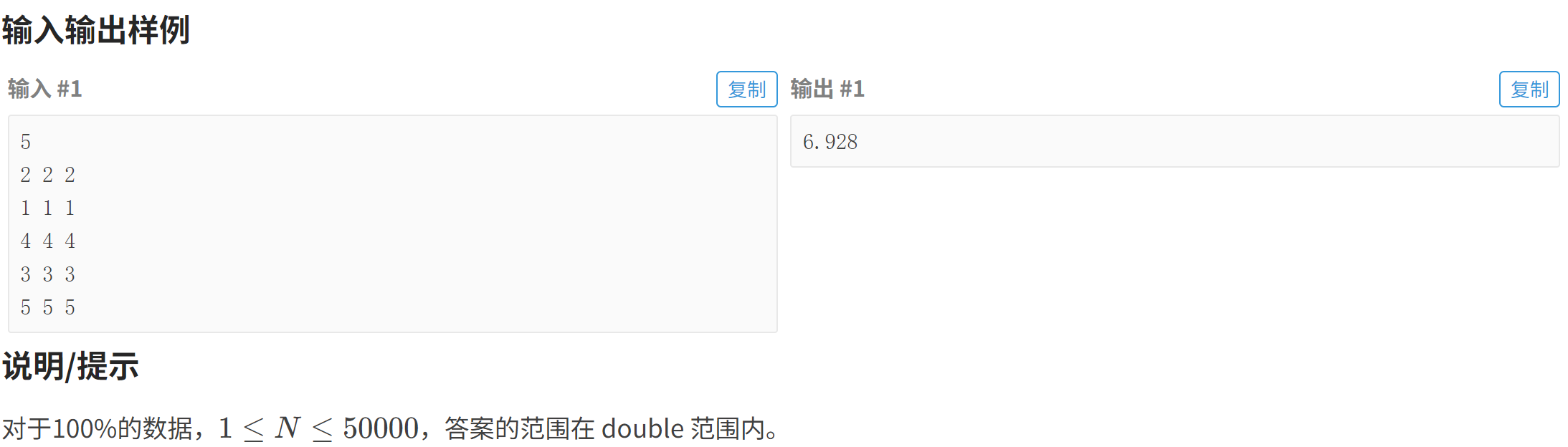
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct zuobiao
{
double x;
double y;
double z;
}dot[50001];
bool cmp(zuobiao a,zuobiao b)
{
return a.z<b.z;
}
double solve(double x1,double x2,double y1,double y2,double z1,double z2)
{
double x=pow(abs(x1-x2),2);
double y=pow(abs(y1-y2),2);
double z=pow(abs(z1-z2),2);
double sum=pow(x+y+z,0.5);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>dot[i].x>>dot[i].y>>dot[i].z;
}
sort(dot,dot+n,cmp);
double ans=0.0;
int tag=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(dot[i].z>dot[tag].z)
{
ans+=solve(dot[tag].x,dot[i].x,dot[tag].y,dot[i].y,dot[tag].z,dot[i].z);
tag=i;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<<ans;
return 0;
}P1012 [NOIP 1998 提高组] 拼数
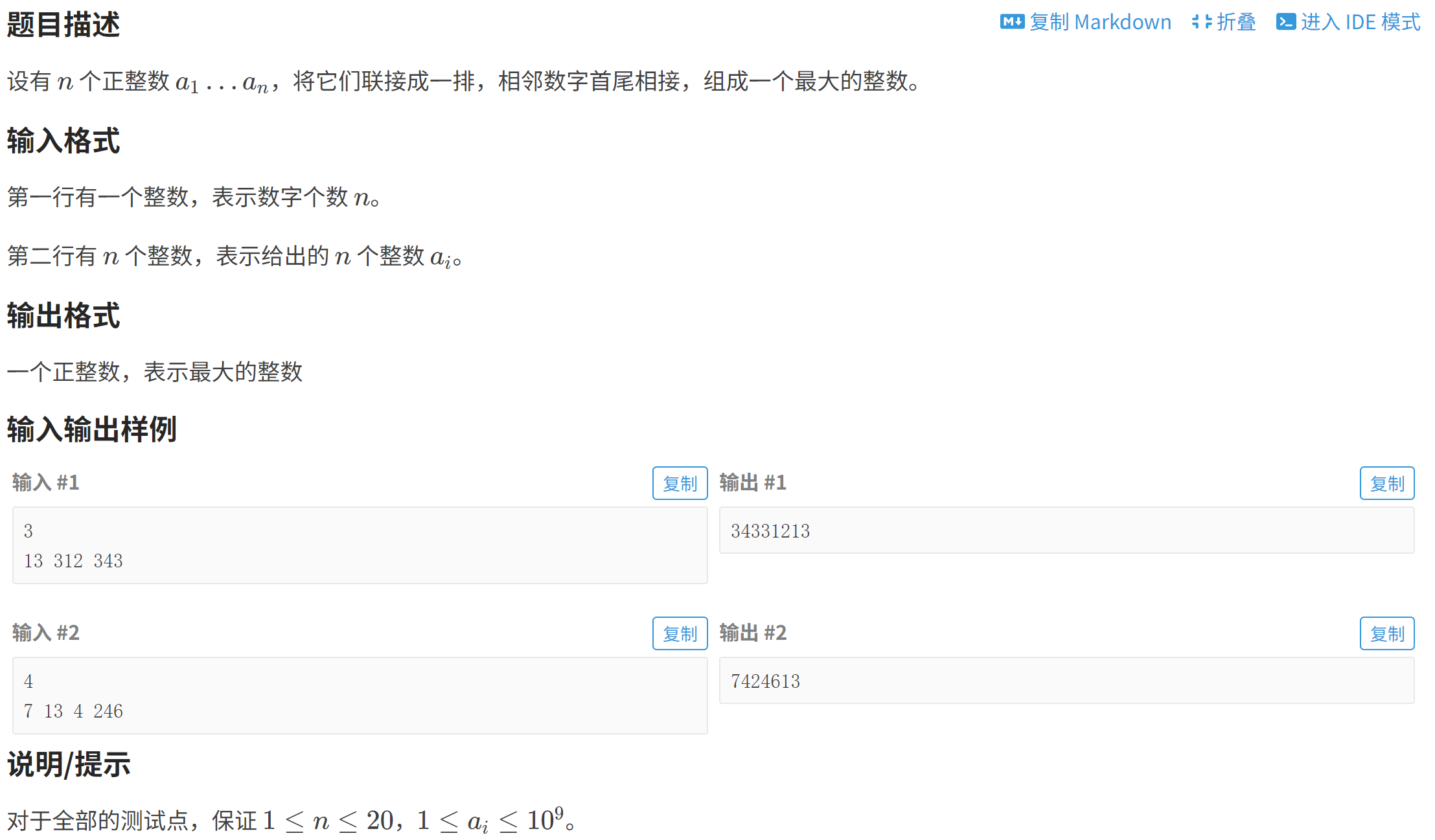
to_string------>可以实现数字向字符串转换(虽然这题没用到)
两个字符串 a,b,如果 a+b>b+a 则 a 排在前面。 这个公式的具体意思是当 a 排在 b 前面比 b 排在 a 前面要好,因为字典序更高,所以 a 自然要排在 b 的前面。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string a[25];
bool cmp(string a,string b)
{
return a+b>b+a;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i];
}
return 0;
}