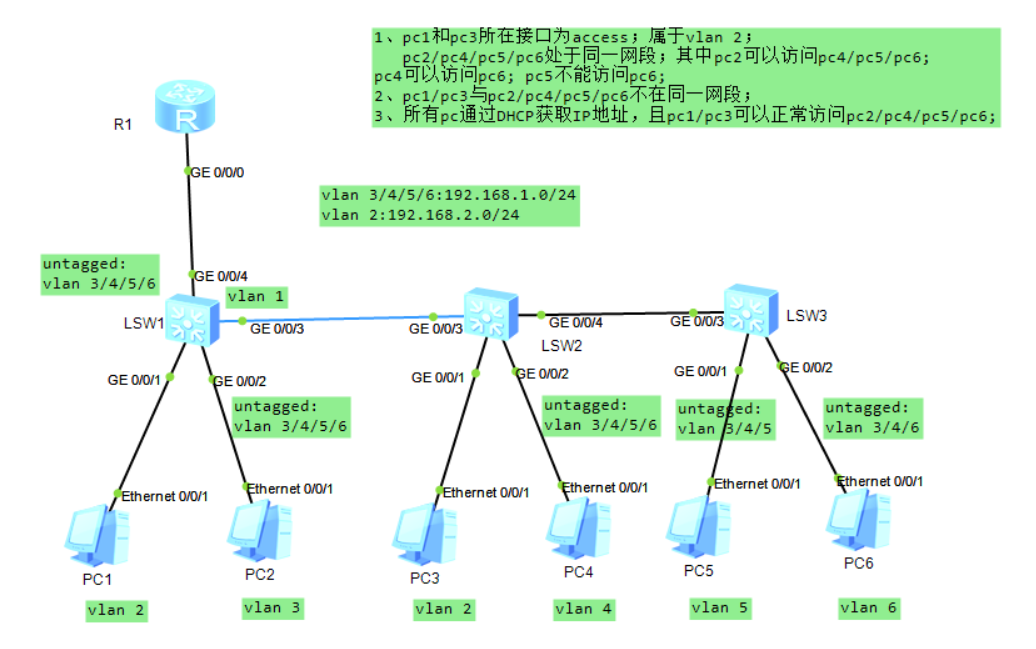
实验要求:
1、pc1和pc3所在接口为access;属于vlan 2;
pc2/pc4/pc5/pc6处于同一网段;其中pc2可以访问pc4/pc5/pc6;
pc4可以访问pc6; pc5不能访问pc6;
2、pc1/pc3与pc2/pc4/pc5/pc6不在同一网段;
3、所有pc通过DHCP获取IP地址,且pc1/pc3可以正常访问pc2/pc4/pc5/pc6;
实验分析
PC2、PC4、PC5、PC6 处于同一广播域,PC1 与 PC3 则位于另一广播域。
需要在交换机上创建所需的 VLAN,并将各端口分配至相应 VLAN,同时配置端口链路模式。
交换机之间应建立 Trunk(或混合)链路,并确保允许相关 VLAN 的数据通过。
路由器需通过子接口实现 VLAN 间路由。
配置 DHCP 服务,为不同 VLAN 下发 IP 地址。
配置步骤
1. 创建 VLAN
在 SW1、SW2、SW3 上分别执行:
vlan batch 2 to 62. 端口划分与链路模式配置
SW1
PC1 接口(Access,VLAN 2):
int g0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 2PC2 接口(Hybrid,PVID VLAN 3,放通 VLAN 3~6 无标签):
int g0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid untagged vlan 3 to 6 port hybrid pvid vlan 3
SW2
PC3 接口(Access,VLAN 2):
int g0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 2PC4 接口(Hybrid,PVID VLAN 4,放通 VLAN 3~6 无标签):
int g0/0/2 port hybrid untagged vlan 3 to 6 port hybrid pvid vlan 4
SW3
PC5 接口(Hybrid,PVID VLAN 5,放通 VLAN 3~5 无标签):
int g0/0/1 port hybrid untagged vlan 3 to 5 port hybrid pvid vlan 5PC6 接口(Hybrid,PVID VLAN 6,放通 VLAN 3、4、6 无标签):
int g0/0/2 port hybrid untagged vlan 3 4 6 port hybrid pvid vlan 6
3. 交换机间 Trunk 链路配置
确保 VLAN 2~6 均可通过:
[SW1]
int g0/0/3
port link-type trunk
port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 6
[SW2]
int g0/0/3
port link-type trunk
port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 6
int g0/0/4
port link-type trunk
port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 6
[SW3]
int g0/0/3
port link-type trunk
port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 6SW1 与路由器连接的接口为 Hybrid 模式,VLAN 2 打标签,其余 VLAN 无标签:
int g0/0/4
port hybrid tagged vlan 2
port hybrid untagged vlan 3 to 64. 路由器子接口配置(VLAN 间路由)
VLAN 2 使用子接口(打标签),其余 VLAN 使用物理接口(无标签):
int g0/0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 24
int g0/0/0.1
ip address 192.168.2.1 24
dot1q termination vid 2
arp broadcast enable5. DHCP 配置
为 VLAN 3~6 配置地址池:
dhcp enable
ip pool aa
network 192.168.1.0 mask 24
gateway-list 192.168.1.1 dns-list 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8为 VLAN 2 配置地址池:
ip pool bb
network 192.168.2.0 mask 24
gateway-list 192.168.2.1 dns-list 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8接口绑定 DHCP 全局池:
int g0/0/0
dhcp select global
int g0/0/0.1
dhcp select global实验验证
PC2 可与 PC4、PC5、PC6 通信。
PC4 可访问 PC6;PC5 无法访问 PC6。
PC1、PC3 可与 PC2、PC4、PC5、PC6 正常通信
PC2> ping 192.168.1.4
Pinging 192.168.1.4 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC2> ping 192.168.1.5
Pinging 192.168.1.5 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.5:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC2> ping 192.168.1.6
Pinging 192.168.1.6 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.6:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC4> ping 192.168.1.6
Pinging 192.168.1.6 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.6:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC5> ping 192.168.1.6
Pinging 192.168.1.6 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.6:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss)
PC1> ping 192.168.1.4
Pinging 192.168.1.4 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.4: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC1> ping 192.168.1.5
Pinging 192.168.1.5 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.5:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC1> ping 192.168.1.6
Pinging 192.168.1.6 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.6: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.6:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms