为了理解@EvenListener注解的底层原理,我们可以自己实现一个类似的注解模拟实现。
1.定义@MyListener注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyListener {
}2.注解使用
@Component
static class SmsService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsService.class);
@MyListener
public void listener(MyEvent event) {
log.debug("发送短信");
}
}3.注解解析
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestMyListener.class);
SmsService smsService = context.getBean(SmsService.class);
for(Method method : SmsService.class.getMethods()){
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)){
ApplicationListener listener = new ApplicationListener<MyEvent>() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
try {
method.invoke(smsService, event);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}1)获取监听器类
2)通过反射拿到方法
判断方法上的注解是否是我们自定义的注解,如果是,创建ApplicationListener对象(这里使用了泛型去指定事件类型,如果不这样做可能会接收到别的事件而报错,比如说容器关闭事件),重写里面的监听事件的方法,通过反射调用加了@MyListener注解的方法。
3)把监听器加入容器里面。
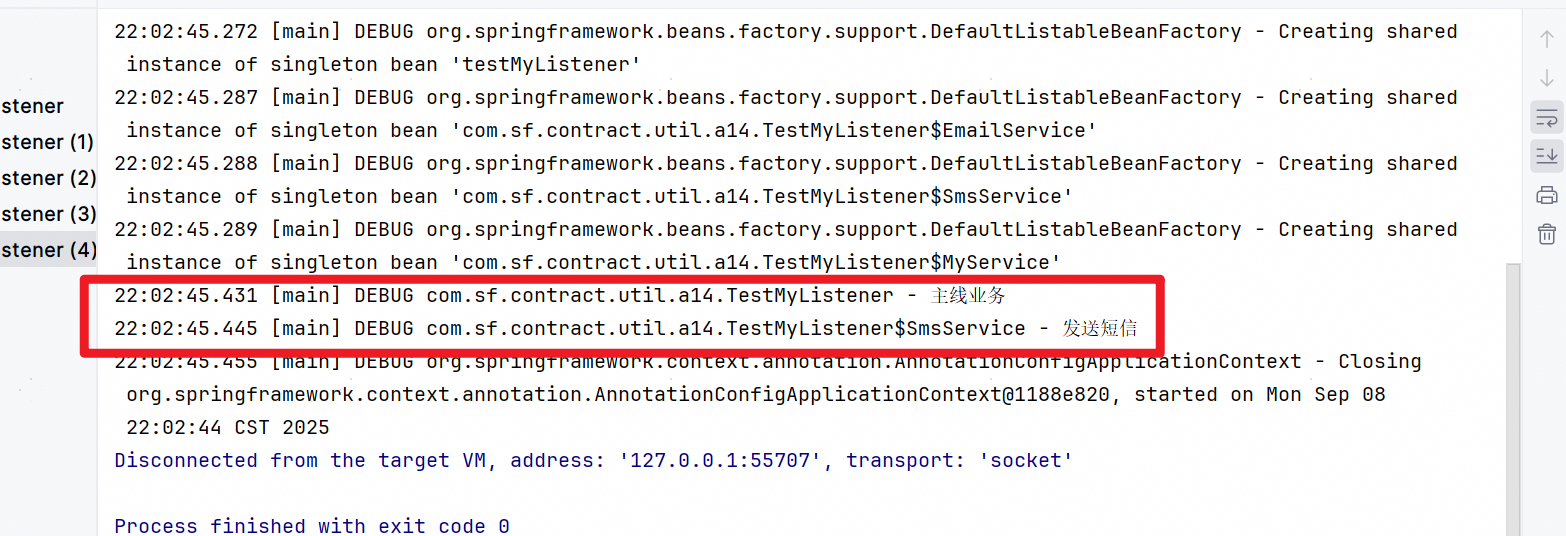
打印结果:
@MyListener注解实现了事件监听机制。
4.改进点
上面我们固定解析了监听类为SmsService类,现实情况是其它类上也可能加了@MyListener注解,我们可以做得更通用一些。
(1)再写一个监听类EmailService。
@Component
static class EmailService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailService.class);
@MyListener
public void listener(MyEvent event) {
log.debug("发送邮件");
}
}2)遍历所有满足条件的bean
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestMyListener.class);
for (String beanName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
Object bean = context.getBean(beanName);
for(Method method : bean.getClass().getMethods()){
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)){
ApplicationListener listener = new ApplicationListener<MyEvent>() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
try {
method.invoke(bean, event);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
}
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}3)测试结果
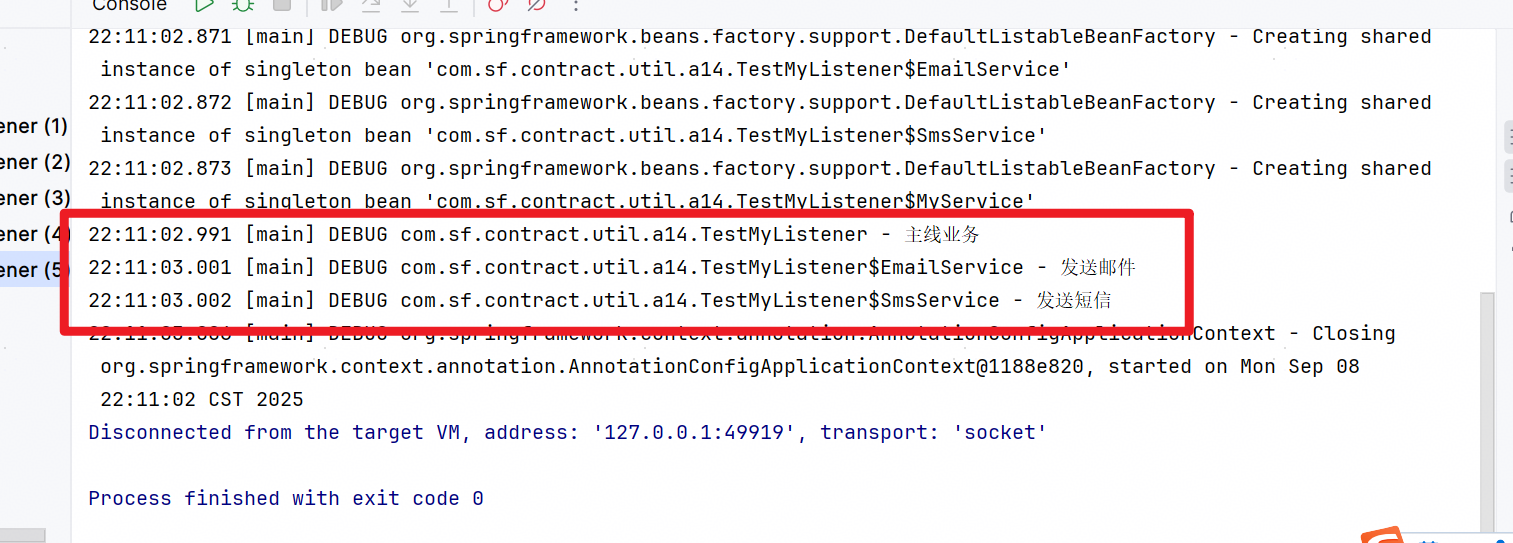
容器监听了所有实现@MyListener注解的方法。