目录
友元:
C++中如果想要外部函数或者类对一个类的private(私有成员)和protected(保护成员),可以通过使用friend关键字对其进行声明。
声明位置灵活,可以在类内任何访问区域进行友元声明。
友元函数:
友元函数一般在运算符重载和需要访问私有数据的全局函数进行使用。友元函数是声明在类内的非成员函数,可以访问该类的所有成员(包括私有和保护成员)。
示例:
通过友元函数访问Student类的私有成员_name,在类内声明GetStudentName()友元函数,在类外进行定义来。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
class Student {
friend void GetStudentName(const Student& student);
public:
Student():_name(""),_age(0),_data(new int(0)) {
std::cout << "无参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(std::string name, int age,int number):_name(name),_age(age),_data(new int(number)) {
std::cout << "有参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(const Student &student):_name(student._name),_age(student._age) {//const可以加可以不加,主要是为了防止对参数进行修改,但是&是必须加
std::cout << "拷贝构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
*_data = *student._data;
}
Student(Student && student):_name(std::move(student._name)),_age(student._age),_thread(std::move(student._thread)){
std::cout << "移动构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
*_data = std::move(*(student._data));
}
~Student() {
std::cout << "析构函数" << std::endl;
delete _data;
}
void GetTarget() {
std::cout << "获取的target的值:";
std::cout << _target << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void ModifyTarget(int target) {
std::cout << "修改target之后的值:";
_target = target;
std::cout << _target<<std::endl;
}
void GetName() {
std::cout << _name << std::endl;
}
void GetAge() {
std::cout << _age << std::endl;
}
void GetData() {
std::cout << _data << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string _name;
int _age;
static int _target;//类内声明,类外初始化
std::thread _thread;
int* _data;
};
int Student::_target = 100;
void GetStudentName(const Student& student) {
std::cout << student._name << std::endl;
}
int main() {
Student student1("小明",16,10);
GetStudentName(student1);
return 0;
}运行结果:

友元类:
友元类是其所有成员均可以访问另一个类的私有成员和保护成员的类。需要注意的是:
类A声明为类B为友元,不意味着类B自动授予类A的访问权限,类B可以访问类A的私有成员和保护成员,但是类A不是类B的友元,所以不能访问类B的私有成员和保护成员。
如果类B是类A的友元类,同时类C是类B的友元,类C是不会自动成为类A的友元,也就是不会有传递性。
基类的派生类不会继承基类的友元关系,也就是没有继承性。
示例:
创建一个获取Student类的私有成员_name的类,在其成员函数中定义获取的成员函数func()。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
class Student {
friend void GetStudentName(const Student& student);
public:
Student():_name(""),_age(0),_data(new int(0)) {
std::cout << "无参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(std::string name, int age,int number):_name(name),_age(age),_data(new int(number)) {
std::cout << "有参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(const Student &student):_name(student._name),_age(student._age) {//const可以加可以不加,主要是为了防止对参数进行修改,但是&是必须加
std::cout << "拷贝构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
*_data = *student._data;
}
Student(Student && student):_name(std::move(student._name)),_age(student._age),_thread(std::move(student._thread)){
std::cout << "移动构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
_data = std::move(student._data);
}
~Student() {
std::cout << "析构函数" << std::endl;
delete _data;
}
void GetTarget() {
std::cout << "获取的target的值:";
std::cout << _target << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void ModifyTarget(int target) {
std::cout << "修改target之后的值:";
_target = target;
std::cout << _target<<std::endl;
}
Student operator+(const Student& other)const {
Student temp;
temp._age=this->_age + other._age;
temp._data = new int(*this->_data + *other._data);
return temp;
}
Student& operator=(const Student& other) {
if (this == &other) {
return *this;
}
delete _data;
this->_name = other._name;
this->_age = other._age;
this->_data = new int();
*this->_data = *other._data;
std::cout << "拷贝赋值运算符" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
Student& operator=(Student&& other)noexcept {
if (this == &other) {
return *this;
}
delete this->_data;
this->_name = std::move(other._name);
this->_age = other._age;
this->_data = other._data;
other._data = nullptr;
std::cout << "移动赋值运算符" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
Student& operator++() {
this->_age++;
(*this->_data)++;
return *this;
}
const Student operator++(int) {
Student temp(*this);
this->_age++;
(*this->_data)++;
return temp;
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Student& other);
private:
std::string _name;
int _age;
static int _target;//类内声明,类外初始化
std::thread _thread;
int* _data;
};
int Student::_target = 100;
void GetStudentName(const Student& student) {
std::cout << student._name << std::endl;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Student& other) {
os << other._name << " "
<< other._age << " "
<< *other._data << std::endl;
return os;
}
int main() {
std::cout << "构造student1和student2:" << std::endl;
Student student1("小明",16,10);
Student student2("小刚", 10, 10);
std::cout << student2;
std::cout << student1;
std::cout << std::endl << "构造student3:" << std::endl;
Student student3;
student3=student1 + student2;
std::cout << student3;
std::cout <<std::endl<< "对student1进行前置++,对student2进行后置++:" << std::endl;
Student student5=++student1;
Student student6=student2++;
std::cout << "前置++:" << std::endl;
std::cout << student1;
std::cout << student5;
std::cout << "后置++:" << std::endl;
std::cout << student2;
std::cout << student6;
std::cout << "移动赋值运算符:" << std::endl;
Student student7;
student7=std::move(student2);
std::cout << student7;
return 0;
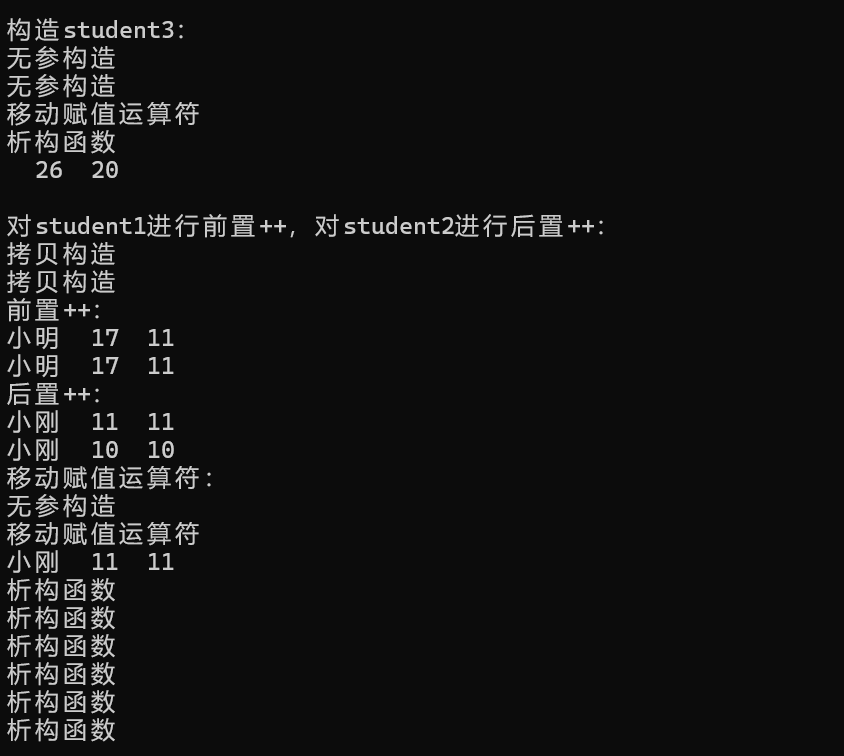
}运行结果:

优点:
避免了共有接口简介访问私有数据,支持特殊的场景,比如运算符重载等。
注意事项:
友元会破坏类的封装性,不能够通过继承或者嵌套自动传递,会导致代码的耦合度增加,维护难度上升。
优先使用成员函数或者公有接口,在必要时使用友元,尽量使用友元函数不使用友元类,减少权限的开放。
运算符重载:
通过成员函数或者友元函数重新定义运算符对自定义类型的操作行为。
注意:
运算符重载不能够创建新的运算符。
不能够改变运算符的优先级和结合性。
并非所有的运算符都能够进行重载,比如成员当问运算符、成员指针运算符、作用域解析运算符、条件运算符、sizeof和typeid运算符不能够进行重载。
示例:
对"+"、"<<"、"="、"前置++"、"后置++"进行重载。"-"、"*"、和"/"和"+"是一样的思路。注意区分前置++和后置++的区别,还需要注意重载时,前置++和后置++的函数参数区别。移动语义操作中一定注意将被移动对象的指针置空,防止出现双重释放或者悬空指针问题。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
class Student {
friend void GetStudentName(const Student& student);
public:
Student():_name(""),_age(0),_data(new int(0)) {
std::cout << "无参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(std::string name, int age,int number):_name(name),_age(age),_data(new int(number)) {
std::cout << "有参构造" << std::endl;
}
Student(const Student &student):_name(student._name),_age(student._age) {//const可以加可以不加,主要是为了防止对参数进行修改,但是&是必须加
std::cout << "拷贝构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
*_data = *student._data;
}
Student(Student && student):_name(std::move(student._name)),_age(student._age),_thread(std::move(student._thread)){
std::cout << "移动构造" << std::endl;
_data = new int();
_data = std::move(student._data);
}
~Student() {
std::cout << "析构函数" << std::endl;
delete _data;
}
void GetTarget() {
std::cout << "获取的target的值:";
std::cout << _target << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void ModifyTarget(int target) {
std::cout << "修改target之后的值:";
_target = target;
std::cout << _target<<std::endl;
}
Student operator+(const Student& other)const {
Student temp;
temp._age=this->_age + other._age;
temp._data = new int(*this->_data + *other._data);
return temp;
}
Student& operator=(const Student& other) {
if (this == &other) {
return *this;
}
delete _data;
this->_name = other._name;
this->_age = other._age;
this->_data = new int();
*this->_data = *other._data;
std::cout << "拷贝赋值运算符" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
Student& operator=(Student&& other)noexcept {
if (this == &other) {
return *this;
}
delete this->_data;
this->_name = std::move(other._name);
this->_age = other._age;
this->_data = other._data;
other._data = nullptr;
std::cout << "移动赋值运算符" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
Student& operator++() {
this->_age++;
(*this->_data)++;
return *this;
}
const Student operator++(int) {
Student temp(*this);
this->_age++;
(*this->_data)++;
return temp;
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Student& other);
private:
std::string _name;
int _age;
static int _target;//类内声明,类外初始化
std::thread _thread;
int* _data;
};
int Student::_target = 100;
void GetStudentName(const Student& student) {
std::cout << student._name << std::endl;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, Student& other) {
os << other._name << " "
<< other._age << " "
<< *other._data << std::endl;
return os;
}
int main() {
std::cout << "构造student1和student2:" << std::endl;
Student student1("小明",16,10);
Student student2("小刚", 10, 10);
std::cout << student2;
std::cout << student1;
std::cout << std::endl << "构造student3:" << std::endl;
Student student3;
student3=student1 + student2;
std::cout << student3;
std::cout <<std::endl<< "对student1进行前置++,对student2进行后置++:" << std::endl;
Student student5=++student1;
Student student6=student2++;
std::cout << "前置++:" << std::endl;
std::cout << student1;
std::cout << student5;
std::cout << "后置++:" << std::endl;
std::cout << student2;
std::cout << student6;
std::cout << "移动赋值运算符:" << std::endl;
Student student7;
student7=std::move(student2);
std::cout << student7;
return 0;
}运行结果: