本篇文章总结分享Vue3学习笔记,深入了解Vue3的11个知识点,希望对大家有所帮助!

如何快速入门VUE3.0:进入学习
《Vue3+Node+Webpack+API 商城项目工程化实战开发课!》
一、为什么选择CompositionAPI
Vue2的局限性
组件逻辑膨胀导致的可读性变差
无法跨组件重用代码
Vue2对TS的支持有限
在传统的OptionsAPI中我们需要将逻辑分散到以下六个部分。【相关推荐:vue.js视频教程】
OptionsAPI
componentspropsdatacomputedmethodslifecycle methods
如何使用CompositionAPI解决问题
最佳的解决方法是将逻辑聚合就可以很好的代码可读性。
这就是我们的CompositionAPI语法能够实现的功能。CompositionAPI是一个完全可选的语法与原来的OptionAPI并没有冲突之处。他可以让我们将相同功能的代码组织在一起,而不需要散落到optionsAPI的各个角落
代码重用方法PK
Vue2中的跨组件重用代码,我们大概会有四个选择
1、Mixin - 混入
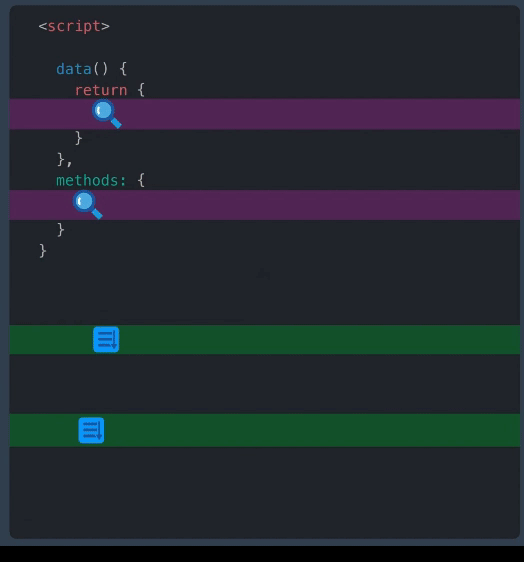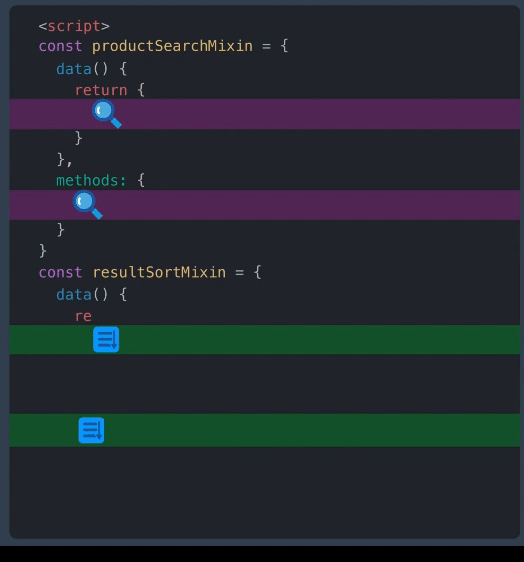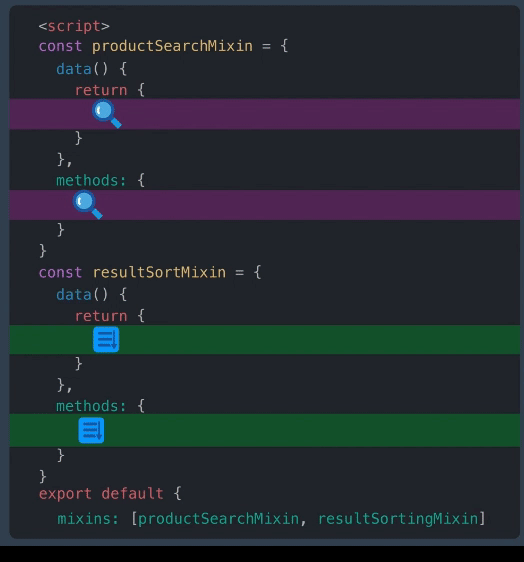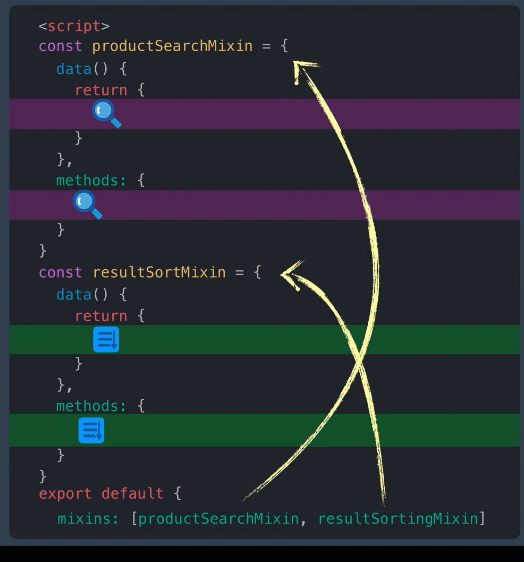
代码混入其实就是设计模式中的混合模式,缺点也非常明显。
可以理解为多重继承,简单的说就是一个人如何有两个父亲
缺点
无法避免属性名冲突
继承关系不清晰
2、Mixin Factory - 混入工厂
返回一个
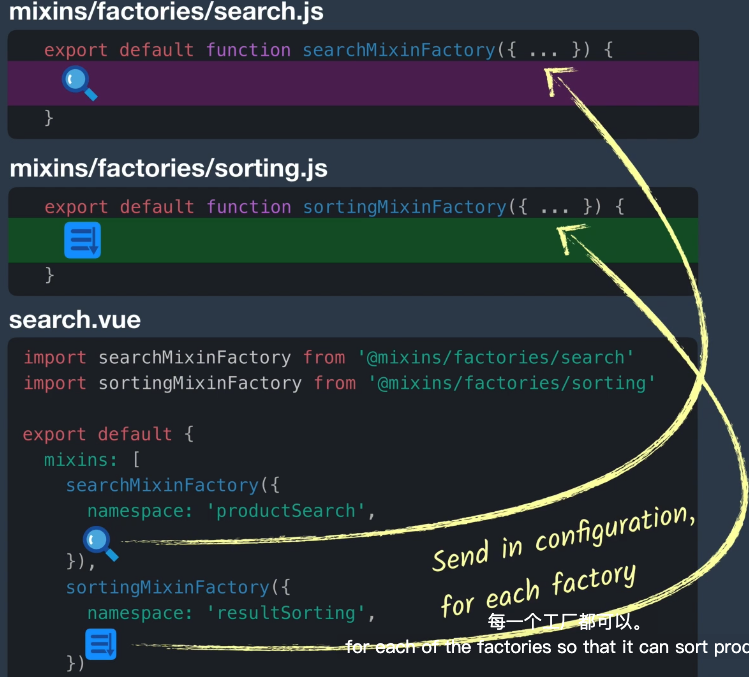
✅代码重用方便
✅继承关系清洗
3、ScopeSlots - 作用域插槽
❌可读性不高
❌配置复杂 - 需要再模板中进行配置
❌性能低 - 每个插槽相当于一个实例
4、CompositionApi - 复合API
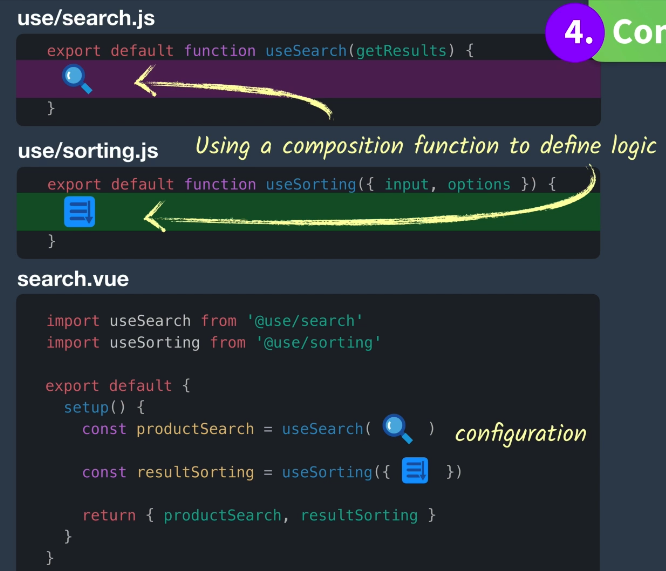
✅代码量少
✅没有引入新的语法,只是单纯函数
✅异常灵活
✅工具语法提示友好 - 因为是单纯函数所以 很容易实现语法提示、自动补偿
二、setup & ref
使用CompositionAPI理由
✅更好的Typescript支持
✅在复杂功能组件中可以实现根据特性组织代码 - 代码内聚性, 比如:
排序和搜索逻辑内聚
✅组件间代码复用
setup是什么
在以下方法前执行:
Components
Props
Data
Methods
Computed Properties
Lifecycle methods
可以不在使用难于理解的this
有两个可选参数
props - 属性 (响应式对象 且 可以监听(watch))
import {watch} from "vue"
export defalut {
props: {
name: String
},
setup(props) {
watch(() => {
console.log(props.name)
})
}
}context 上下文对象 - 用于代替以前的this方法可以访问的属性
setup (props,context) {
const {attrs,slots,parent,root,emit} = context
}ref是什么
对基本数据类型数据进行装箱操作使得成为一个响应式对象,可以跟踪数据变化。
总结
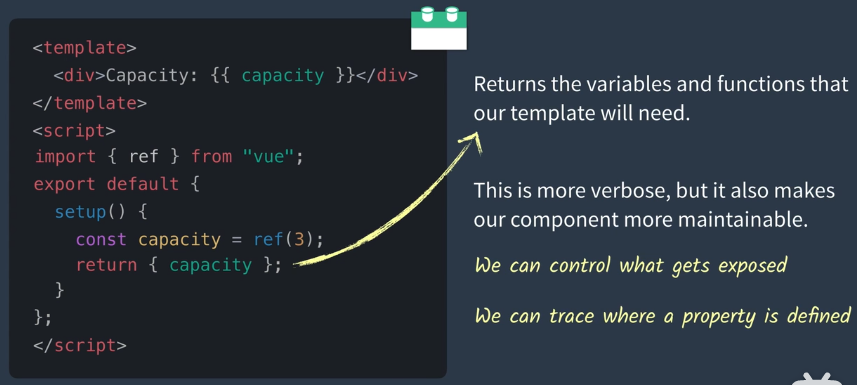
可维护性明显提高
可以控制哪些变量暴露
可以跟中哪些属性被定义 (属性继承与引用透明)
三、Methods
基础用法
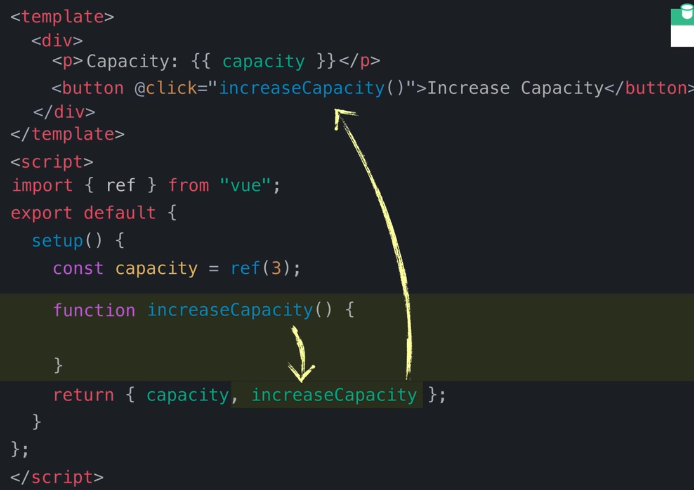
自动拆装箱总结
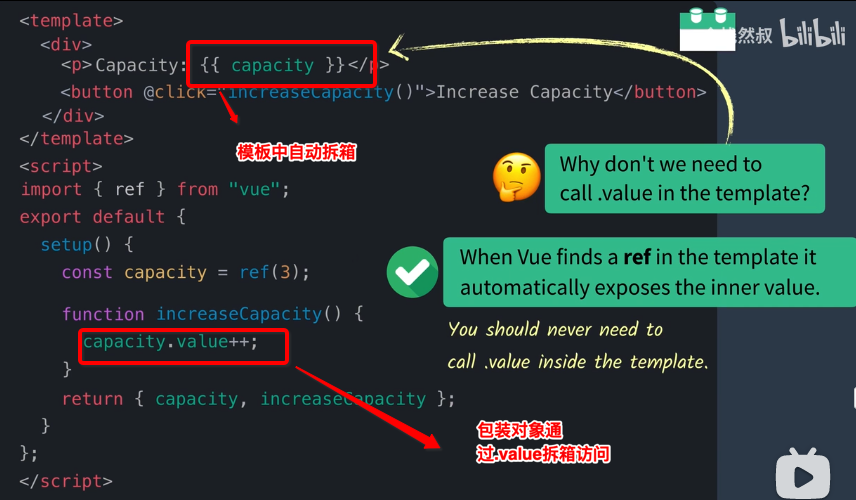
JS :需要通过.value访问包装对象
模板: 自动拆箱
四、 Computed - 计算属性
这个地方实在没什么好讲的,和Vue2没变化
<template>
<div>
<div>Capacity: {{ capacity }}</div>
<p>Spases Left: {{ sapcesLeft }} out of {{ capacity }}</p>
<button @click="increaseCapacity()">Increase Capacity</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, computed, watch } from "vue";
export default {
setup(props, context) {
const capacity = ref(3);
const attending = ref(["Tim", "Bob", "Joe"]);
function increaseCapacity() {
capacity.value++;
}
const sapcesLeft = computed(() => {
return capacity.value - attending.value.length;
});
return { capacity, increaseCapacity, attending, sapcesLeft };
},
};
</script>五、Reactive - 响应式语法
之前reactive 的 Ref 去声明所有的响应式属性
import { ref,computed } from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
const capacity = ref(4);
const attending = ref(["Tim","Bob","Joe"]);
const spacesLeft = computed(()=>{
return capacity.value - attending.value.length
})
function increaseCapacity(){ capacity.value ++;}
return { capacity,increaseCapacity,attending,spacesLeft}
}
}但是有另一个等效的方法用它去代替 reactive 的Ref
import { reactive,computed } from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
const event = reactive({
capacity:4,
attending:["Tim","Bob","Joe"],
spacesLeft:computed(()=>{
return event.capacity - event.attending.length;
})
})
}
}过去我们用vue2.0的data来声明响应式对象,但是现在在这里每一个属性都是响应式的包括computed 计算属性
这2种方式相比于第一种没有使用.
接下来 我们再声明method 这2种语法都ok,取决于你选择哪一种
setup(){
const event = reactive(){
capacity:4,
attending:["Tim","Bob","Joe"],
spacesLeft:computed(()=>{
return event.capacity - event.attending.length;
})
function increaseCapacity(){event.capacity++}
//return整个对象
return {event,increaseCapacity}
}
}
<p>Spaces Left:{{event.spacesLeft}} out of {{event.capacity}}</p>
<h2>Attending</h2>
<ul>>
<li v-for="(name,index) in event.attending" :key="index">
{{name}}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="increaseCapacity()"> Increase Capacity</button>在这里我们使用对象都是.属性的方式,但是如果 这个结构变化了,event分开了编程了一个个片段,这个时候就不能用.属性的方式了
//在这里可以使用toRefs
import {reactive,computed,toRefs} from 'vue'
export default{
setup(){
const event = reactive({
capacity:4,
attending:["Tim","Bob","Joe"],
spacesLeft:computed(()=>{
return event.capacity -event.attending.length;
})
})
function increaseCapacity(){ event.capacity ++ }
return {...toRefs(event),increaseCapacity}
}
}如果没有 increaseCapacity() 这个方法 直接可以简化为
return toRefs(event)
完整代码
<div>
<p>Space Left : {{event.spacesLeft}} out of {{event.capacity}} </p>
<h2>Attending</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(name,index)" in event.attending :key="index">{{name}}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="increaseCapacity">Increase Capacity</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//第一种
import {ref,computed } from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
const capacity = ref(4)
const attending = ref(["Tim","Bob","Joe"])
const spaceLeft = computed(()=>{
return capacity.value - attending.value.length;
});
function increaseCapacity(){ capacity.value++; }
return {capacity,increaseCapacity,attending,spaceLeft}
}
}
//返回一个响应式函数 第二种
import { reactive,computed } from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
const event = reactive({
capacity:4,
attending:["Tim","Bob","Joe"],
spaceLeft:computed(()=>{
return event.capacity - event.attending.length;
})
})
//我们不再使用.value
function increaseCapacity() { event.capacity++; }
//把这个event放入到template中
return { event,increaseCapacity}
}
}
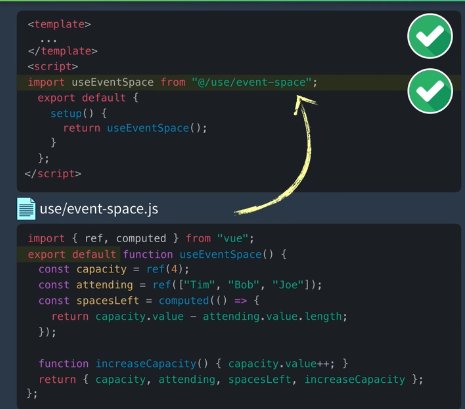
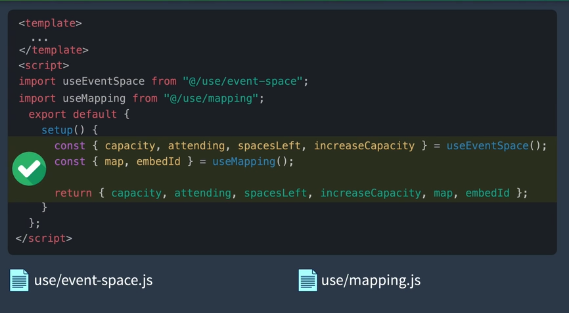
</script>六、 Modularizing
使用CompositionAPI的两个理由
1、可以按照功能组织代码

2、组件间功能代码复用
七、 LifecycleHooks - 生命周期钩子
| Vue2 | Vue3 |
|---|---|
| beforeCreate | ❌setup(替代) |
| created | ❌setup(替代) |
| beforeMount | onBeforeMount |
| mounted | onMounted |
| beforeUpdate | onBeforeUpdate |
| updated | onUpdated |
| beforeDestroy | onBeforeUnmount |
| destroyed | onUnmounted |
| errorCaptured | onErrorCaptured |
| - | ?onRenderTracked |
| - | ?onRenderTriggered |
setup中调用生命周期钩子
import { onBeforeMount,onMounted } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log('Before Mount!')
})
onMounted(() => {
console.log('Before Mount!')
})
},
};八、Watch - 监听器
// 所有依赖响应式对象监听
watchEffect(() => {
results.value = getEventCount(searchInput.value);
});
// 特定响应式对象监听
watch(
searchInput,
() => {
console.log("watch searchInput:");
}
);
// 特定响应式对象监听 可以获取新旧值
watch(
searchInput,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("watch searchInput:", newVal, oldVal);
},
);
// 多响应式对象监听
watch(
[firstName,lastName],
([newFirst,newLast], [oldFirst,oldlast]) => {
// .....
},
);
// 非懒加载方式监听 可以设置初始值
watch(
searchInput,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log("watch searchInput:", newVal, oldVal);
},
{
immediate: true,
}
);九、Sharing State - 共享状态
编写一个公共函数usePromise函数需求如下:
results : 返回Promise执行结果
loading: 返回Promise运行状态
PENDING :true
REJECTED : false
RESOLVED: false
error : 返回执行错误
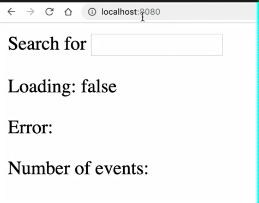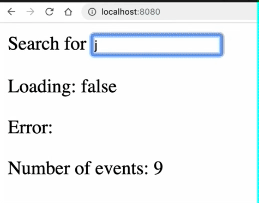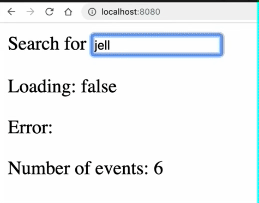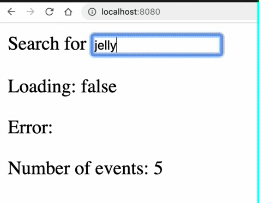
import { ref } from "vue";
export default function usePromise(fn) {
const results = ref(null);
// is PENDING
const loading = ref(false);
const error = ref(null);
const createPromise = async (...args) => {
loading.value = true;
error.value = null;
results.value = null;
try {
results.value = await fn(...args);
} catch (err) {
error.value = err;
} finally {
loading.value = false;
}
};
return { results, loading, error, createPromise };
}应用
import { ref, watch } from "vue";
import usePromise from "./usePromise";
export default {
setup() {
const searchInput = ref("");
function getEventCount() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000);
});
}
const getEvents = usePromise((searchInput) => getEventCount());
watch(searchInput, () => {
if (searchInput.value !== "") {
getEvents.createPromise(searchInput);
} else {
getEvents.results.value = null;
}
});
return { searchInput, ...getEvents };
},
};十、Suspense - 悬念
复杂的Loading实现
我们考虑一下当你加载一个远程数据时,如何显示loading状态
通常我们可以在模板中使用v-if
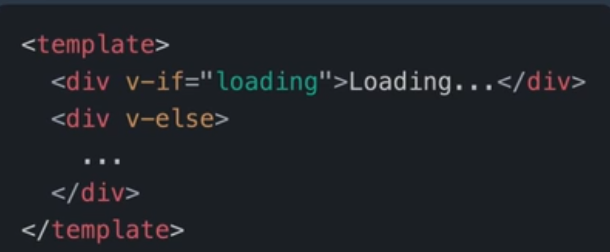
但是在一个组件树中,其中几个子组件需要远程加载数据,当加载完成前父组件希望处于Loading状态时我们就必须借助全局状态管理来管理这个Loading状态
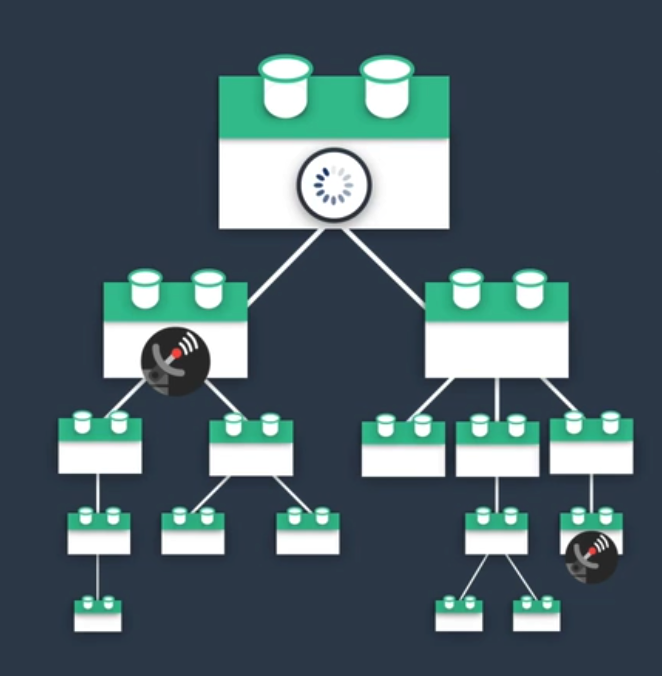
Suspense基础语法
这个问题在Vue3中有一个全新的解决方法。
这就是Suspense Component,悬念组件。

<template>
<div>
<div v-if="error">Uh oh .. {{ error }}</div>
<Suspense>
<template #default>
<div>
<Event />
<AsyncEvent />
</div>
</template>
<template #fallback> Loading.... </template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, onErrorCaptured, defineAsyncComponent } from "vue";
import Event from "./Event.vue";
const AsyncEvent = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./Event.vue"));
export default {
components: {
Event,
AsyncEvent,
},
setup() {
const error = ref(null);
onErrorCaptured((e) => {
error.value = e;
// 阻止错误继续冒泡
return true;
});
return { error };
},
};
</script>骨架屏实现


十一、Teleport - 传送门
功能
类似React中的Portal, 可以将特定的html模板传送到Dom的任何位置

基础语法
通过选择器QuerySelector配置
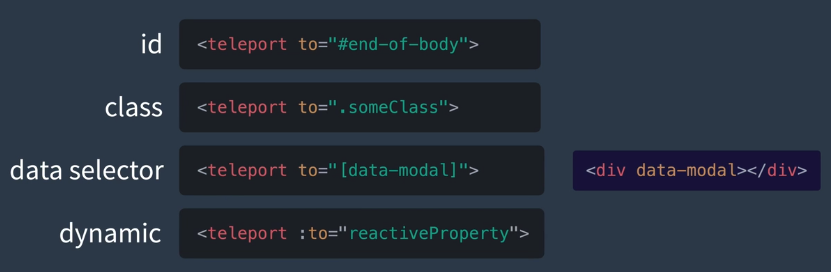
示例代码

<template>
<div>
<teleport to="#end-of-body" :disabled="!showText">
<!-- 【Teleport : This should be at the end 】 -->
<div>
<video src="../assets/flower.webm" muted controls="controls" autoplay="autoplay" loop="loop">
</video>
</div>
</teleport>
<div>【Teleport : This should be at the top】</div>
<button @click="showText = !showText">Toggle showText</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const showText = ref(false);
setInterval(() => {
showText.value = !showText.value;
}, 1000);
return { showText };
},
};
</script>更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
以上就是【整理总结】详解Vue3的11个知识点的详细内容,更多请关注likekyus日记其它相关文章!