BeanFactory与ApplicationContext
SpringBoot启动类中
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A01.class, args);返回值是ApplicationContext子接口类型,最上层是BeanFactory。下图是类图(ctrl+alt+u)
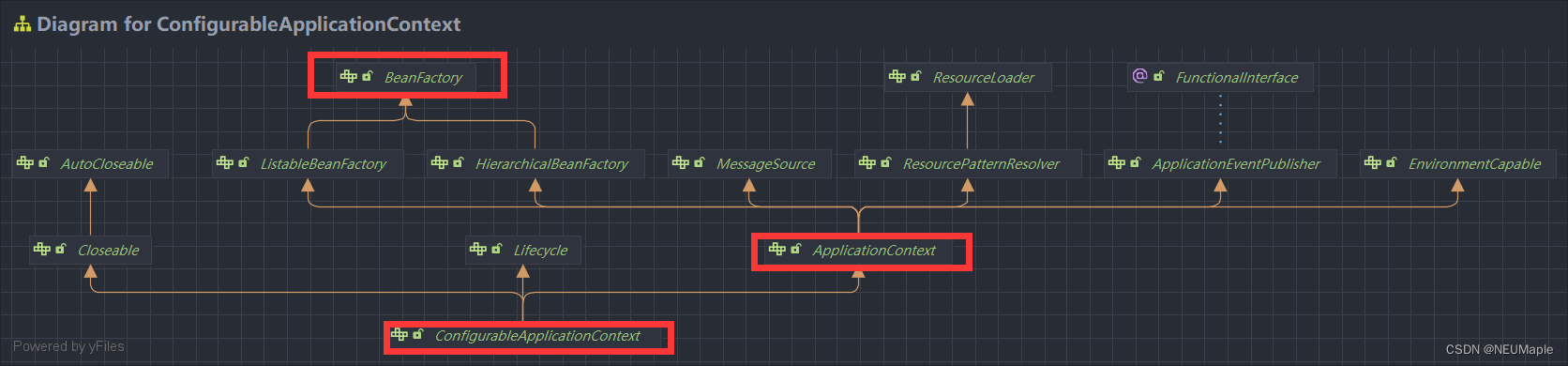
1. BeanFactory
1.1 什么是BeanFactory?
- ApplicationContext父接口
- 它才是 Spring 的核心容器, 主要的 ApplicationContext 实现都【组合】了它的功能,【组合】是指 ApplicationContext 的一个重要成员变量就是 BeanFactory。
1.2 BeanFactory 能干点啥
表面上只有 getBean
实际上控制反转、基本的依赖注入、直至 Bean 的生命周期的各种功能,都由它的实现类提供。有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory。
1.3 ApplicationContext 比 BeanFactory 多点啥

就多上面那四个功能
- MessageSource:国际化处理
- ResourcePatternResolver:通配符方式获取一组 Resource 资源
- EnvironmentCapable:整合 Environment 环境
- ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发布与监听(可以实现解耦)
其中的ApplicationEventPublisher可以实现解耦。
例:注册后实现发短信或者其他操作
首先得有一个事件类继承ApplicationEvent
public class UserRegisteredEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public UserRegisteredEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
component1中发布事件
@Component
public class Component1 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Component1.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher context;
public void register() {
log.debug("用户注册");
context.publishEvent(new UserRegisteredEvent(this));
}
}component2中监听事件并进行处理
@Component
public class Component2 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Component2.class);
@EventListener
public void aaa(UserRegisteredEvent event) {
log.debug("发送短信");
}
}2. 容器实现
2.1 BeanFactory实现
DefaultListableBeanFactory,是 BeanFactory 最重要的实现,像控制反转和依赖注入功能,都是它来实现
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从类路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧)
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,从磁盘路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧)
XmlWebApplicationContext,传统 SSM 整合时,基于 XML 配置文件的容器(旧)
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,传统 SSM 整合时,基于 java 配置类的容器(旧)
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,Spring boot 中非 web 环境容器(新)
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,Spring boot 中 servlet web 环境容器(新)
AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,Spring boot 中 reactive web 环境容器(新)
另外要注意的是,后面这些带有 ApplicationContext 的类都是 ApplicationContext 接口的实现,但它们是组合了 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的功能,并非继承而来。
2.2 DefaultListableBeanFactory
- beanFactory 可以通过 registerBeanDefinition 注册一个 bean definition 对象
我们平时使用的配置类、xml、组件扫描等方式都是生成 bean definition 对象注册到 beanFactory 当中
bean definition 描述了这个 bean 的创建蓝图:scope 是什么、用构造还是工厂创建、初始化销毁方法是什么,等等
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// bean 的定义(class, scope, 初始化, 销毁)
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition =
BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Config.class).setScope("singleton").
getBeanDefinition();
//将这个bean添加到beanFactory工厂中
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("config", beanDefinition);
//查看有哪些bean
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
结果是只有config,但config类里面还有 Bean1,Bean2没加入进去,所以说是那些注解还没有解析。
- beanFactory 需要手动调用 beanFactory 后处理器对它做增强
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor对象
例如通过解析 @Bean、@ComponentScan 等注解,来补充一些 bean definition
// 给 BeanFactory 添加一些常用的后处理器
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory);
// BeanFactory 后处理器主要功能,补充了一些 bean 定义
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class).values().
forEach(beanFactoryPostProcessor -> {
beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
});
查看结果后多了几个bean

beanFactory 需要手动调用方法来初始化单例
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); // 准备好所有单例(懒加载)
beanFactory 需要额外设置才能解析 ${} 与 #{}
bean后处理器有排序逻辑
3. ApplicationContext
3.1 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
从类路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧)
// ⬇️较为经典的容器, 基于 classpath 下 xml 格式的配置文件来创建
private static void testClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("a02.xml");
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
}实现原理:
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
System.out.println("读取之前...");
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("读取之后...");
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new FileSystemResource("src\\main\\resources\\a02.xml"));
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
从磁盘路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧)
// ⬇️基于磁盘路径下 xml 格式的配置文件来创建
private static void testFileSystemXmlApplicationContext() {
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
"src\\main\\resources\\a02.xml");
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
}AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
Spring boot 中非 web 环境容器(新)
// ⬇️较为经典的容器, 基于 java 配置类来创建
private static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
Spring boot 中 servlet web 环境容器(新)
// ⬇️较为经典的容器, 基于 java 配置类来创建, 用于 web 环境
private static void testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(WebConfig.class);
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}