现在时间
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int totalSeconds = time(0);
int CurrentSecond = totalSeconds%60;
int totalMinutes = totalSeconds/60;
int CurrentMinutes = totalMinutes%60;
int totalHours = totalMinutes/60;
int CurrentHours = (totalHours+8)%24;
cout << "Current time is " << ":" << CurrentHours << ":" << CurrentMinutes << ":"
<< CurrentSecond << "GMT" << endl ;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
布尔值不必再测试
if (even == true)---------if (even)
常见错误 两浮点值的相等性测试
浮点有精度限制 一旦涉及计算 就会导致舍入,所以 要用数学表达
非常接近
就是||<epsilon
减法练习
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>//for rand and srand fuction
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(time(0));
int number1 = rand() % 10;
int number2 = rand() % 10;
if (number1 < number2)
{
int temp = number1;
number1 = number2;
number2 = temp;
}
cout << "题目是:" << number1 << "-" << number2 << endl
<< " 你的答案是:";
int ans;
cin >> ans;
if(ans == number1 - number2)
cout << "yes!";
else
cout << "wrong!";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
十六进制转十进制
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>//测试和转换字符
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "enter a digit :";
char hexDigit;
cin >> hexDigit;
hexDigit = toupper(hexDigit);//daxie
if (hexDigit <= 'F' && hexDigit >= 'A')
{
int value = 10 + hexDigit - 'A';
cout << hexDigit << "is" << value;
}
system ("pause");
}
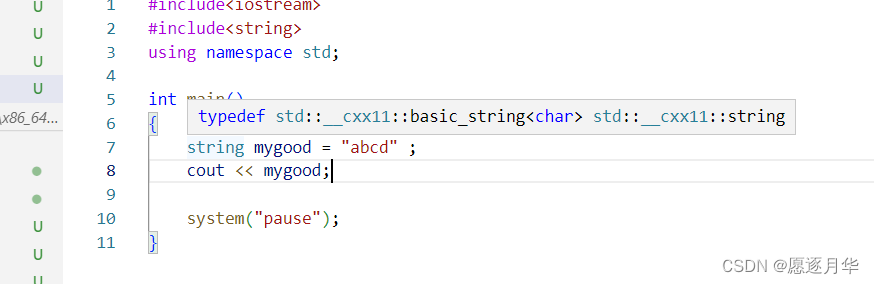
String 是一个对象类型
// Forward declarations -- C++ --
// Copyright © 2001-2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// This file is part of the GNU ISO C++ Library. This library is free
// software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
// terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the
// Free Software Foundation; either version 3, or (at your option)
// any later version.
// This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
// Under Section 7 of GPL version 3, you are granted additional
// permissions described in the GCC Runtime Library Exception, version
// 3.1, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License and
// a copy of the GCC Runtime Library Exception along with this program;
// see the files COPYING3 and COPYING.RUNTIME respectively. If not, see
// http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
/** @file bits/stringfwd.h
- This is an internal header file, included by other library headers.
- Do not attempt to use it directly. @headername{string}
*/
//
// ISO C++ 14882: 21 Strings library
//
写入文件
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ofstream output;
output.open("numbers.txt");
output << 95 <<" "<< 56 << " " << 88;
output.close();
cout << "Done" << endl;
system ("pause");
}
const int NUMBER_OF_QUESTIONS = 5;
输入和输出重定向–键盘输入太过于笨拙 Sentinel value.exe > output.txt
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream input("numbers.txt");
double sum = 0;
double number;
while(!input.eof())
{
input >> number;
cout << number <<" " ;
sum += number;
}
input.close();
cout << "Done" << sum << endl;
system ("pause");
}
函数—和c一致
和c一致
–传值方式
函数的重载–同名不同参数
函数原型 prototype – int max (int num1, int num2)后面再实现
缺省参数–设置一个缺省值 --默认值 int max (int num1 ,int num2=5)–只能后面的缺省
内联函数-提高性能-避免函数调用压栈的开销
inline void f(int a)
{
cout << a;
}
static int x = 1;— 会一直驻留在内存
引用传参-特殊变量 引用变量
int& a;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int& num1,int& num2)
{
int temp;
temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
int main()
{
int num1=1,num2=2;
cout << num1 << " " << num2 <<endl;
swap(num1, num2);
cout << num1 << " " << num2;
system ("pause");
}
常量引用传递 int max (const int& num1)—不可改变
设置桩函数–自顶向下设计—逐步求精
一维数组array和C字符串
shuffling 洗牌 数组—数组 天生的 引用传递
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
void shuffling(int team[], int arraySize)
{
srand(time(0));
for(int i=arraySize-1; i>0; i--)
{
int j = rand()%(i + 1);
int temp = team[i];
team[i]=team[j];
team[j]=temp;
}
}
int main()
{
int team[100];
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
team[i] = i;
}
shuffling(team, 100);
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
cout << team[i] << " ";
}
system("pause");
}
防止数组修改 void f( const int list【】,int arraySize)
数组作为返回值–反转array
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
void reverse(int team[],int newteam[],int size){
for(int i=0,j=size-1;i<size;i++,j--){
newteam[j]=team[i];
}
}
void printArray(int team[], int size){
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
cout << team[i] << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int team[100];
int newteam[100];
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
team[i] = i;
}
reverse(team, newteam, 100);
printArray(newteam,100);
system("pause");
}
二分搜索
#include<iostream>
#include"ShufflingArray.cpp"
using namespace std;
void reverse(int team[],int newteam[],int size){
for(int i=0,j=size-1;i<size;i++,j--){
newteam[j]=team[i];
}
}
void printArray(int team[], int size){
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
cout << team[i] << " ";
}
}
int binarySearch(int team[],int size,int key)
{
int low=0,high=size-1;
while(low<=high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
cout << low << " " << mid << " "<< high<< endl;
if(team[mid]>key){
high=mid-1;
}
else if (team[mid == key]){
return mid;
}
else{
low=mid+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int team[100];
int newteam[100];
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
team[i] = i;
}
shuffling(team,100);
int key = 33;
int a = binarySearch(team,100,key);
cout << a;
//reverse(team, newteam, 100);
//printArray(newteam,100);
system("pause");
}
选择排序
#include<iostream>
#include"ShufflingArray.cpp"
using namespace std;
void printArray(int team[], int size){
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
cout << team[i] << " ";
}
}
void selectionSort(int team[], int size){
for(int i = 0; i < size ; i ++ )
{
int currentMin = team[i];
int currentMinIndex = i;
for(int j = i + 1 ; j < size ; j ++)
{
if(currentMin > team[j]){
currentMin = team[j];
currentMinIndex = j;
}
}
if(currentMinIndex != i)
{
team[currentMinIndex] = team[i];
team[i] = currentMin;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int team[100];
for(int i = 0; i < 100 ; i ++ )
{
team[i] = i;
}
shuffling(team,100);
selectionSort(team,100);
printArray(team,100);
system("pause");
}
c的字符串 string—结尾是’\0’
itoa()
二维数组做参数----------需要a【】【column_size】–
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
double getDistance(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
return sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)*(y2-y1));
}
int main()
{
const int NUMBER_OF_POINTS = 8;
double points[NUMBER_OF_POINTS][2];
cout << "Enter " << NUMBER_OF_POINTS << " points:";
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_POINTS; i ++)
{
cin >> points[i][0] >> points[i][1];
}
int p1=0,p2=1;
double shortestDistance = getDistance(points[p1][0], points[p1][1]
, points[p2][0], points[p2][1]);
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_POINTS; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < NUMBER_OF_POINTS; j++)
{
double distance = getDistance(points[i][0], points[i][1]
, points[j][0], points[j][1]);
if(shortestDistance > distance)
{
shortestDistance = distance;
}
cout << shortestDistance;
}
}
cout << "shortest:" << shortestDistance;
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}
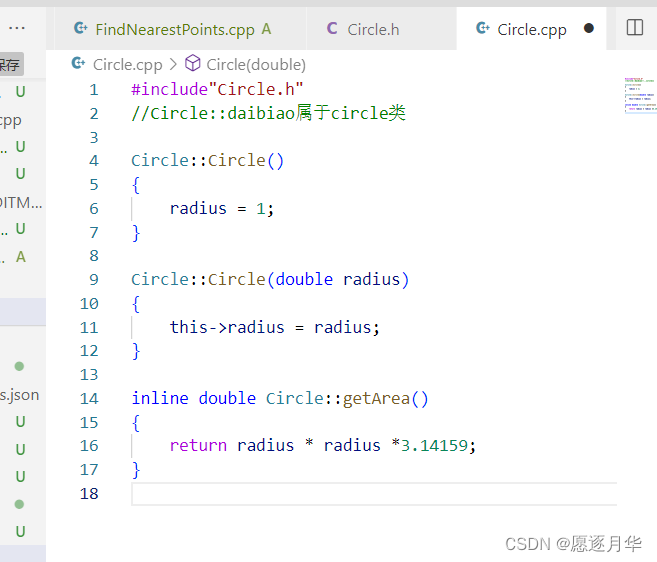
对象和类
初始化列表来初始化数据域
Circle ::Circle()
:radius(1)
{
}
Circle ::Circle()
{
radius = 1;
}
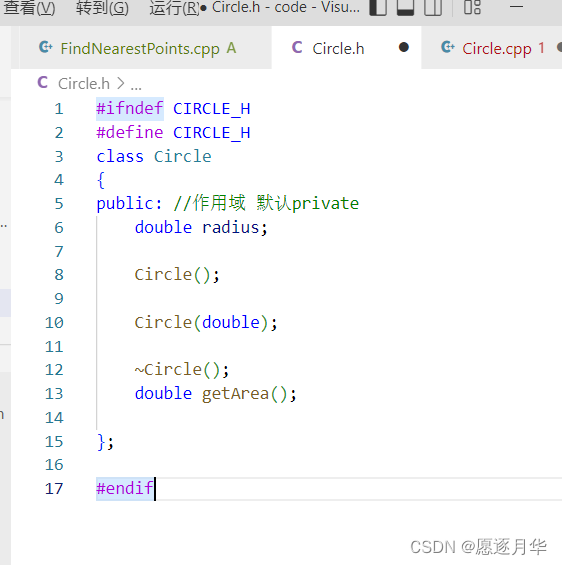
类定义实现分离
。h ---------意味 头head
相同名字 不同扩展名
::二元作用域解析符号 -binary scope resolution operator
如 std ::cout<< “hello”;
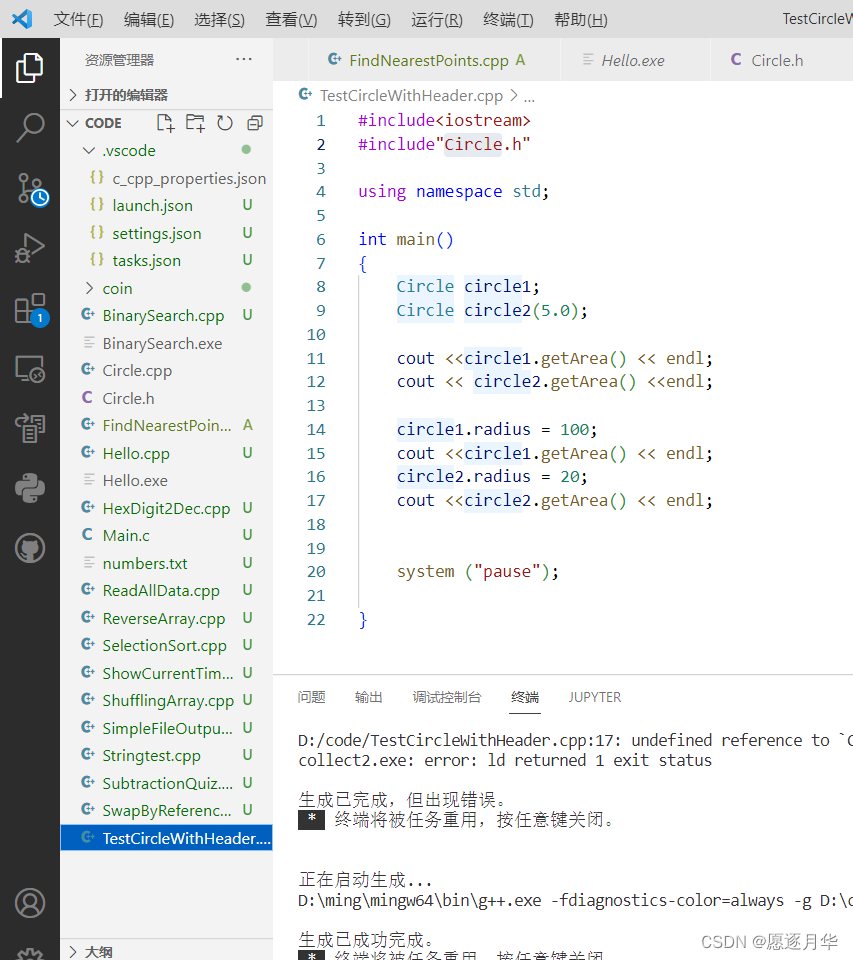
避免多次包含-包含保护 inclusion guard
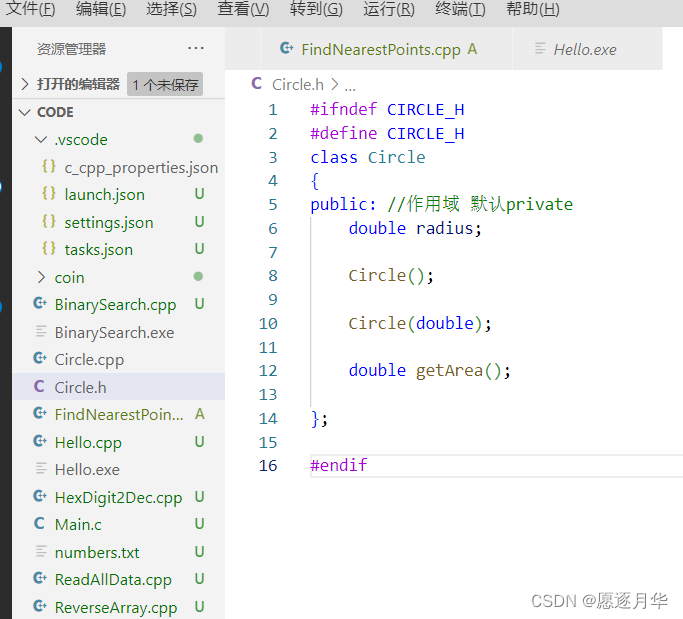
类中的 内联函数—内联定义
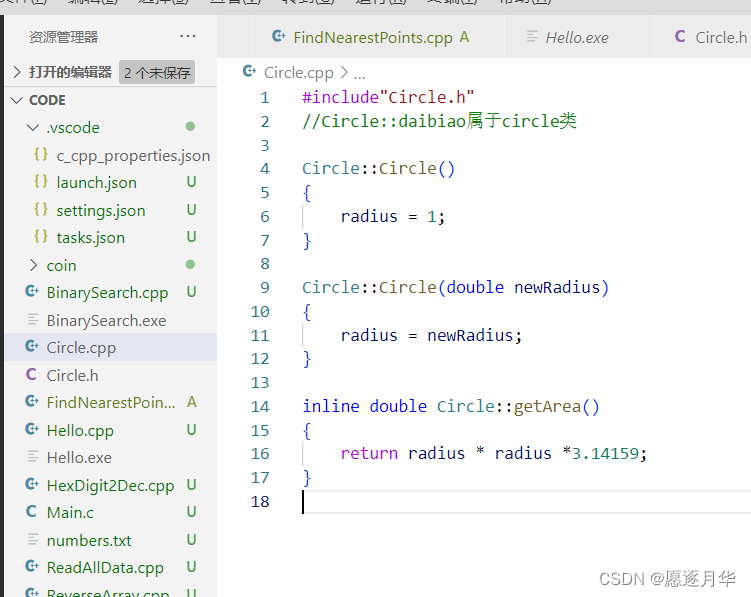
面对对象思想
数字转字符串 ss.str()
类的设计–内聚 。。。
指针 动态内存管理–原来如此 为什么当初我的老师要这样教我,让我产生如此巨大的误解!-指针也不过是个变量 用四个字节存一个地址
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int count = 5;
int* pCount = &count;
cout << count <<endl;
cout << pCount<<endl;
cout << &count << endl;
cout << *pCount << endl;
system ("pause");
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int count = 5;
int* pCount = &count;//*用于声明
cout << count <<endl;
cout << pCount<<endl;
cout << &count << endl;
cout << *pCount << endl;//*用于解引用
system ("pause");
}
常量数据 常量指针
const double* const pValue = &radius;
数组名实际上是 指向数组第一个元素的常量指针
指针从 list +0 开始 所以数组下标从0开始
指针交换
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap3(int* p1, int* p2)//交换指针的值
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;//把指针指向的变量换了
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
swap3(&num1,&num2);//传进去指针变量
cout << num1 << num2;
system ("pause");
}
动态持久内存分配//局部变量在栈中 new分配在堆中–动态数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int* reverse(const int* list,int size)
{
int* result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0 , j=size-1; i < size ; i++,j--)
{
result[i]=list[j];
}
return result;
}
void printArray(int team[], int size){
for(int i = 0; i < size ; i ++ )
{
cout << team[i] << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int list[]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
int* p = reverse(list, 6);//动态数组:int* list =new int【size】;
printArray(p, 6);
system ("pause");
}
this指针—指向被调用对象本身-访问被屏蔽的数据域–局部变量同名,所以屏蔽对象本身的变量
访问被屏蔽的数据域
析构函数destructor
每个类都有一个析构函数 , 当一个对象销毁时候自动调用该析构函数
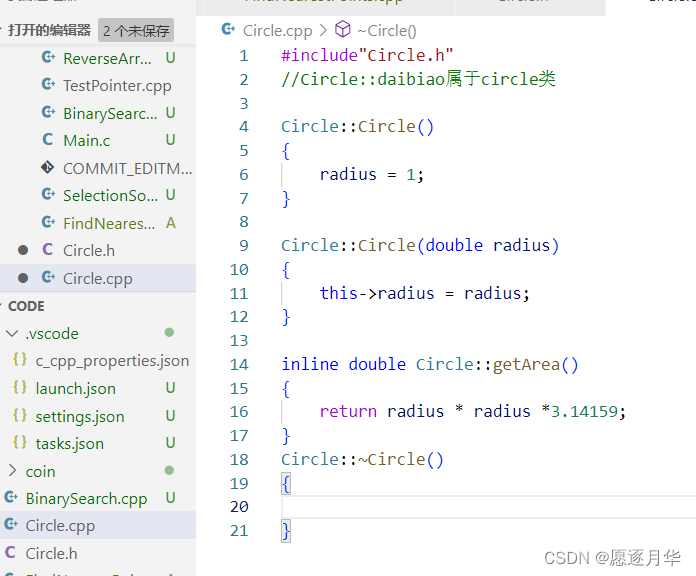
delete circle1;
模板、向量、栈
模板栈
template<class T>
class Stack
{
private:
class Node
{
public:
T x;
Node* next;
Node(){}
Node(T t,Node* next){
this->x = t;
this->next = next;
}
Node(Node& node){
this->x = node.x;
this->next = node.next;
}
};
Node* top;
int num;
public:
Stack(){
top = new Node(0,nullptr);
num = 0;
}
~Stack(){
while(top->next!=nullptr){
Node* temp = top->next;
top->next = top->next->next;
delete temp;
}
delete top;
num = 0;
}
void push(T t){
Node* oldfirst = top->next;
Node* newfirst = new Node(t,nullptr);
newfirst->next = oldfirst;
top->next = newfirst;
num++;
}
T pop(){
if(top->next!=nullptr){
Node* temp = top->next;
top->next = top->next->next;
T val = temp->x;
delete temp;
num--;
return val;
}
}
int getlength(){
return num;
}
};
向量类vector–更灵活vector intVector(10); 使用intVector【0】=5;要保证里面有元素!
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> intVector;
for(int i = 0; i<3;i++)
intVector.push_back(i+1);
cout << intVector[0];
vector<string> stringVector;
stringVector.push_back("Dalao");
cout << stringVector[0];
system ("pause");
}
向量表示二维数组
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > matrix(4);
for(int i = 0; i<4;i++)
matrix[i]=vector<int>(3);
matrix[0][0]=1;
system ("pause");
}