六、string类
2. 反向迭代器
一般来说,迭代器都是正向的遍历容器,虽然可以通过从 end ** 遍历到 begin 的方法来反向遍历容器,但是有这样一种迭代器,叫做反向迭代器**,可以做到反向遍历容器。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
string s1("hello,world");
// 反向迭代器 -- reverse_iterator
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << ' ';
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}

反向迭代器就是反方向跑,每次+1其实都是往左跑。
const迭代器
当构造时使用 const 修饰,普通的迭代器就不能够使用了。
void test2()
{
const string s1("hello,world");
// 这里会出现报错
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
此时由于类型不匹配,我们需要调整迭代器。

使用 const_iterator 就可以了。那么普通迭代器和 const迭代器 有什么区别呢?其实知道const就知道了,普通迭代器对容器是可读可写的,const迭代器就只可读。
string类对象的容量操作(补)
size()
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test3()
{
string s1("hello,world");
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test3();
return 0;
}
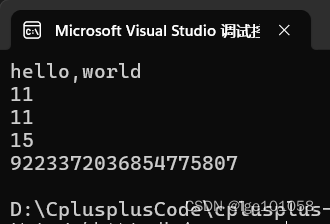
size() 函数返回string类中的元素个数。
length() 函数和 size() 函数作用一样,返回元素个数。
capacity() 函数返回容器的当前容量,即分配的空间,size() 是使用的空间。
max_size() 函数不常用,返回这个容器能够存储的最大长度,跟编译器有关,输出结果不唯一。
既然知道了 capacity ,我们来看一看VS环境下的C++扩容机制吧。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test4()
{
string s;
// 初始容量
int sz = s.capacity();
cout << sz << endl;
// 循环插入数据
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
s.push_back('a');
// 容量有变化时
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
// 输出新的容量
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
test4();
return 0;
}
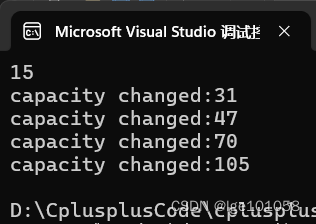
也不需要让大家找什么规律,我直接说了:①capacity 求的是不包含字符串末尾的 ‘\0’ 的空间,初始实际上是分配了 16 的空间大小,可用空间只有 15 个数据长度。②第一次扩容是 2倍扩容。③剩下的扩容都是 1.5倍扩容。在其他环境下不一定是这种扩容机制哦。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test5()
{
string s("hello,world!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s.empty() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.empty() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test5();
return 0;
}
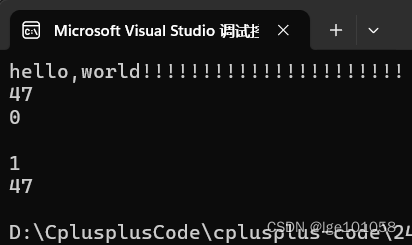
empty() 函数翻译过来就知道功能就是判断容器是否为空,为空返回true,非空返回false。
clear() 函数就是清理的意思,它会将容易里的数据都清除。但是,我们发现,capacity() 并没有相应的减少,说明 clear 只清理了数据,并没有释放空间。那我们想要释放空间该怎么办?
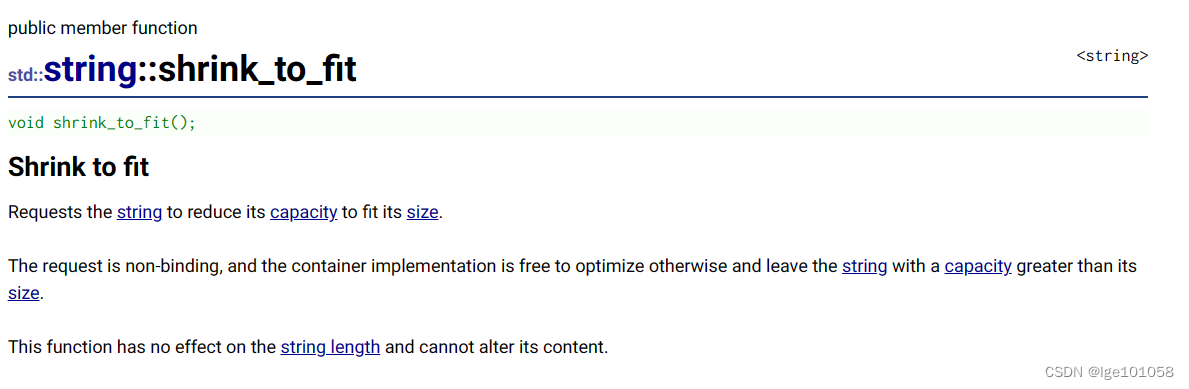
string 提供了这样一个函数,作用是将 capacity 缩小到 size 大小。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test5()
{
string s("hello,world!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!");
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s.empty() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.empty() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
// 缩容操作
s.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test5();
return 0;
}
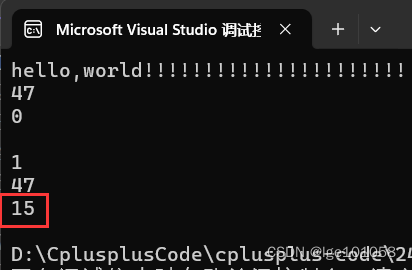
实际上它并不能把空间全部释放掉,最小缩容到 16 (有一个’\0’)。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test6()
{
string s("hello,worlddddddddddddddddd");
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(100);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test6();
return 0;
}
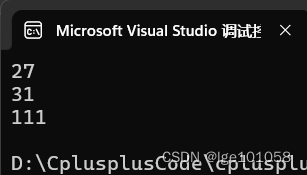
reserve() 函数的作用就是手动分配空间,但是不一定刚刚好分派到你想要的大小。那么,reserve 可以缩容吗?上面情况是想要分配的空间比原来的 capacity 大,假如想要分配的空间比 size 大,比 capacity 小会怎样?比 size 小会怎样?
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test6()
{
string s1("hello,worlddddddddddddddddd");
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
string s2("hello,worlddddddddddddddddd");
s2.reserve(100);
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.reserve(50);
cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;
string s3("hello,worlddddddddddddddddd");
s3.reserve(100);
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl;
s3.reserve(10);
cout << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
test6();
return 0;
}
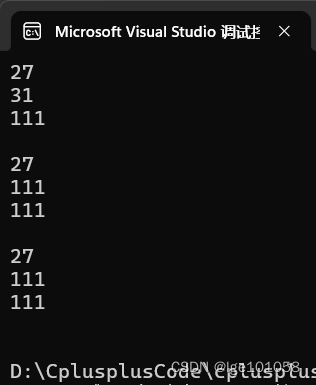
所以我们知道,reserve 只有比 capacity 大时才扩容。
reserve 是改变容量,resize() 就是改变数据个数。

由上图可知:①给 resize 的值比 size 小时,resize 会将多余的给删除,不会修改 capacity 的值。②当给 resize 的值比 size 大,比 capacity 小时,字符串后面会默认插入 ‘\0’,或者给定的值。③当给 resize 的值比 capacity 大时,字符串会扩容至 resize,然后赋值 ‘\0’ 或给定值。
3. string类的元素访问
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test8()
{
string s("hello,world");
// [] 访问
cout << s[6] << endl;
// at 访问
cout << s.at(6) << endl;
// 直接取头部数据
cout << s.front() << endl;
// 直接取尾部数据
cout << s.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test8();
return 0;
}
其中 [] 和 at 访问几乎没区别,只是对越界的检查方式不同。
4. string类的修改

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void test9()
{
string s("123456789");
cout << s << endl;
// 字符串末尾追加
s += '0';
cout << s << endl;
// 末尾追加
s.append("987");
cout << s << endl;
// 尾插一个字符
s.push_back('6');
cout << s << endl;
// 完全覆盖
s.assign("13345889");
cout << s << endl;
// 从下标1开始插入
s.insert(1, "23");
cout << s << endl;
// 从下标3开始删除两个字符
s.erase(3, 2);
cout << s << endl;
// 从下标5开始,将1个字符给替换成
s.replace(5, 1, "67");
cout << s << endl;;
}
int main()
{
test9();
return 0;
}
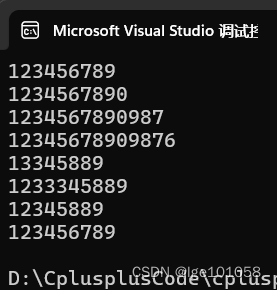
insert / erase / replace 需要挪动数据,复杂度大,能不用就不用。这里函数太多,就不一一介绍了,多看看文档就会用了。