ROS-DWA模块
在之前的学习中我们了解到,设定机器人的导航目标位置后,会在
MoveBase::executeCb函数中执行全局路径规划,并通过while循环反复执行 executeCycle函数控制机器人跟踪全局路径,这里控制机器人跟踪就是我们常说的局部规划,常用的局部规划方法有dwa、teb、pid、mpc、pure pursuit等,这一节对dwa算法进行研究。
主要流程
bool DWAPlannerROS::setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& orig_global_plan) {
if (! isInitialized()) {
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized, please call initialize() before using this planner");
return false;
}
//when we get a new plan, we also want to clear any latch we may have on goal tolerances
latchedStopRotateController_.resetLatching();
ROS_INFO("Got new plan");
return dp_->setPlan(orig_global_plan);
}
这里调用的是dp_的setPlan(),dp_是指向DWAPlanner的指针。
bool DWAPlanner::setPlan(const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& orig_global_plan) {
oscillation_costs_.resetOscillationFlags();
return planner_util_->setPlan(orig_global_plan); // 将orig_global_plan设置给LocalPlannerUtil的global_plan_
}
接着就是调用tc_->computeVelocityCommands(cmd_vel)进行局部规划。
DWAPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands
bool DWAPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel) {
// dispatches to either dwa sampling control or stop and rotate control, depending on whether we have been close enough to goal
// 获取当前位姿
if ( ! costmap_ros_->getRobotPose(current_pose_)) {
ROS_ERROR("Could not get robot pose");
return false;
}
// 调用planner_util_的getLocalPlan方法,以当前位姿为起点,
// 获取局部路径,并将其存储在transformed_plan中。如果失败,则返回false。
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> transformed_plan;
if ( ! planner_util_.getLocalPlan(current_pose_, transformed_plan)) {
ROS_ERROR("Could not get local plan");
return false;
}
//if the global plan passed in is empty... we won't do anything
if(transformed_plan.empty()) {
ROS_WARN_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "Received an empty transformed plan.");
return false;
}
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "Received a transformed plan with %zu points.", transformed_plan.size());
// update plan in dwa_planner even if we just stop and rotate, to allow checkTrajectory
dp_->updatePlanAndLocalCosts(current_pose_, transformed_plan, costmap_ros_->getRobotFootprint());
// 使用latchedStopRotateController_来检查是否到达了目标位置。如果到达了,则执行停止和旋转的逻辑。
if (latchedStopRotateController_.isPositionReached(&planner_util_, current_pose_)) {
//publish an empty plan because we've reached our goal position
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> local_plan;
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> transformed_plan;
publishGlobalPlan(transformed_plan);
publishLocalPlan(local_plan);
base_local_planner::LocalPlannerLimits limits = planner_util_.getCurrentLimits();
return latchedStopRotateController_.computeVelocityCommandsStopRotate(
cmd_vel,
limits.getAccLimits(),
dp_->getSimPeriod(),
&planner_util_,
odom_helper_,
current_pose_,
boost::bind(&DWAPlanner::checkTrajectory, dp_, _1, _2, _3));
} else {
// 计算DWA规划器的速度命令
bool isOk = dwaComputeVelocityCommands(current_pose_, cmd_vel);
if (isOk) {
publishGlobalPlan(transformed_plan);
} else {
ROS_WARN_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "DWA planner failed to produce path.");
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> empty_plan;
publishGlobalPlan(empty_plan);
}
return isOk;
}
}
主要的几个函数是:
1、
通过DWAPlannerROS::dwaComputeVelocityCommands计算施加在机器人上的控制速度,在该函数内部调用了dp_->findBestPath, 机器人控制命令通过drive_cmds拿到。
DWAPlannerROS::dwaComputeVelocityCommands
bool DWAPlannerROS::dwaComputeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::PoseStamped &global_pose, geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel) {
// dynamic window sampling approach to get useful velocity commands
if(! isInitialized()){
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized, please call initialize() before using this planner");
return false;
}
// 获取odom速度
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped robot_vel;
odom_helper_.getRobotVel(robot_vel);
/* For timing uncomment
struct timeval start, end;
double start_t, end_t, t_diff;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
*/
//compute what trajectory to drive along
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped drive_cmds;
drive_cmds.header.frame_id = costmap_ros_->getBaseFrameID();
// call with updated footprint
base_local_planner::Trajectory path = dp_->findBestPath(global_pose, robot_vel, drive_cmds);
//ROS_ERROR("Best: %.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f", path.xv_, path.yv_, path.thetav_, path.cost_);
//pass along drive commands
cmd_vel.linear.x = drive_cmds.pose.position.x;
cmd_vel.linear.y = drive_cmds.pose.position.y;
cmd_vel.angular.z = tf2::getYaw(drive_cmds.pose.orientation);
//if we cannot move... tell someone
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> local_plan;
if(path.cost_ < 0) {
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner",
"The dwa local planner failed to find a valid plan, cost functions discarded all candidates. This can mean there is an obstacle too close to the robot.");
local_plan.clear();
publishLocalPlan(local_plan);
return false;
}
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "A valid velocity command of (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f) was found for this cycle.",
cmd_vel.linear.x, cmd_vel.linear.y, cmd_vel.angular.z);
return true;
}
DWAPlanner::findBestPath
base_local_planner::Trajectory DWAPlanner::findBestPath(
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_vel,
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& drive_velocities) {
//make sure that our configuration doesn't change mid-run
boost::mutex::scoped_lock l(configuration_mutex_);
Eigen::Vector3f pos(global_pose.pose.position.x, global_pose.pose.position.y, tf2::getYaw(global_pose.pose.orientation));
Eigen::Vector3f vel(global_vel.pose.position.x, global_vel.pose.position.y, tf2::getYaw(global_vel.pose.orientation));
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped goal_pose = global_plan_.back();
Eigen::Vector3f goal(goal_pose.pose.position.x, goal_pose.pose.position.y, tf2::getYaw(goal_pose.pose.orientation));
base_local_planner::LocalPlannerLimits limits = planner_util_->getCurrentLimits();
// prepare cost functions and generators for this run
generator_.initialise(pos,
vel,
goal,
&limits,
vsamples_);
result_traj_.cost_ = -7;
// find best trajectory by sampling and scoring the samples
std::vector<base_local_planner::Trajectory> all_explored;
scored_sampling_planner_.findBestTrajectory(result_traj_, &all_explored);
// debrief stateful scoring functions
oscillation_costs_.updateOscillationFlags(pos, &result_traj_, planner_util_->getCurrentLimits().min_vel_trans);
//if we don't have a legal trajectory, we'll just command zero
if (result_traj_.cost_ < 0) {
drive_velocities.pose.position.x = 0;
drive_velocities.pose.position.y = 0;
drive_velocities.pose.position.z = 0;
drive_velocities.pose.orientation.w = 1;
drive_velocities.pose.orientation.x = 0;
drive_velocities.pose.orientation.y = 0;
drive_velocities.pose.orientation.z = 0;
} else {
drive_velocities.pose.position.x = result_traj_.xv_;
drive_velocities.pose.position.y = result_traj_.yv_;
drive_velocities.pose.position.z = 0;
tf2::Quaternion q;
q.setRPY(0, 0, result_traj_.thetav_);
tf2::convert(q, drive_velocities.pose.orientation);
}
return result_traj_;
}
generator_是轨迹生成器base_local_planner::SimpleTrajectoryGenerator,在DWAPlanner的构造函数中,可以看到,generator_被放置到了generator_list,然后传入了base_local_planner::SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner的构造函数构造出了scored_sampling_planner_。
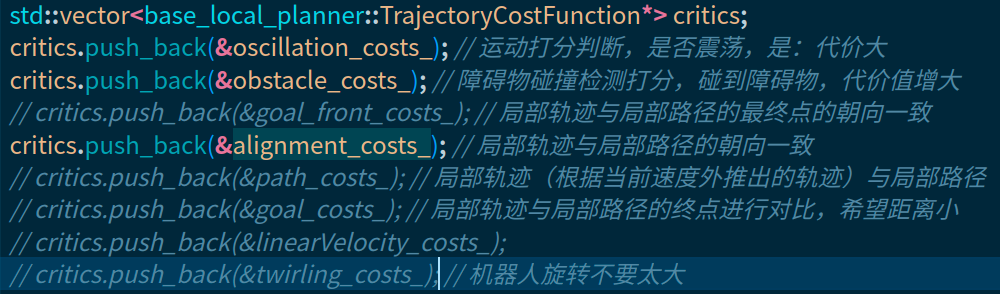
std::vector<base_local_planner::TrajectoryCostFunction*> critics;
critics.push_back(&oscillation_costs_); // discards oscillating motions (assisgns cost -1)
critics.push_back(&obstacle_costs_); // discards trajectories that move into obstacles
critics.push_back(&goal_front_costs_); // prefers trajectories that make the nose go towards (local) nose goal
critics.push_back(&alignment_costs_); // prefers trajectories that keep the robot nose on nose path
critics.push_back(&path_costs_); // prefers trajectories on global path
critics.push_back(&goal_costs_); // prefers trajectories that go towards (local) goal, based on wave propagation
critics.push_back(&twirling_costs_); // optionally prefer trajectories that don't spin
// trajectory generators
std::vector<base_local_planner::TrajectorySampleGenerator*> generator_list;
generator_list.push_back(&generator_);
scored_sampling_planner_ = base_local_planner::SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner(generator_list, critics);
因此,DWAPlanner::findBestPath中下面这部分代码,就是对scored_sampling_planner_中所使用的轨迹生成器进行初始化。
generator_.initialise(pos,
vel,
goal,
&limits,
vsamples_);
vsamples_表示采样的数量。
接着调用了SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::findBestTrajectory函数,dwa的最优轨迹通过参数traj返回,而参数all_explored则保存了DWA的所有搜索轨迹,下面来重点看这个函数。。
SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::findBestTrajectory
bool SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::findBestTrajectory(Trajectory& traj, std::vector<Trajectory>* all_explored) {
Trajectory loop_traj;
Trajectory best_traj;
double loop_traj_cost, best_traj_cost = -1;
bool gen_success;
int count, count_valid;
// 检查所有的TrajectoryCostFunction是否准备好
for (std::vector<TrajectoryCostFunction*>::iterator loop_critic = critics_.begin(); loop_critic != critics_.end(); ++loop_critic) {
TrajectoryCostFunction* loop_critic_p = *loop_critic;
if (loop_critic_p->prepare() == false) {
ROS_WARN("A scoring function failed to prepare");
return false;
}
}
for (std::vector<TrajectorySampleGenerator*>::iterator loop_gen = gen_list_.begin(); loop_gen != gen_list_.end(); ++loop_gen) {
count = 0;
count_valid = 0;
TrajectorySampleGenerator* gen_ = *loop_gen;
// 遍历轨迹生成器生成的全部轨迹
while (gen_->hasMoreTrajectories()) {
gen_success = gen_->nextTrajectory(loop_traj);
if (gen_success == false) {
// TODO use this for debugging
continue;
}
// 对该轨迹进行打分
loop_traj_cost = scoreTrajectory(loop_traj, best_traj_cost);
if (all_explored != NULL) {
loop_traj.cost_ = loop_traj_cost;
all_explored->push_back(loop_traj);
}
if (loop_traj_cost >= 0) {
count_valid++;
if (best_traj_cost < 0 || loop_traj_cost < best_traj_cost) {
best_traj_cost = loop_traj_cost; // 更新最佳得分
best_traj = loop_traj; // 更新最佳轨迹
}
}
count++;
if (max_samples_ > 0 && count >= max_samples_) {
break;
}
}
// 最佳轨迹的得分是合法的,说明找到了最佳轨迹 ,将最佳轨迹信息交给traj
if (best_traj_cost >= 0) {
traj.xv_ = best_traj.xv_;
traj.yv_ = best_traj.yv_;
traj.thetav_ = best_traj.thetav_;
traj.cost_ = best_traj_cost;
traj.resetPoints();
double px, py, pth;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < best_traj.getPointsSize(); i++) {
best_traj.getPoint(i, px, py, pth);
traj.addPoint(px, py, pth);
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("Evaluated %d trajectories, found %d valid", count, count_valid);
if (best_traj_cost >= 0) {
// do not try fallback generators
break;
}
}
return best_traj_cost >= 0;
}
调参技巧
DWA被目标点过度吸引,且不听全局规划器指挥
如下图:
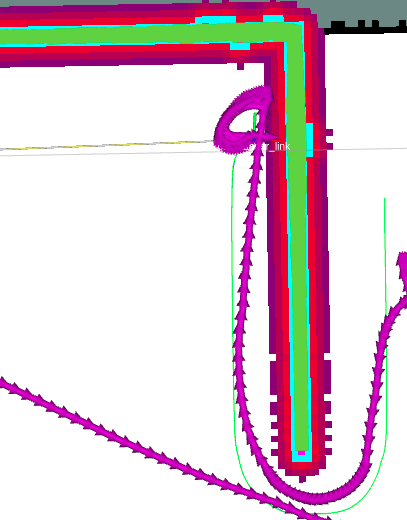
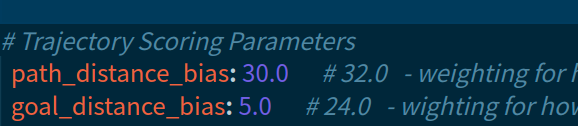
这是由于目标吸引的权重过大导致的,应该提高轨迹对齐的权重降低目标吸引的权重,如下,将goal_distance_bias的权重由24下降到5,机器人就能按照全局轨迹走而不是被目标吸引的卡住不动。
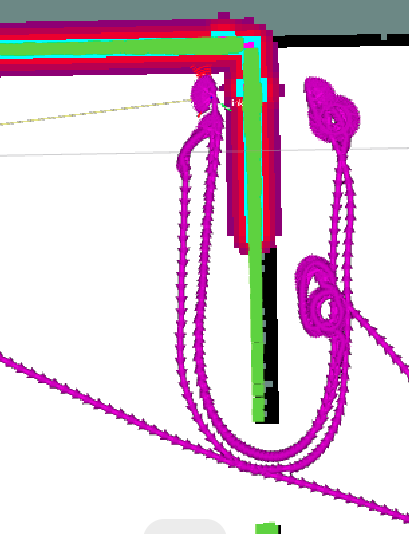
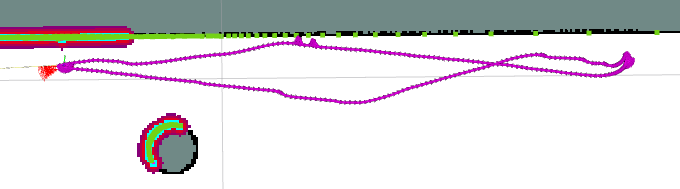
消融实验
goal_front_costs_

轨迹歪歪扭扭的,还喜欢拼命往墙上靠,感觉这个cost就是瞎搞的,还不如不要。。
alignment_costs_
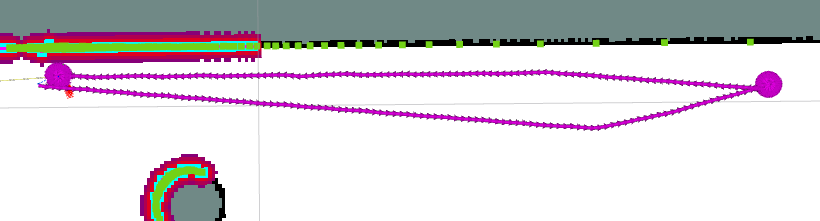
轨迹平滑了很多,也不会往墙上靠,但是,变得很慢,而且到目的地后原地转圈。。
path_costs_

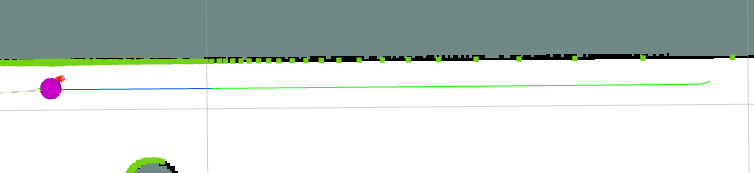
不按全局规划的路径走,原地转圈,怀疑原地转圈是属于恢复行为,但是速度为0,应该是由于该cost计算的是当前位姿和规划路径的偏移,而速度为0时偏移最小。
goal_costs_


按照对这个cost的理解,应该是始终的往离目的地最近的地方开,但是实际轨迹却歪歪扭扭,原地转圈,撞墙。
评价
ros dwa_local_planner包原生的这几个cost的实现各有各的问题,不是很好的实现,最好的解决办法就是直接抛弃重写。。。