字节流:
应用场景:操作二进制数据(音频、视频、图片)
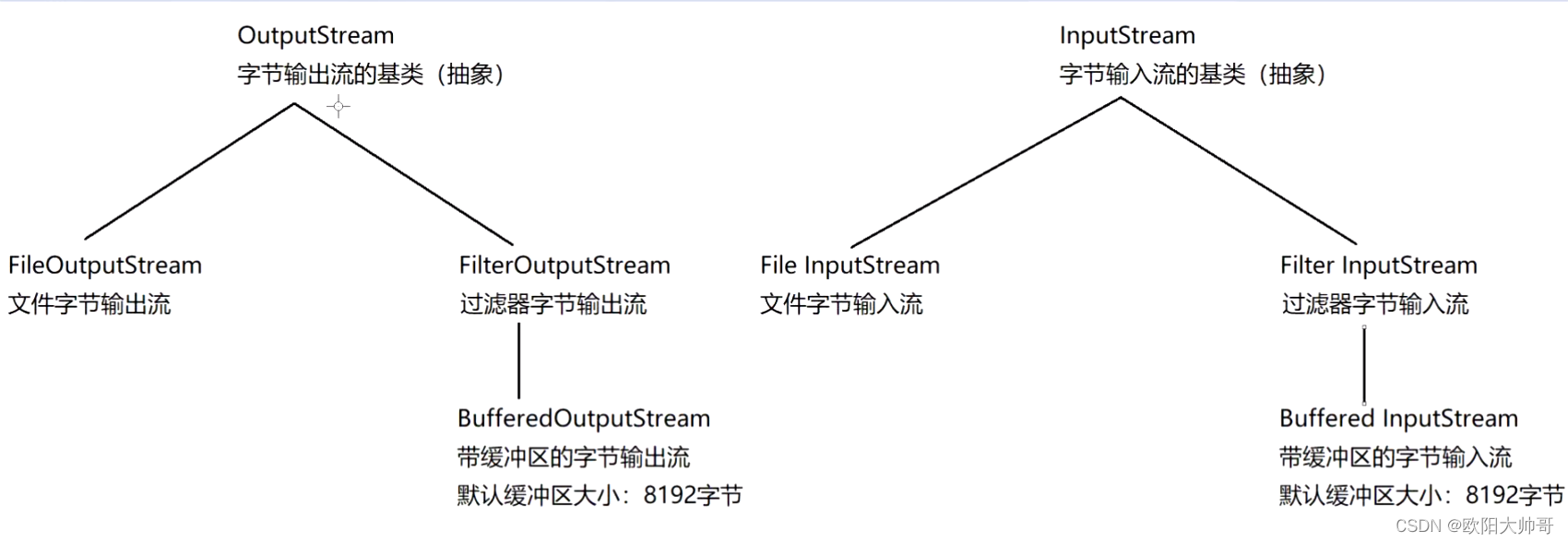
abstract class InputStream – 字节输入流的基类(抽象类)
abstract class OutputStream – 字节输出流的基类(抽象类)
class FileInputStream extends InputStream – 文件字节输入流
class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream – 文件字节输出流
class FilterInputStream extends InputStream – 过滤器字节输入流
class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream – 过滤器字节输出流
class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream – 带缓冲区的字节输入流
class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream – 带缓冲区的字节输出流
默认缓冲区大小:8192字节----> new byte[8192]
操作:
文件字节输入输出流 :
写入数据:
利用 文件字节输出流 向文件 写入 数据。
1. 不处理异常 2. 当文件存在时
3. 当文件不存在时
经验:所有的输出流,当文件不存在时都会创建该文件。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("io.txt");
//2.写入数据
//fos.write(97);//写入UniCode码
//fos.write("123abc".getBytes());//字符串转为byte数组,并写入文件中
fos.write("123abc".getBytes(), 2, 3);//写入byte数组、偏移量、写入长度
//3.关闭资源
fos.close();
}
利用 文件字节输出流 向文件 写入 数据。
1. 不处理异常 2. 当文件存在时
3. 当文件不存在时
4. 在文件末尾追加内容
经验:在文件末尾追加考虑基础流的构造方法。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象 + 设置在文件末尾追加
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("io.txt",true);
//2.写入数据
fos.write("123abc".getBytes());//写入byte数组
//3.关闭资源
fos.close();
}
利用 文件字节输出流 向文件 写入 数据。
1. 不处理异常 2. 当文件存在时
3. 当文件不存在时
4. 在文件末尾追加内容
5. 处理异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1.创建流对象 + 设置在文件末尾追加
fos = new FileOutputStream("io.txt",true);
//2.写入数据
fos.write("123abc".getBytes());//写入byte数组
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.关闭资源
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
读取数据:
利用 文件字节输入流 读取文件里的数据。
1. 不处理异常 2. 文件存在
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("io.txt");
//2.读取数据
//read():一个字节一个字节的读取数据,读取到文件末尾返回-1
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
//3.关闭资源
fis.close();
}
改进:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("io.txt");
//2.读取数据
//read():一个字节一个字节的读取数据,读取到文件末尾返回-1
int read;
while((read = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)read);
}
//3.关闭资源
fis.close();
}
再改进:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//1.创建流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("io.txt");
//2.读取数据
//read(bs):读取bs长度的数据,并把数据放入数组,返回读取到的有效字节数,如果读取到文件末尾则返回-1
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, len));
}
//3.关闭资源
fis.close();
}
利用 文件字节输入流 读取文件里的数据。
1. 不处理异常
2. 文件存在
3. 文件不存在
4. 处理异常
public static void main(String[] args){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.创建流对象
fis = new FileInputStream("io.txt");
//2.读取数据
//read(bs):读取bs长度的数据,并把数据放入数组,返回读取到的有效字节数,如果读取到文件末尾则返回-1
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.关闭资源
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
文件拷贝:
读取源文件,写入目标文件。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Original.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.mp4");
//一个一个字节的拷贝,速度太慢
int read;
while((read = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(read);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
改进:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Original.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.mp4");
//read(bs):读取bs长度的数据,并把数据放入数组,
//返回读取到的有效字节数,如果读取到文件末尾则返回-1
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
fos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
异常处理:
public static void main(String[] args){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("Original.mp4");
fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.mp4");
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
fos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
改进:
public static void main(String[] args){
//注意:小括号里创建的流会在try...catch后自动关闭
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Original.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.mp4");) {
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
fos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
带缓冲区的字节输入输出流:
拷贝文件:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Original.mp4"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.mp4"));
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1){
bos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
写入数据:
利用 带缓冲区的字节输出流 向文件写入数据
1. 不处理异常的方式 2. 文件存在的情况
3. 文件不存在的情况
经验:所有的输出流,文件不存在的情况都会创建文件。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt"));
//2.写入数据
bos.write("123abc".getBytes());
//3.关闭资源
bos.close();
}
利用 带缓冲区的字节输出流 向文件写入数据
不处理异常的方式
文件存在的情况
文件不存在的情况
在文件末尾追加内容
经验:在文件末尾追加考虑基础流的构造方法。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt",true));
//2.写入数据
bos.write("123abc".getBytes());
//3.关闭资源
bos.close();
}
利用 带缓冲区的字节输出流 向文件写入数据
不处理异常的方式
文件存在的情况
文件不存在的情况
在文件末尾追加内容
处理异常
public static void main(String[] args){
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.创建流对象
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt",true));
//2.写入数据
bos.write("123abc".getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.关闭资源
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
读取数据:
利用 带有缓冲区的字节输入流 读取文件里的数据。
不处理异常
文件存在
文件不存在
经验:所有输入流,当文件不存在都会报错
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建流对象 (默认缓冲区大小:8192字节)
//BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("io.txt"));
//1.创建流对象 (自定义缓冲区大小:2048字节)
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("io.txt"),2048);
//2.读取数据
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, len));
}
//3.关闭资源
bis.close();
}
利用 带有缓冲区的字节输入流 读取文件里的数据。
- 不处理异常
- 文件存在
- 文件不存在
- 异常处理
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
try {
//1.创建流对象 (默认缓冲区大小:8192字节)
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("io.txt"));
//2.读取数据
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.关闭资源
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
深入 带缓冲区的字节输出流 :
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("io.txt");
// //写几次,就和硬盘交互几次 -- 6次(内存与硬盘交互的次数)
// fos.write("1".getBytes());
// fos.write("2".getBytes());
// fos.write("3".getBytes());
// fos.write("a".getBytes());
// fos.write("b".getBytes());
// fos.write("c".getBytes());
// fos.close();
// BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt"));
// //将数据写入到字节缓冲数组中 -- 1次(内存与硬盘交互的次数)
// bos.write("1".getBytes());
// bos.write("2".getBytes());
// bos.write("3".getBytes());
// bos.write("a".getBytes());
// bos.write("b".getBytes());
// bos.write("c".getBytes());
// //关闭时才将数据写入到文件中
// bos.close();
//默认缓冲区 -- 8192个字节(8*1024)
//BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt"));
//自定义缓冲区大小 -- 2048个字节
// BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io.txt"), 2048);
}
底层源码:
//继承关系
public class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream {
protected OutputStream out;//0x001
//out - 0x001
public FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this.out = out;
}
//b - [65]
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException {
this.write(b, 0, b.length);
}
@SuppressWarnings("try")
public void close() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream ostream = out) {
flush();
}
}
}
//源码
public class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream {
//缓冲区数组
protected byte[] buf;//new byte[8192]
//缓冲区存放数据的个数
protected int count;//1
//out - 0x001
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}
//out - 0x001
//size - 8192
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {
super(out);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
//b - [65]
//off - 0
//len - 1
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
//判断现在需要写出的数据长度是否大于缓冲区数组
if (len >= buf.length) {//1 >= 8192
//将缓冲区数组里的数据写入到文件,将缓冲区清空
flushBuffer();
//将线程需要写出的数据写入到文件
out.write(b, off, len);
return;
}
//判断现在需要写出的数据长度 超过了缓冲区剩余的存储长度
if (len > buf.length - count) {//1 > 8192-0
//将缓冲区数组里的数据写入到文件,将缓冲区清空
flushBuffer();
}
//将数据写入到缓冲区数组里
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
//更新缓冲区数组数据个数
count += len;
}
private void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
//count > 0说明缓冲区数组里有数据
if (count > 0) {
super.out.write(buf, 0, count);//调用的是FileOutputSteam的write()
count = 0;//缓冲区清空
}
}
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {
//将缓冲区数组里的数据写入到文件,将缓冲区清空
flushBuffer();
super.out.flush();//调用的是FileOutputSteam的close() -- 关流
}
}
//应用场景
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("io.txt");//0x001
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
bos.write("1".getBytes());
bos.write("2".getBytes());
bos.write("3".getBytes());
bos.write("a".getBytes());
bos.write("b".getBytes());
bos.write("c".getBytes());
bos.close();