目录
本文也录制了详细的视频讲解:
[IT超016] 大模型:源码分析Qwen2.5VL视频抽帧模块(附加FFmpeg性能对比测试)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
qwen 视频理解能力
Qwen2.5-VL 是由阿里云 Qwen 团队开发的多模态大型语言模型系列,仓库地址:https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen2.5-VL
messages 构建 demo
# 方式一:输入视频文件(这种才会走抽帧逻辑)
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "video",
"video": "file:///path/to/video1.mp4",
"max_pixels": 360 * 420,
"fps": 1.0,
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this video."},
],
}
]
# 方式二:直接输入多图
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "video",
"video": [
"file:///path/to/frame1.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame2.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame3.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame4.jpg",
],
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this video."},
],
}
]qwen 抽帧代码分析
视频 message 处理的核心代码:https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen2.5-VL/blob/main/qwen-vl-utils/src/qwen_vl_utils/vision_process.py
视频解析抽帧能力依赖——decord 库:https://github.com/dmlc/decord?tab=readme-ov-file#install-from-source
Decord 是一个专门为视频数据处理和深度学习设计的轻量级、高性能的视频解码库,擅长处理帧的随机访问模式,避免了像 FFmpeg 那样从头开始逐帧解码——Qwen 抽帧模块用的这个库
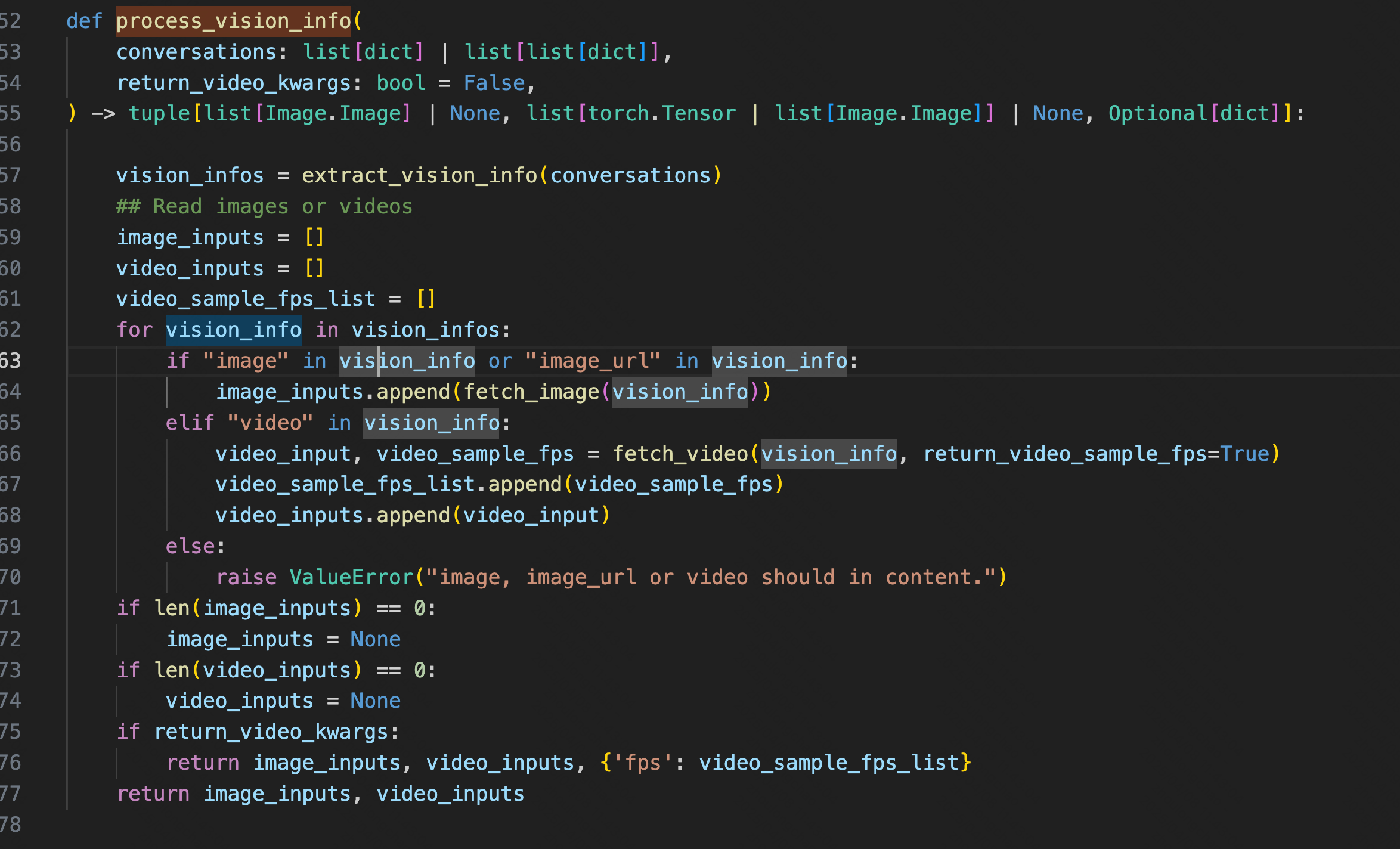
1、vision_process.py # process_vision_info:处理 messages 中的 图像 / 视频 输入
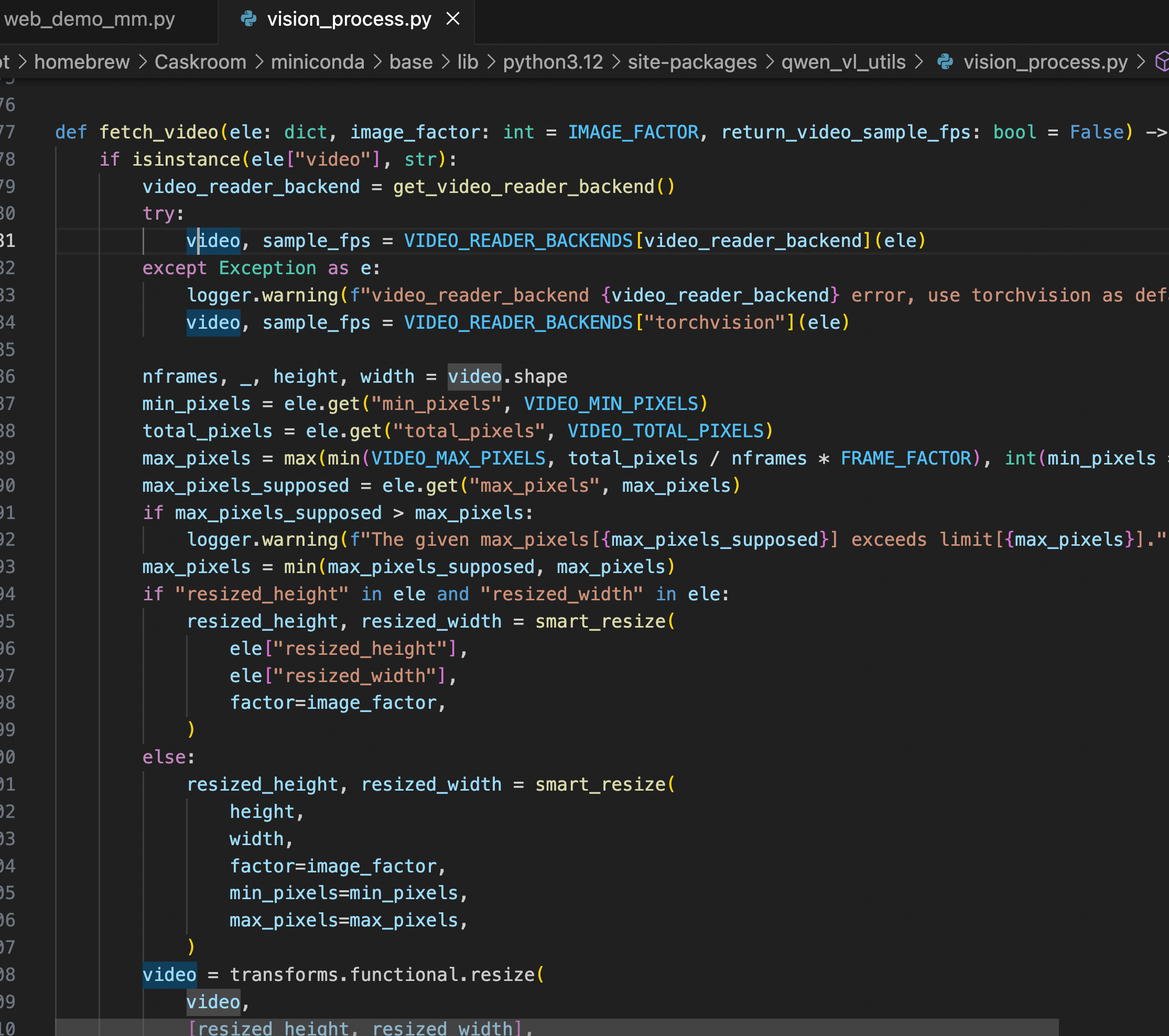
2、vision_process.py # fetch_video:处理 messages 中的 视频 输入
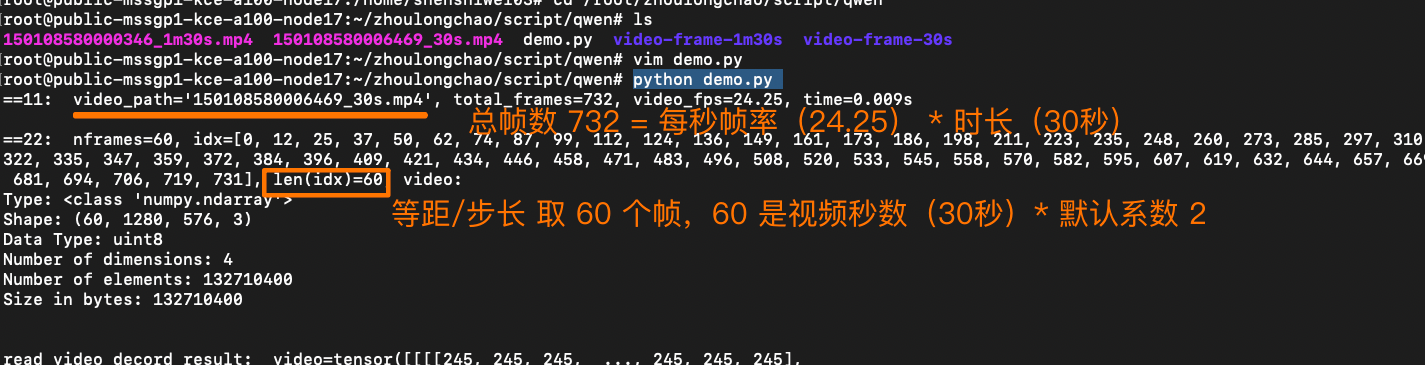
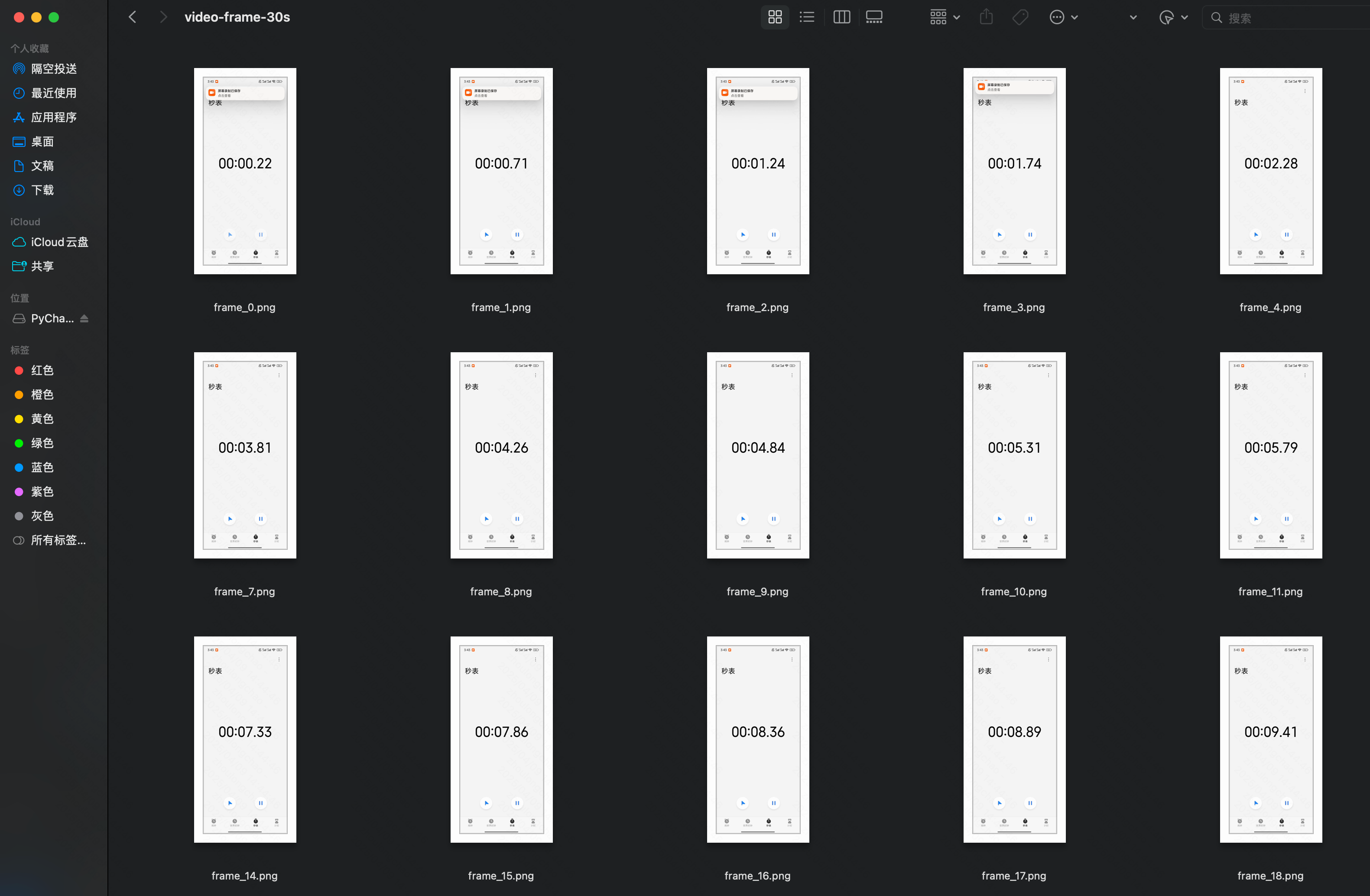
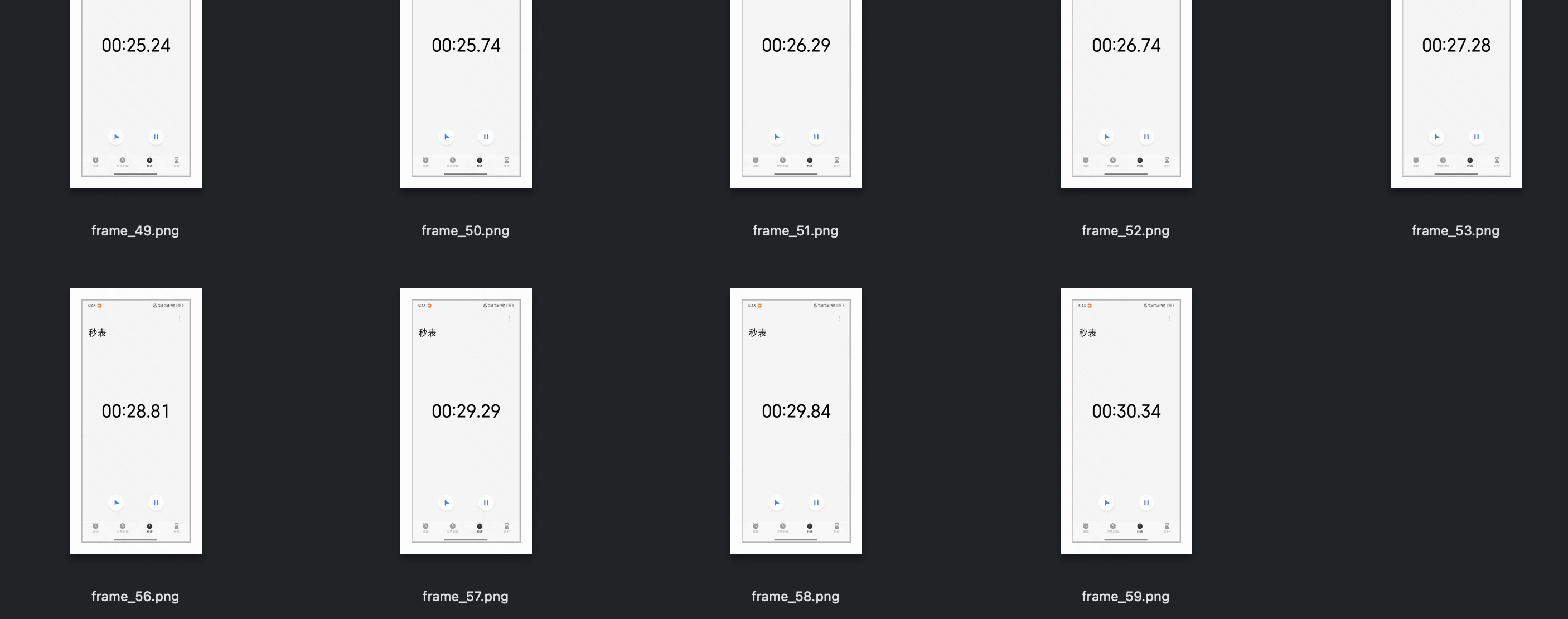
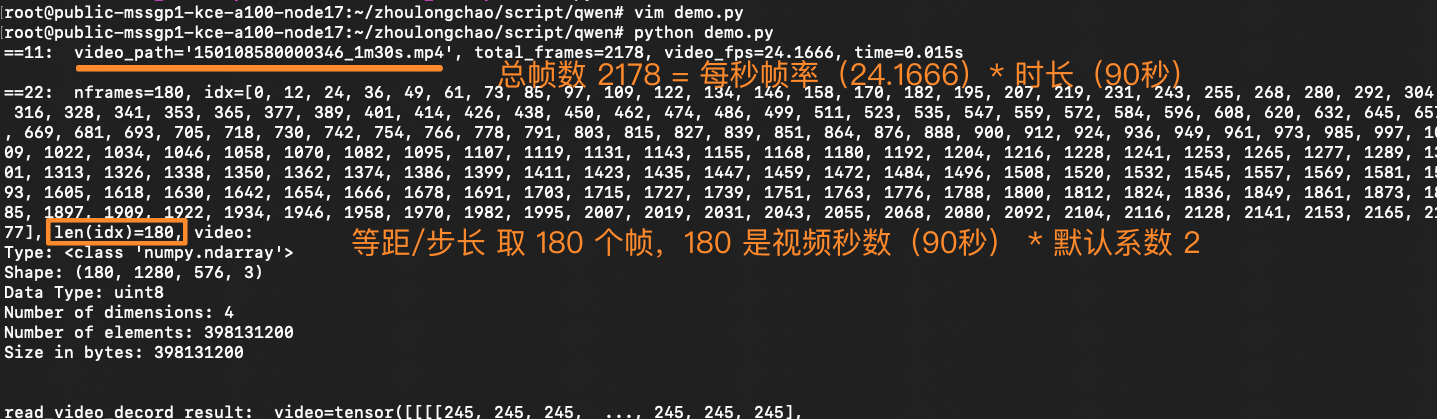
🚩 核心抽帧逻辑(简单来说:0.5 秒抽一张)(30 秒视频,最终抽帧是 60 张)
根据 FPS 常数(默认 2)、视频总帧数(秒时长 * 原始 fps)计算抽帧数量 nframes,之后等距离/步长抽取 nframes 张帧图
- 可解析总帧数 = 秒时长 * 原始 fps ———— 例如 30s 视频,24 fps,值为 720
- 抽帧数 = FPS 常数(默认 2)* 秒时长 ————例如 30s 视频,值为 60张
- 抽帧步长:默认 0.5 秒————(等距步长平均分割,和 FPS 常数有关)
验证两个实际 case
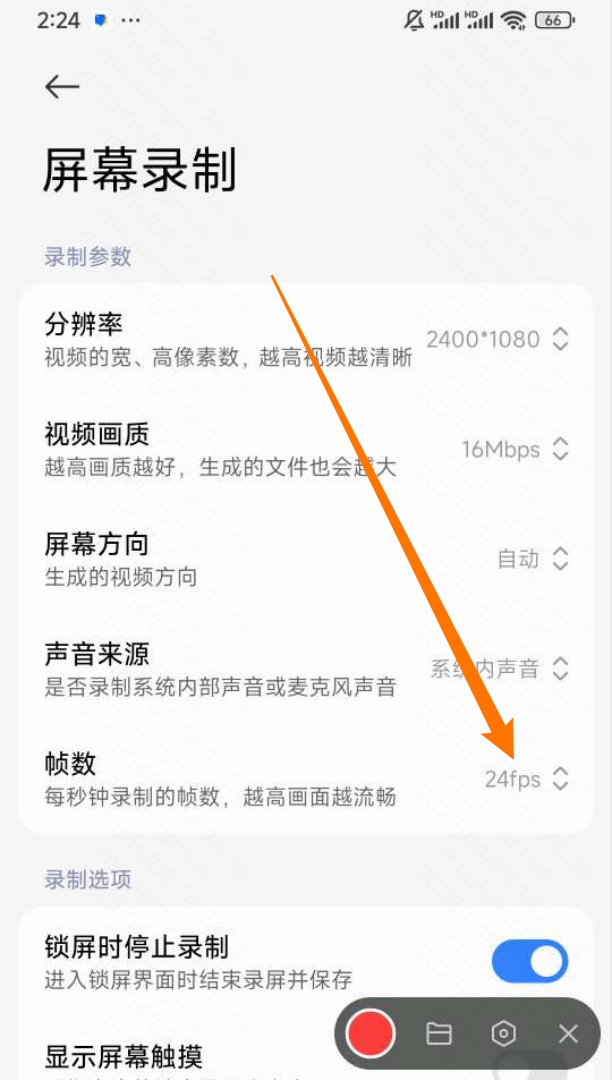
录屏设置:24 fps
方案 |
30秒 的视频 |
1分30秒 的视频 |
qwen 抽帧 |
加入日志
...
|
加入日志
...
|
摘出 qwen 2.5-vl 抽帧模块代码(增加自定义日志)
import torch
import time
import math
from typing import Tuple
from torchvision.utils import save_image
IMAGE_FACTOR = 28
MIN_PIXELS = 4 * 28 * 28
MAX_PIXELS = 16384 * 28 * 28
MAX_RATIO = 200
VIDEO_MIN_PIXELS = 128 * 28 * 28
VIDEO_MAX_PIXELS = 768 * 28 * 28
FRAME_FACTOR = 2
FPS = 2.0
FPS_MIN_FRAMES = 4
FPS_MAX_FRAMES = 768
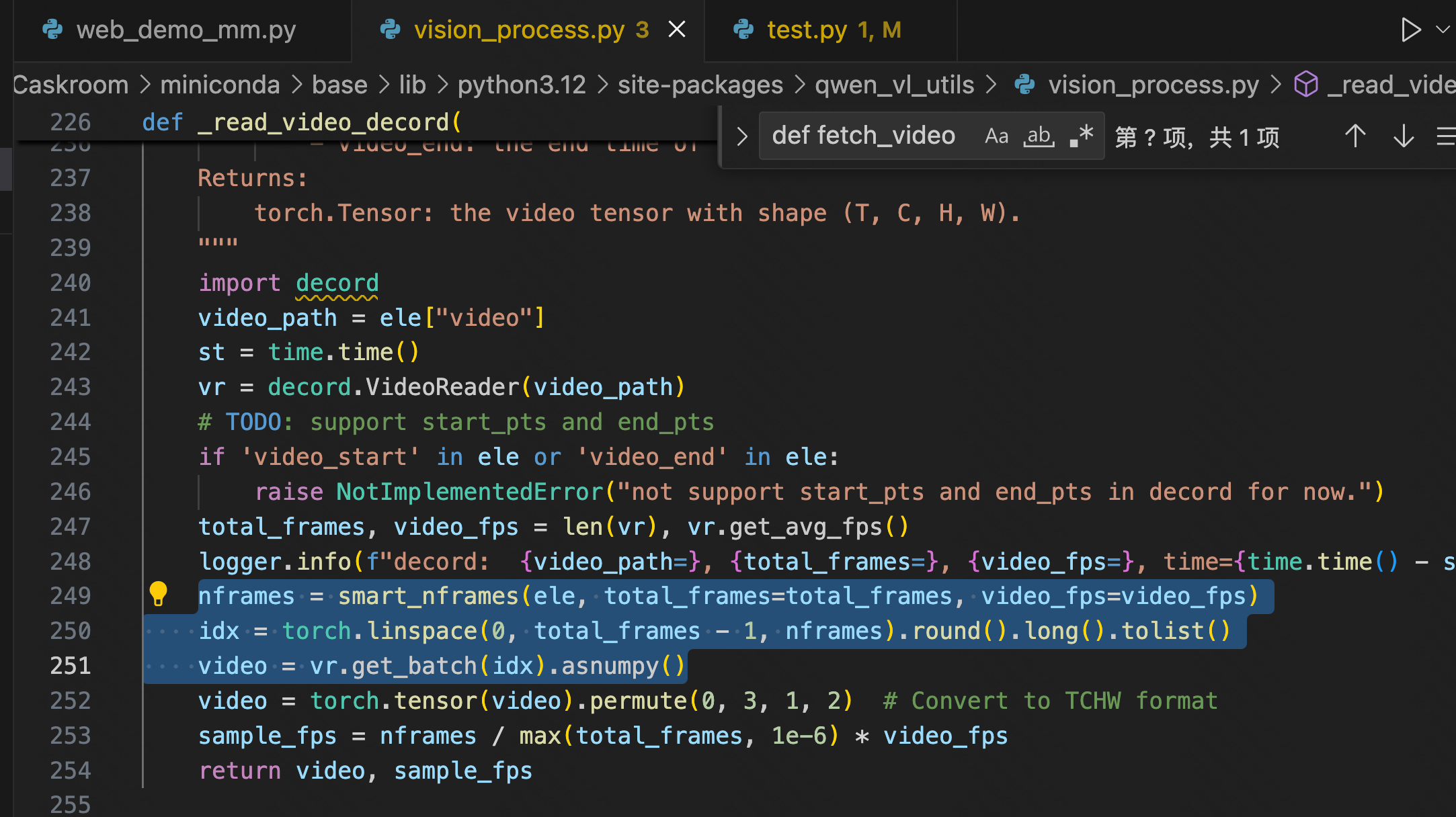
def _read_video_decord(
ele: dict,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, float]:
"""read video using decord.VideoReader
Args:
ele (dict): a dict contains the configuration of video.
support keys:
- video: the path of video. support "file://", "http://", "https://" and local path.
- video_start: the start time of video.
- video_end: the end time of video.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: the video tensor with shape (T, C, H, W).
"""
import decord
video_path = ele["video"]
st = time.time()
vr = decord.VideoReader(video_path)
# TODO: support start_pts and end_pts
if 'video_start' in ele or 'video_end' in ele:
raise NotImplementedError("not support start_pts and end_pts in decord for now.")
total_frames, video_fps = len(vr), vr.get_avg_fps()
print(f"==11: {video_path=}, {total_frames=}, {video_fps=}, time={time.time() - st:.3f}s\n")
nframes = smart_nframes(ele, total_frames=total_frames, video_fps=video_fps)
idx = torch.linspace(0, total_frames - 1, nframes).round().long().tolist()
video = vr.get_batch(idx).asnumpy()
print(f"==22: {nframes=}, {idx=}, {len(idx)=}, video: ")
print("Type:", type(video))
print("Shape:", video.shape)
print("Data Type:", video.dtype)
print("Number of dimensions:", video.ndim)
print("Number of elements:", video.size)
print("Size in bytes:", video.nbytes)
print('\n')
video = torch.tensor(video).permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # Convert to TCHW format
sample_fps = nframes / max(total_frames, 1e-6) * video_fps
return video, sample_fps
def smart_nframes(
ele: dict,
total_frames: int,
video_fps: float,
) -> int:
"""calculate the number of frames for video used for model inputs.
Args:
ele (dict): a dict contains the configuration of video.
support either `fps` or `nframes`:
- nframes: the number of frames to extract for model inputs.
- fps: the fps to extract frames for model inputs.
- min_frames: the minimum number of frames of the video, only used when fps is provided.
- max_frames: the maximum number of frames of the video, only used when fps is provided.
total_frames (int): the original total number of frames of the video.
video_fps (int | float): the original fps of the video.
Raises:
ValueError: nframes should in interval [FRAME_FACTOR, total_frames].
Returns:
int: the number of frames for video used for model inputs.
"""
assert not ("fps" in ele and "nframes" in ele), "Only accept either `fps` or `nframes`"
if "nframes" in ele:
nframes = round_by_factor(ele["nframes"], FRAME_FACTOR)
else:
fps = ele.get("fps", FPS)
min_frames = ceil_by_factor(ele.get("min_frames", FPS_MIN_FRAMES), FRAME_FACTOR)
max_frames = floor_by_factor(ele.get("max_frames", min(FPS_MAX_FRAMES, total_frames)), FRAME_FACTOR)
nframes = total_frames / video_fps * fps
if nframes > total_frames:
print(f"smart_nframes: nframes[{nframes}] > total_frames[{total_frames}]")
nframes = min(min(max(nframes, min_frames), max_frames), total_frames)
nframes = floor_by_factor(nframes, FRAME_FACTOR)
if not (FRAME_FACTOR <= nframes and nframes <= total_frames):
raise ValueError(f"nframes should in interval [{FRAME_FACTOR}, {total_frames}], but got {nframes}.")
return nframes
def round_by_factor(number: int, factor: int) -> int:
"""Returns the closest integer to 'number' that is divisible by 'factor'."""
return round(number / factor) * factor
def ceil_by_factor(number: int, factor: int) -> int:
"""Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to 'number' that is divisible by 'factor'."""
return math.ceil(number / factor) * factor
def floor_by_factor(number: int, factor: int) -> int:
"""Returns the largest integer less than or equal to 'number' that is divisible by 'factor'."""
return math.floor(number / factor) * factor
video, sample_fps = _read_video_decord(ele={"video": "150108580006469_30s.mp4"})
print(f"read_video_decord result: {video=}, {sample_fps=}\n")
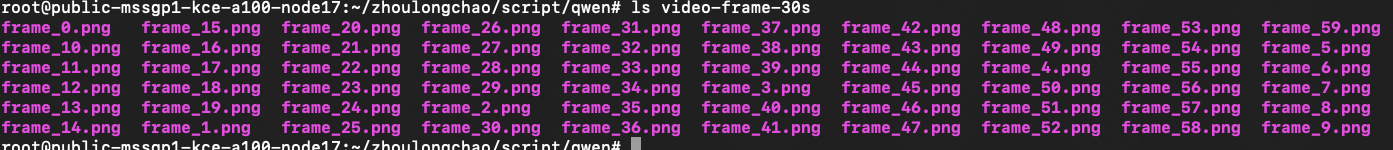
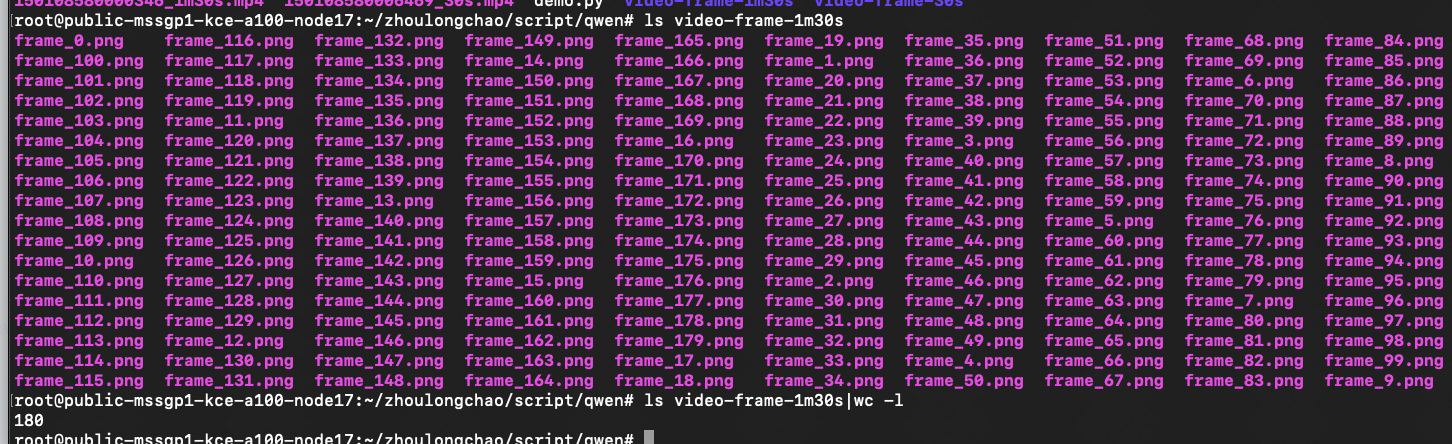
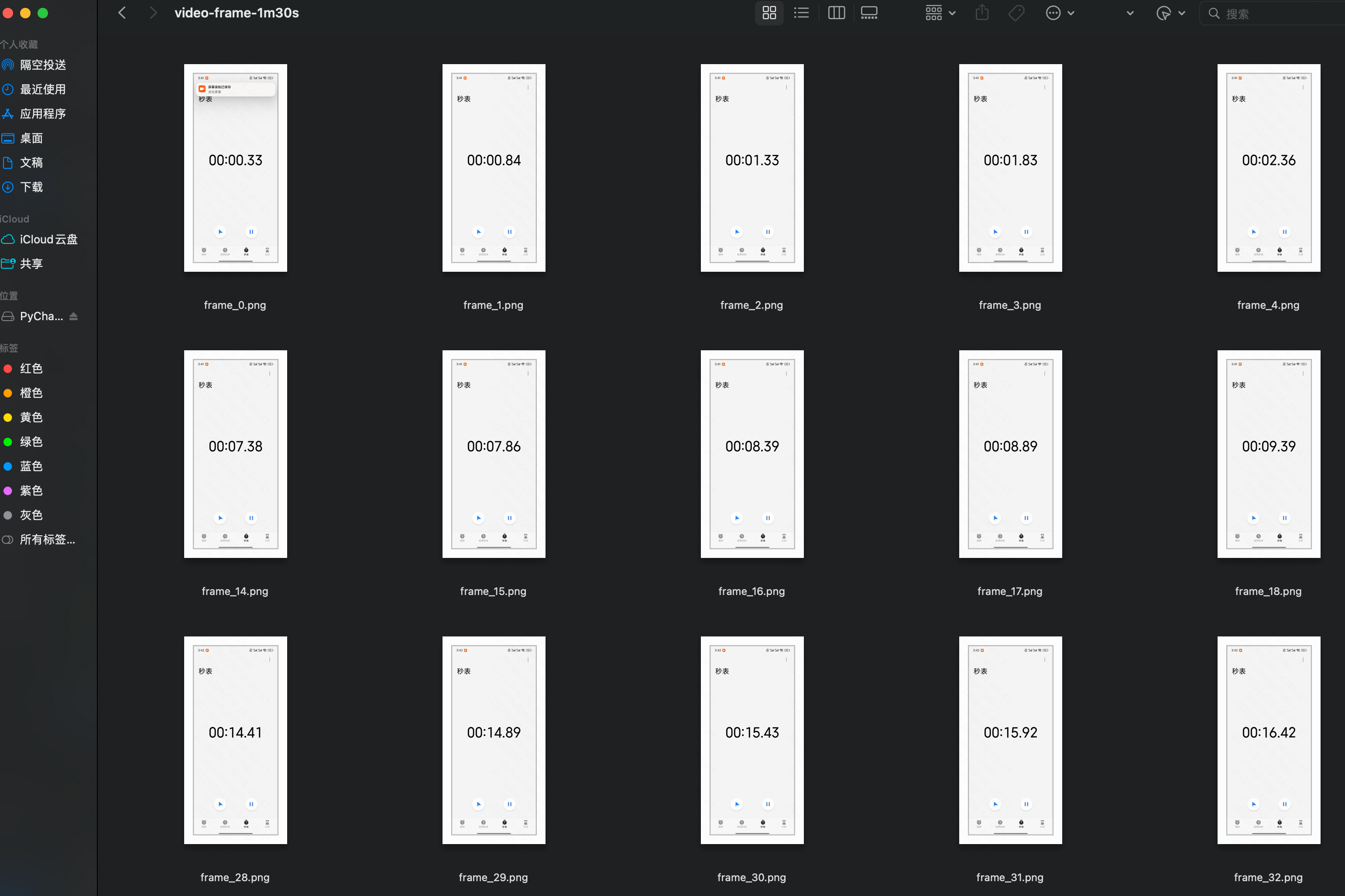
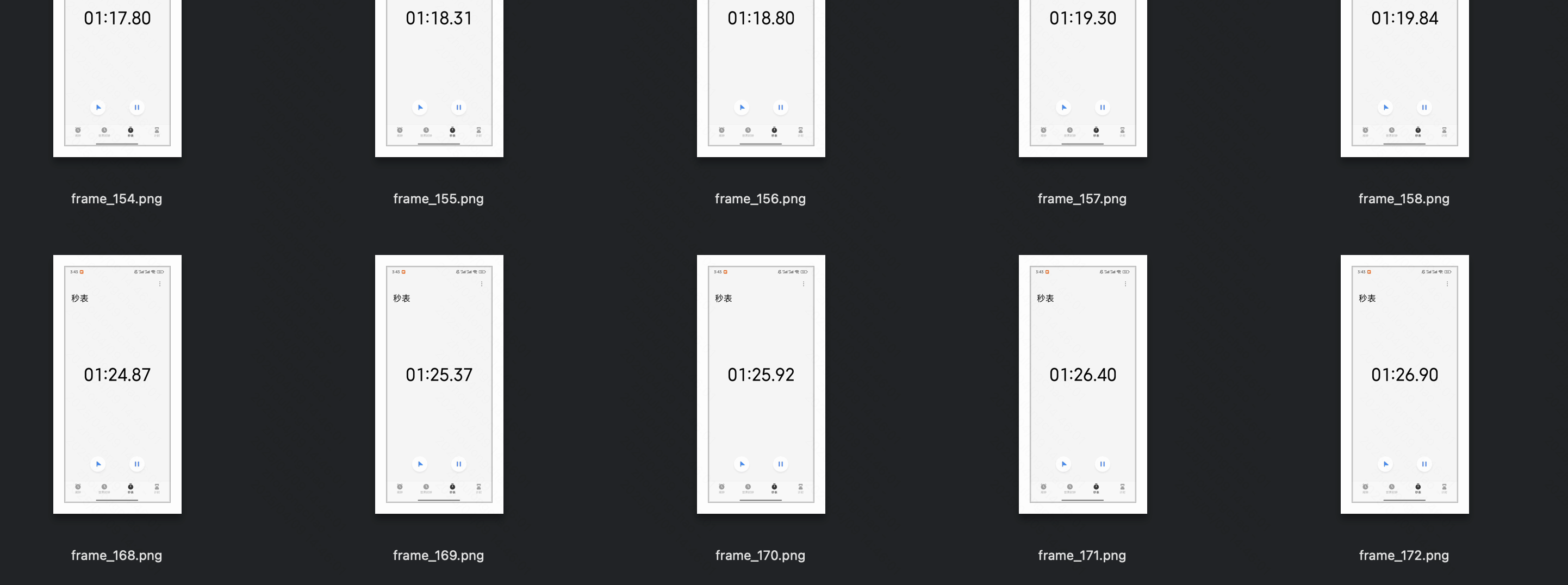
# 将视频帧保存为本地图片
for i, frame in enumerate(video):
# 将像素值缩放到 [0, 1] 范围
frame = frame.float() / 255.0
save_image(frame, f'./video-frame-30s/frame_{i}.png')
# save_image(frame, f'./video-frame-1m30s/frame_{i}.png')
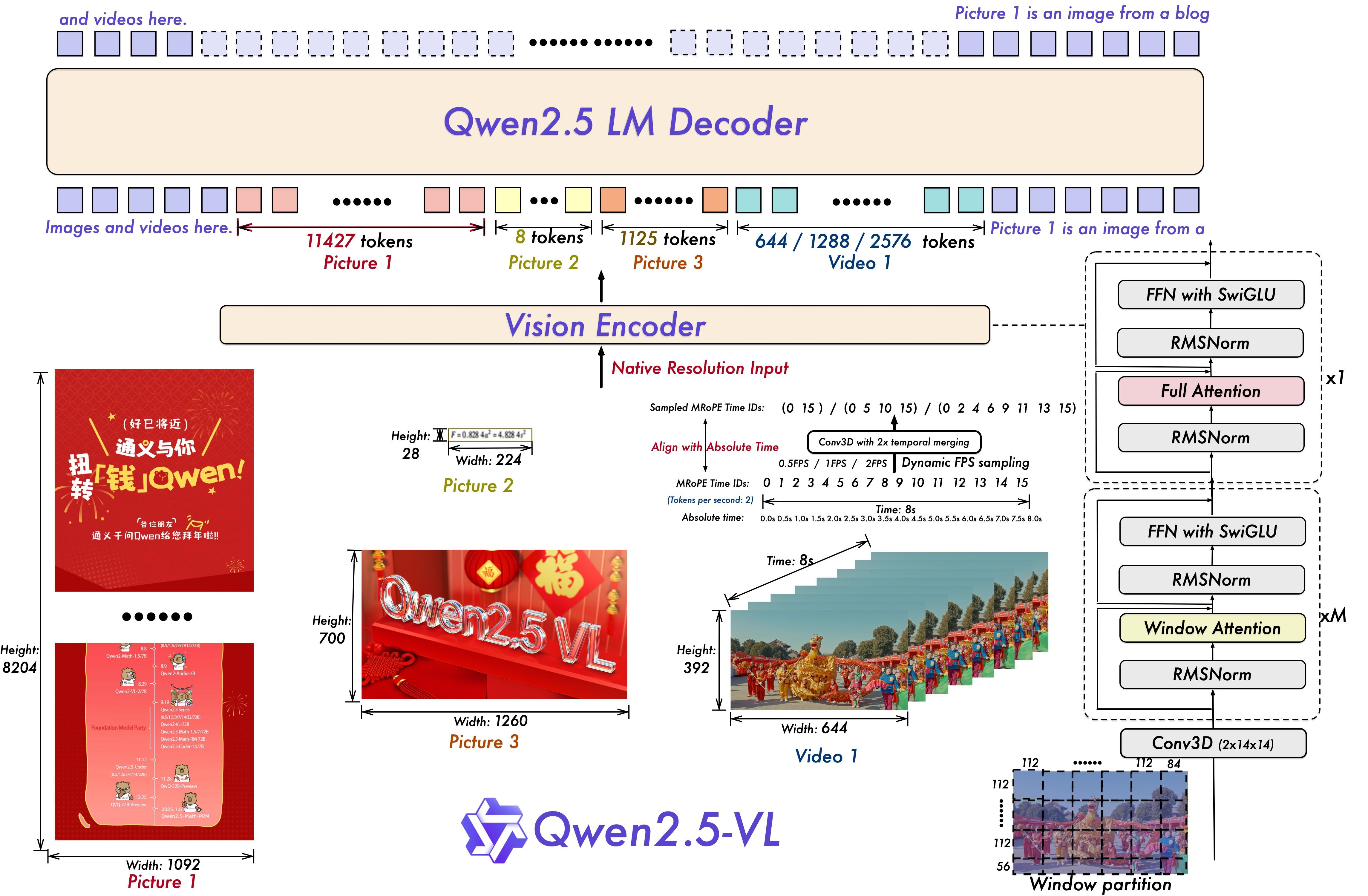
print(f"Frame {i} saved as frame_{i}.png")官网介绍图
性能对比:ffmpeg 抽帧、decord 库抽帧
介绍
ffmpeg 是一个强大且广泛使用的开源多媒体框架,它由多个库和工具组成,例如libavformat(处理音视频封装格式)、libavcodec(进行音视频编解码)、libavutil(提供通用的工具函数)等。在抽帧时,FFmpeg 会利用这些库协同工作。
Decord 是一个专门为视频数据处理和深度学习设计的轻量级、高性能的视频解码库,擅长处理帧的随机访问模式,避免了像 FFmpeg 那样从头开始逐帧解码
联系
decord 依赖 ffmpeg 的核心库
对比
- 速度:ffmpeg 更优,比 decord 快 16%
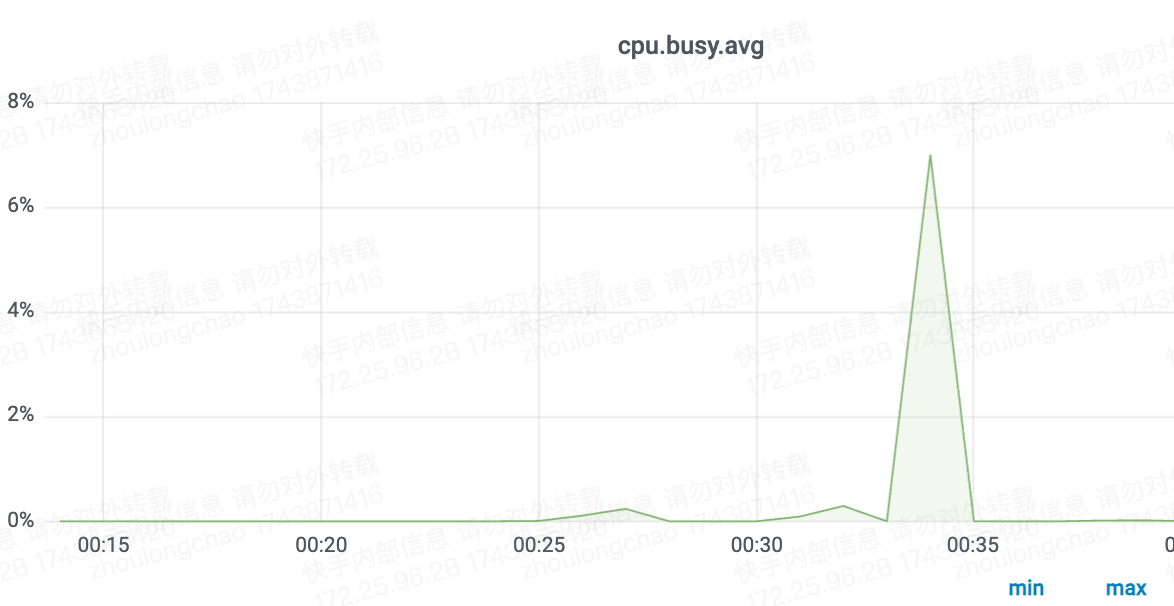
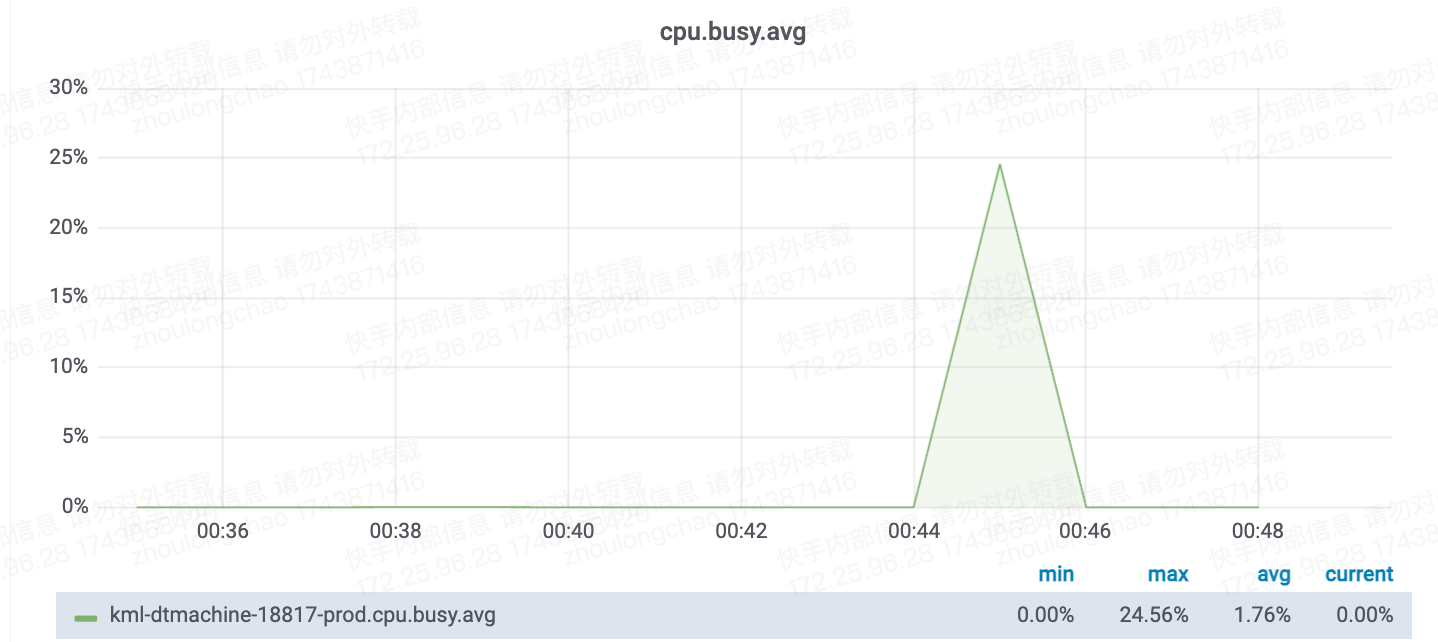
- 资源消耗:ffmpeg 更优,比 decord 节省资源 25%(只测了下 cpu 抽帧)
- 官方维护:
-
- ffmpeg 一直在更新,社区也更活跃,48.9k star
- decord 库已经 3 年未更新,2.1k star
测试结果
测试指标:
- 100 batch 视频文件测试
- 开发机:train-A100-6 配置为 94核 - 860GiB - 4卡A100
|
抽帧方案 |
测试样本(37秒视频) video_150108527915923_37s.mp4 |
测试样本(1分21秒视频)video_150108525914511_1m21s.mp4 |
现状 |
ffmpeg - cpu |
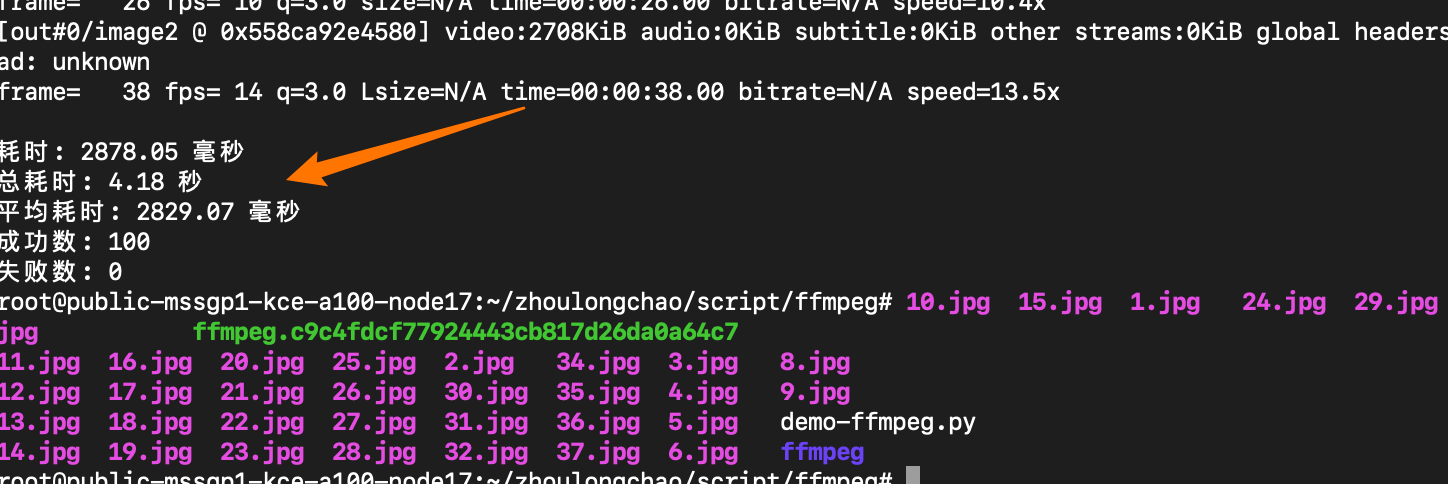
总耗时: 4.18 秒 平均耗时: 2829.07 毫秒 成功数: 100 失败数: 0
抽出 37 张 + 写入磁盘
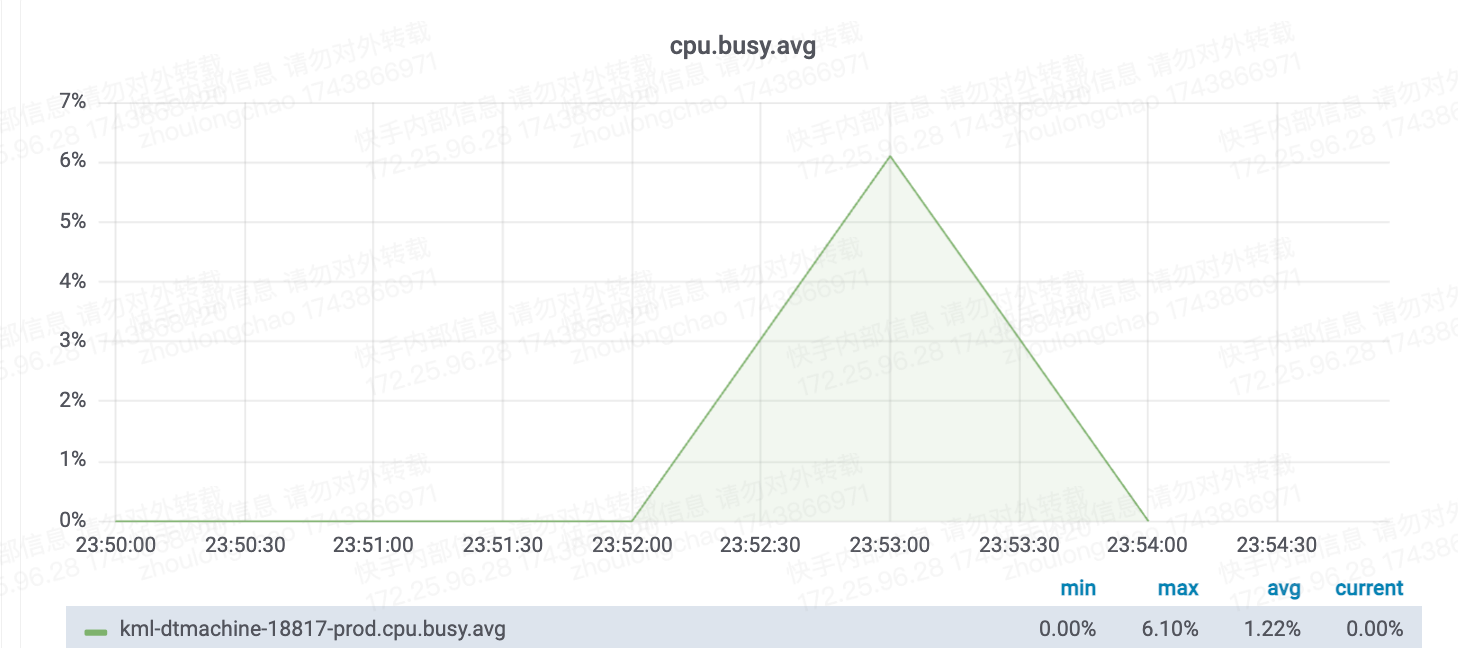
CPU核数换算——需 7 核(94*6%*120%)
|
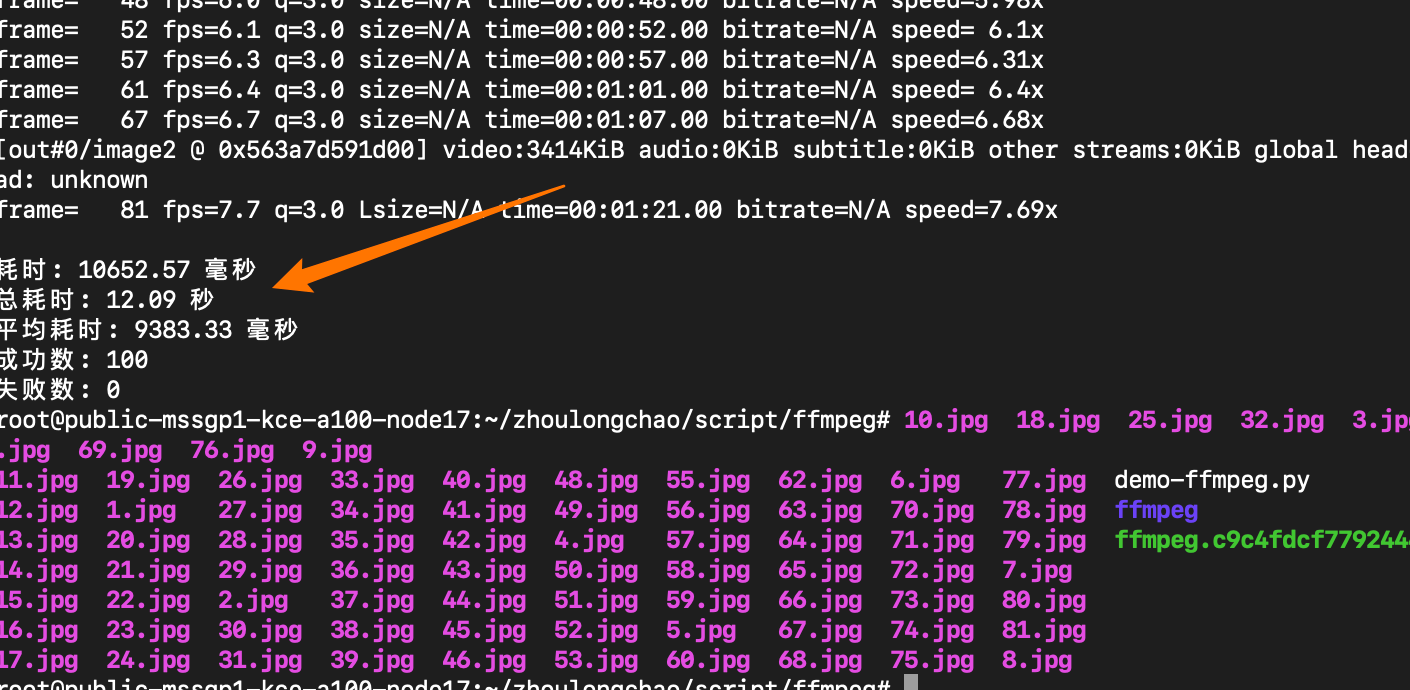
总耗时: 12.09 秒 平均耗时: 9383.33 毫秒 成功数: 100 失败数: 0
抽出 81 张 + 写入磁盘
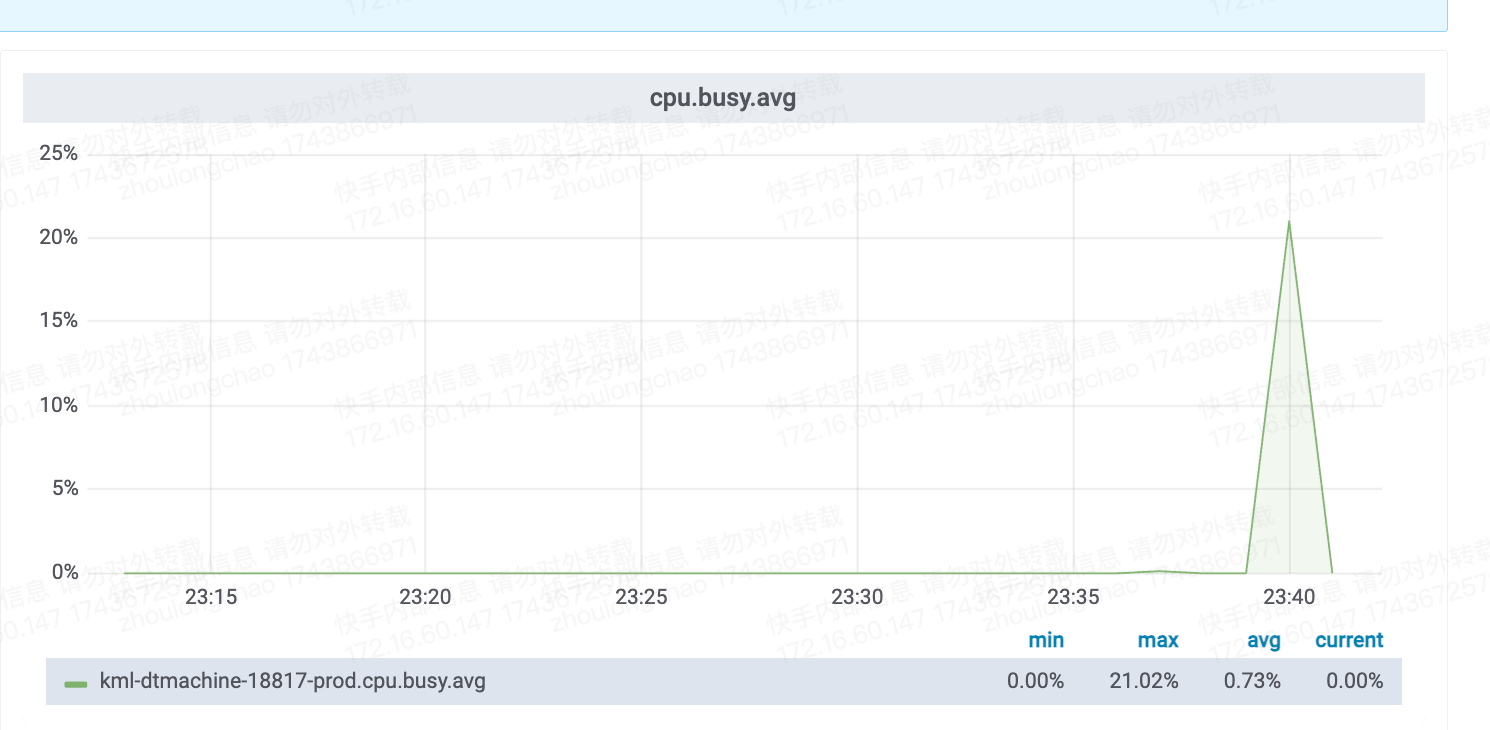
CPU核数换算——需 23 核(94*22%*120%)
|
新方案 |
decord - cpu |
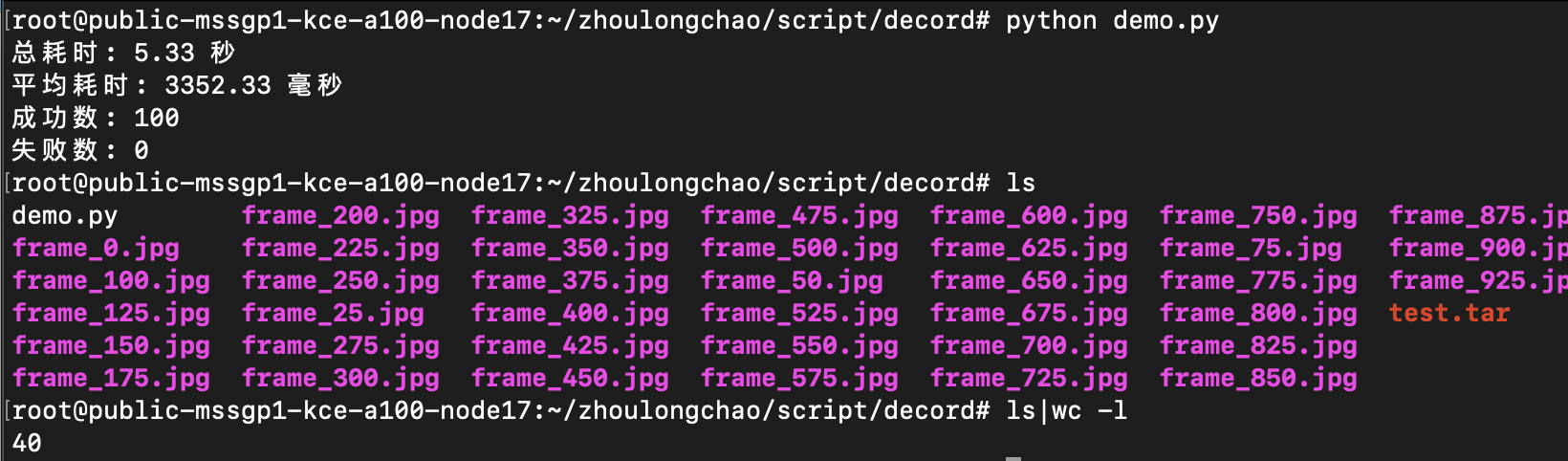
总耗时: 5.33 秒 平均耗时: 3352.33 毫秒 成功数: 100 失败数: 0
抽出 38 张 + 写入磁盘
CPU核数换算——需 7 核(94*7%*120%)
|
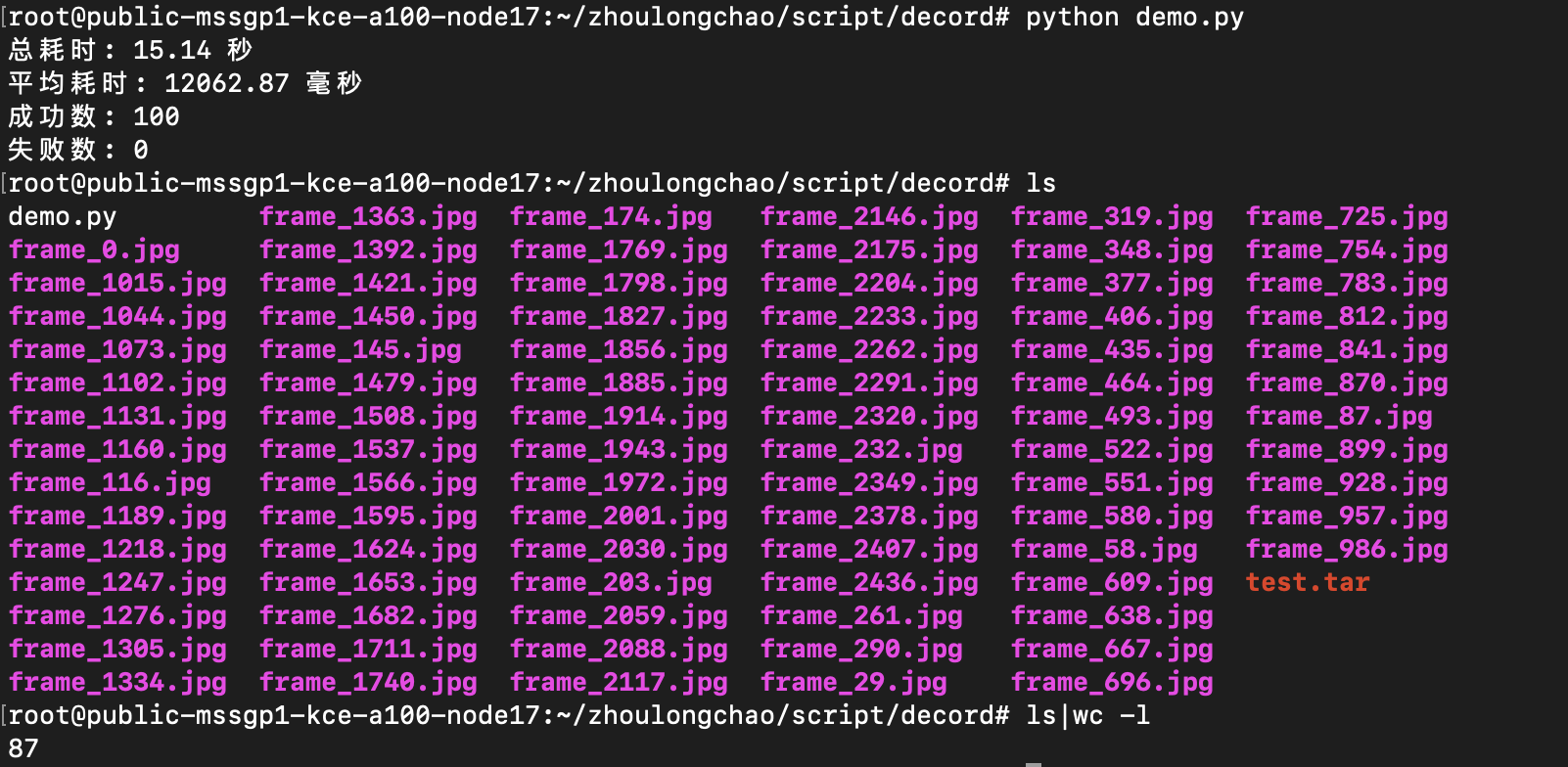
总耗时: 15.89 秒 平均耗时: 12617.40 毫秒 成功数: 100 失败数: 0
抽出 85 张 + 写入磁盘
CPU核数换算——需 24 核(94*25%*120%)
|
|
decord - gpu |
环境不兼容 |
环境不兼容 |
测试明细
ffmpeg
# 登陆开发机
ffmpeg -i /root/zhoulongchao/script/resource/video_150108527915923_37s.mp4 -map 0:v -q:v 3 -vsync 0 -f image2 -vf fps=1 -y ./%d.jpg
100 qps 测试(CPU)
cd /root/zhoulongchao/script/ffmpeg
vim demo-ffmpeg.py
python demo-ffmpeg.py
import subprocess
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def run_ffmpeg_command():
# FFmpeg 命令
command = [
'ffmpeg', '-i', '/root/zhoulongchao/script/resource/video_150108525914511_1m21s.mp4',
'-map', '0:v', '-q:v', '3', '-vsync', '0', '-f', 'image2', '-vf', 'fps=1', '-y', './%d.jpg'
]
start_time = time.time()
# 运行 FFmpeg 命令
result = subprocess.run(command, capture_output=True, text=True)
end_time = time.time()
# 计算耗时(毫秒)
elapsed_time_ms = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
print("FFmpeg 输出:")
print(result.stdout)
print("错误信息:")
print(result.stderr)
print(f"耗时: {elapsed_time_ms:.2f} 毫秒")
# 根据返回码判断是否成功
success = result.returncode == 0
return elapsed_time_ms, success
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 目标 QPS
target_qps = 100
# 每个请求的间隔时间(秒)
interval = 1 / target_qps
total_elapsed_time = 0
all_elapsed_times = []
success_count = 0
failure_count = 0
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=target_qps) as executor:
start_time = time.time()
futures = []
for _ in range(target_qps):
future = executor.submit(run_ffmpeg_command)
futures.append(future)
time.sleep(interval)
for future in futures:
elapsed_time, success = future.result()
all_elapsed_times.append(elapsed_time)
total_elapsed_time += elapsed_time
if success:
success_count += 1
else:
failure_count += 1
end_time = time.time()
average_elapsed_time = total_elapsed_time / target_qps if target_qps > 0 else 0
print(f"总耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f} 秒")
print(f"平均耗时: {average_elapsed_time:.2f} 毫秒")
print(f"成功数: {success_count}")
print(f"失败数: {failure_count}")
decord
cd /root/zhoulongchao/script/decord
vim main.py
python main.py
100 qps 测试(CPU)
import cv2
import time
from decord import VideoReader
from decord import cpu
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
import multiprocessing
def process_video(video_path):
start_time = time.time()
try:
vr = VideoReader(video_path, ctx=cpu(0))
fps = vr.get_avg_fps()
interval = int(fps)
for i in range(0, len(vr), interval):
frame = vr[i].asnumpy()
frame_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(f'frame_{i}.jpg', frame_bgr)
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
return elapsed_time, True
except Exception:
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
return elapsed_time, False
if __name__ == "__main__":
video_path = '/root/zhoulongchao/script/resource/video_150108527915923_37s.mp4'
target_qps = 100
interval = 1 / target_qps
total_elapsed_time = 0
success_count = 0
failure_count = 0
# 获取系统的 CPU 核心数量
cpu_count = multiprocessing.cpu_count()
with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=cpu_count) as executor:
start_time = time.time()
futures = []
for _ in range(target_qps):
future = executor.submit(process_video, video_path)
futures.append(future)
time.sleep(interval)
for future in futures:
elapsed_time, success = future.result()
total_elapsed_time += elapsed_time
if success:
success_count += 1
else:
failure_count += 1
end_time = time.time()
average_elapsed_time = total_elapsed_time / target_qps if target_qps > 0 else 0
print(f"总耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f} 秒")
print(f"平均耗时: {average_elapsed_time:.2f} 毫秒")
print(f"成功数: {success_count}")
print(f"失败数: {failure_count}")
100 qps 测试(GPU)
》这种方式环境配置失败了,暂时只写了一半
1、安装用于构建共享库的系统包 Ubuntu 运行:
# official PPA comes with ffmpeg 2.8, which lacks tons of features, we use ffmpeg 4.0 here
add-apt-repository ppa:jonathonf/ffmpeg-4 # for ubuntu20.04 official PPA is already version 4.2, you may skip this step
apt-get update
apt-get install -y build-essential python3-dev python3-setuptools make cmake
apt-get install -y ffmpeg libavcodec-dev libavfilter-dev libavformat-dev libavutil-dev
# note: make sure you have cmake 3.8 or later, you can install from cmake official website if it's too old
2、递归克隆 repo(重要)
git clone --recursivehttps://github.com/dmlc/decord
3、在源根目录中构建共享库(指定-DUSE_CUDA=ON或-DUSE_CUDA=/path/to/cuda或-DUSE_CUDA=ON-DCMAKE_CUDA_COMPILER=/path/to/cuda/nvcc启用 NVDEC 硬件加速解码)(要指定自定义的 FFMPEG 库路径,请使用“-DFFMPEG_DIR=/path/to/ffmpeg”):
cd /root/zhoulongchao/script/decord
cd decord
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DUSE_CUDA=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make请注意,如果您遇到了问题libnvcuvid.so,可能是由于缺少链接 libnvcuvid.so,可以手动找到它(ldconfig -p | grep libnvcuvid)并将库链接到,CUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR\lib64以便decord顺利检测并链接正确的库。或者——
Video Codec SDK - Get Started | NVIDIA Developer
mv libnvcuvid.so /usr/local/cuda/lib64/
4、安装python绑定:
cd ../python
# option 1: add python path to $PYTHONPATH, you will need to install numpy separately
pwd=$PWD
echo "PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$pwd" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
# option 2: install with setuptools
python3 setup.py install --user
make
import cv2
import time
from decord import VideoReader
from decord import gpu
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
import multiprocessing
def process_video(video_path):
start_time = time.time()
try:
# 修改为使用 GPU 进行解码
vr = VideoReader(video_path, ctx=gpu(0))
fps = vr.get_avg_fps()
interval = int(fps)
for i in range(0, len(vr), interval):
frame = vr[i].asnumpy()
frame_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite(f'frame_{i}.jpg', frame_bgr)
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
return elapsed_time, True
except Exception:
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = (end_time - start_time) * 1000
return elapsed_time, False
if __name__ == "__main__":
video_path = '/root/zhoulongchao/script/resource/video_150108527915923_37s.mp4'
target_qps = 100
interval = 1 / target_qps
total_elapsed_time = 0
success_count = 0
failure_count = 0
# 获取系统的 CPU 核心数量
cpu_count = multiprocessing.cpu_count()
with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=cpu_count) as executor:
start_time = time.time()
futures = []
for _ in range(target_qps):
future = executor.submit(process_video, video_path)
futures.append(future)
time.sleep(interval)
for future in futures:
elapsed_time, success = future.result()
total_elapsed_time += elapsed_time
if success:
success_count += 1
else:
failure_count += 1
end_time = time.time()
average_elapsed_time = total_elapsed_time / target_qps if target_qps > 0 else 0
print(f"总耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f} 秒")
print(f"平均耗时: {average_elapsed_time:.2f} 毫秒")
print(f"成功数: {success_count}")
print(f"失败数: {failure_count}")