最终实现效果:
左上:原图 中上:灰色图 右上:黑白图
左下:缩小图 中下:最相似的图 右下:第二相似的图)
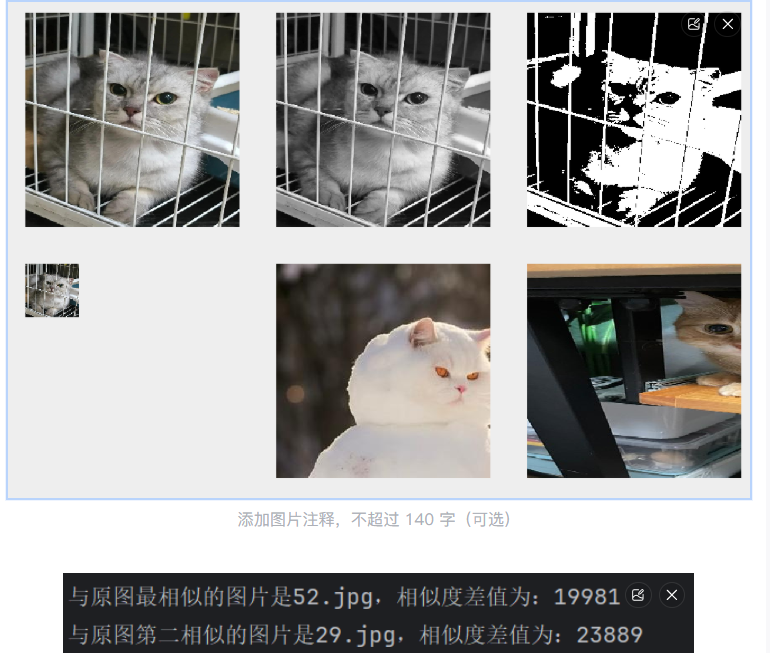
实现思路:
目标:实现在一个界面中:左上角是原图(用来测试的图),中间是灰色图,右上角是黑白图
左下角是缩小图 下面是最与之相似的图,右下角是第二相似的图
下面是这个图片文件夹中最与之相似的图片。
1.获取并绘制原图 获取图片+读取图片
2.灰度化
3.按照比例缩小成128*128的图
获取文件夹中所有图片,获取对应图片的二进制编码,与原图比对,选差值最小者进行绘制
搞定找出最相似的,第二相似的图并打印,遍历文件夹里的各图片 获取各自图片的二值编码,取差值最小者和差值第二小者。
(一)创建一个可显示图片的页面,注意不能是单纯的JFrame jf=new JFrame然后再给jf设置方法的步骤,而是要让界面继承JFrame,以便后续能调用getGraphics方法。
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
(二)在另一个ImgProgress类中处理图片。
创建第一个方法:根据路径将该图片转成文件类,再使用ImageIO类读取file文件将其转换成BufferedImage对象,然后创建数组,将图片的RGB值一个一个传进去。可以将BufferedImage的对象理解为一个存储了图片信息的对象,可以从中获取该图片的长宽,方便确立好一个数组。
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ImagineProgress {
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
(三)创建一个绘画方法接收该数组,并实际根据每个像素点的RGB的值把该点颜色赋给画笔,调好画笔初始数据。
并且返回显示界面将窗口与“画布”关联起来,否则画笔无法知道其上下文环境画不出东西来,因此需要继承父类中的paint函数,这也是为什么ImgaineUI类需要继承父类JFrame,是为了便于后续创建的paint函数继承父类中的方法。也就是说你想在窗口上画东西的时候,是需要调用paint函数的,不过不需要去刻意调用,因为当窗口可视化的时候,paint函数自动就调用了,但要注意往paint函数中传入g,相当与不仅要有动作(paint),还要有动作发出者(g)。然后完成窗口的paint函数后,还要注意在窗口中加入ip.g=getGraphics(),因为要与窗口上的画布绑定联系,要不然画笔无处可画。
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
ip.g=getGraphics();
}
//
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
ip.ArrProgress(Arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ImagineProgress {
Graphics g;
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void ArrProgress(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100,100,1,1);
}
}
}
}
然后笔者出现了两个疏忽的小错误,我没有把照片按照128128的格式或者256256的格式去搞,导致原图片加载过慢。并且把画笔和画布绑定在一块的操作给搞到可视化后面去了,因此可视化的时候调用paint函数画布画笔还没联系上呢。
修改后代码如下:
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
ip.g=getGraphics();
}
//
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
ip.ArrProgress(Arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ImagineProgress {
Graphics g;
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void ArrProgress(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/256;
int hi=h/256;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
}
此外还收获关于fillRect(x,y)的x,y的理解,这是绘画点,不是起始点。需要根据当前获得的像素点位置不同而改变值
(四)实现灰白像,使之居中。实现黑白像,使之去往右上角。再创建一个方法ArrProcess2,原先那个变成…1。里面得到红绿蓝三色值后/3再把这个颜色变成画笔的颜色,然后调一下起始点位置从100变到400就行。
再创建一个ArrProcess3,灰度值大于128,就统一变成黑,灰度值<128就统一变成白,再调一下起始位置就行,过程都差不多,这里就一块写掉。
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
ip.g=getGraphics();
}
//
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
ip.ArrProgress1(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress2(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress3(Arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ImagineProgress {
Graphics g;
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void ArrProgress1(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/256;
int hi=h/256;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress2(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/256;
int hi=h/256;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(400+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress3(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/256;
int hi=h/256;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
if(gray>128){
gray=255;
}else {
gray=0;
}
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(700+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
}
(五)实现缩小像。其实就是把bit调小一点,这里就是变成64,然后起始点调一点就没问题
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ImagineProgress {
Graphics g;
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void ArrProgress1(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress2(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(400+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress3(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
if(gray>128){
gray=255;
}else {
gray=0;
}
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(700+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress4(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=64;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,400+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
}
(六)找出最相似的图像,置于最下方;找出第二相似的图像,置于右下方。
这就需要遍历与测试图像在同一层的所有图片了,还要得到每个图片的二值码,并且图片大小还得一摸一样,这里统一采取256*256的。先搞定最相似的图片,第二相似的图片与之的区别后面再说。
(1)先在主函数中实现获得该层的路径,确保能遍历到每一个图片,并且能够得到每一个文件的名称,与经过处理后每个文件所对应的数组。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
File file=new File("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
ArrayList<String> fileNameList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){
File eachFile=files[i];
String eachName=eachFile.getName();
fileNameList.add(eachName);
int [][] arr=ip.imgProgress(eachFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
(2)在ImageProcess类中创建一个得到文件二值码的函数,注意文件的二值码是根据图片的黑白情况来辨别的。
public String CodeProgress(int [][] arr){
int w=arr.length;
int h=arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
String code="";
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
if(gray>128){
code+="1";
}else {
code+="0";
}
}
}
return code;
}
(3)在imageUI类中也要得到原图片的二值码,然后在主函数中分别得到对应图片的二值码,并与之比较,得到的差值存入动态数组中。
package com11.fjm0402;
import preKnowledgeReview.A;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
ip.g=getGraphics();
}
//
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
ip.ArrProgress1(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress2(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress3(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress4(Arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String testCode =ip.CodeProgress(Arr);
File file=new File("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
ArrayList<String> fileNameList=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> gapList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){
File eachFile=files[i];
String eachName=eachFile.getName();
fileNameList.add(eachName);
int [][] arr=ip.imgProgress(eachFile.getAbsolutePath());
String eachCode=ip.CodeProgress(arr);
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<eachCode.length();j++){
char t=testCode.charAt(j);
char e=eachCode.charAt(j);
if(t!=e){
count++;
}
}
gapList.add(count);
}
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
(4)继续遍历差值数组,找到最小值,并且输出 与原图最相似的图片是(图片名)相似度差值为:(差值),然后为了能画出来,就需要这个照片的数组,想要得到这个照片的数组就需要得到他的路径,因此需要能够在paint函数中得到其路径,而在主函数中写显然是达不到这一目的,因此把主函数的代码全部封装成一个函数
public String SimiMostCode(int [][] arr){
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String testCode =ip.CodeProgress(Arr);
File file=new File("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
ArrayList<String> fileNameList=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> gapList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){
File eachFile=files[i];
String eachName=eachFile.getName();
fileNameList.add(eachName);
int [][] eachArr=ip.imgProgress(eachFile.getAbsolutePath());
String eachCode=ip.CodeProgress(eachArr);
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<eachCode.length();j++){
char t=testCode.charAt(j);
char e=eachCode.charAt(j);
if(t!=e){
count++;
}
}
gapList.add(count);
}
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int j=-1;
for(int i=0;i<gapList.size();i++){
if(gapList.get(i)<min){
min= gapList.get(i);
j=i;
}
}
System.out.println("与原图最相似的图片是"+fileNameList.get(j)+",相似度差值为:"+min);
return fileNameList.get(j);
}
(5)在ImagineUI中得到最相近图片的名字,然后拼接路径得到该图片数组。然后调用第五个progress方法
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String simiMost=ip.SimiMostCode(Arr);
int [][] MostArr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\"+simiMost);
ip.ArrProgress1(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress2(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress3(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress4(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress5(MostArr);
}
(6)然后如法炮制得到第二相似的图片,不过要在求取最相似的图片方法的基础上实现这样一个逻辑,只需要求得和最小值差值最小的那个数就可以,那个数就是第二小的数。然后如法炮制前面的做法,得到路径,传入progress方法中绘制。
package com11.fjm0402;
import preKnowledgeReview.A;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ImagineUI extends JFrame {
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
public void showUI(){
setTitle("图片识别");
setLocation(200,100);
setSize(1100,700);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
ip.g=getGraphics();
}
//
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String simiMost=ip.SimiMostCode(Arr);
String simiSecond=ip.SimiSecondCode(Arr);
int [][] MostArr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\"+simiMost);
int [][]SecondArr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\"+simiSecond);
ip.ArrProgress1(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress2(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress3(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress4(Arr);
ip.ArrProgress5(MostArr);
ip.ArrProgress6(SecondArr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImagineUI ui=new ImagineUI();
ui.showUI();
}
}
package com11.fjm0402;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ImagineProgress {
Graphics g;
public int [][] imgProgress(String Path){
File file=new File(Path);
try {
BufferedImage bim= ImageIO.read(file);
int w=bim.getWidth();
int h=bim.getHeight();
int [][] arr=new int [w][h];
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
for(int j=0;j<h;j++){
arr[i][j]=bim.getRGB(i,j);
}
}
return arr;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void ArrProgress1(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress2(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(400+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress3(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
if(gray>128){
gray=255;
}else {
gray=0;
}
Color Gray =new Color(gray,gray,gray);
g.setColor(Gray);
g.fillRect(700+i/wi,100+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress4(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=64;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(100+i/wi,400+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress5(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(400+i/wi,400+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public void ArrProgress6(int [][] Arr){
int w=Arr.length;
int h=Arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=Arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(700+i/wi,400+j/hi,1,1);
}
}
}
public String CodeProgress(int [][] arr){
int w=arr.length;
int h=arr[0].length;
int bit=256;
w-=w%bit;
h-=h%bit;
int wi=w/bit;
int hi=h/bit;
String code="";
for(int i=0;i<w;i+=wi){
for(int j=0;j<h;j+=hi){
int pixNum=arr[i][j];
Color color=new Color(pixNum);
int red=color.getRed();
int green=color.getGreen();
int blue=color.getBlue();
int gray=(red+green+blue)/3;
if(gray>128){
code+="1";
}else {
code+="0";
}
}
}
return code;
}
public String SimiMostCode(int [][] arr){
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String testCode =ip.CodeProgress(Arr);
File file=new File("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
ArrayList<String> fileNameList=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> gapList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){
File eachFile=files[i];
String eachName=eachFile.getName();
fileNameList.add(eachName);
int [][] eachArr=ip.imgProgress(eachFile.getAbsolutePath());
String eachCode=ip.CodeProgress(eachArr);
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<eachCode.length();j++){
char t=testCode.charAt(j);
char e=eachCode.charAt(j);
if(t!=e){
count++;
}
}
gapList.add(count);
}
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int j=-1;
for(int i=0;i<gapList.size();i++){
if(gapList.get(i)<min && gapList.get(i)!=0){
min= gapList.get(i);
j=i;
}
}
System.out.println("与原图最相似的图片是"+fileNameList.get(j)+",相似度差值为:"+min);
return fileNameList.get(j);
}
public String SimiSecondCode(int [][] arr){
ImagineProgress ip=new ImagineProgress();
int [][] Arr=ip.imgProgress("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫\\41.jpg");
String testCode =ip.CodeProgress(Arr);
File file=new File("D:\\新建文件夹\\imgs猫");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
ArrayList<String> fileNameList=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> gapList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){
File eachFile=files[i];
String eachName=eachFile.getName();
fileNameList.add(eachName);
int [][] eachArr=ip.imgProgress(eachFile.getAbsolutePath());
String eachCode=ip.CodeProgress(eachArr);
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<eachCode.length();j++){
char t=testCode.charAt(j);
char e=eachCode.charAt(j);
if(t!=e){
count++;
}
}
gapList.add(count);
}
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int j=-1;
for(int i=0;i<gapList.size();i++){
if(gapList.get(i)<min && gapList.get(i)!=0){
min= gapList.get(i);
j=i;
}
}
int gap=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<gapList.size();i++){
if(gapList.get(i)!=0){
int d=gapList.get(i)-min;
if(d<gap && d!=0){
gap=d;
j=i;
}
}
}
System.out.println("与原图第二相似的图片是"+fileNameList.get(j)+",相似度差值为:"+gapList.get(j));
return fileNameList.get(j);
}
}
至此,已经可以独立实现图像识别项目。