摘要:
本文详细介绍了C++中string类的核心操作,主要包含以下内容:
1.多种构造函数的使用方法;
2.operator[]运算符重载实现字符访问;
3.正向/反向迭代器的使用;
4.auto和范围for语法糖的应用;
5.size/length/capacity等容量相关函数;
6.push_back/insert等插入操作;
7.append字符串拼接;
8.pop_back/erase删除操作;
9.find查找功能;
10.compare字符串比较方法。
文章通过具体示例代码演示了string类的各种常用操作,帮助开发者更好地理解和使用C++字符串处理功能。
目录
一、string的构造函数
string类实现了多个构造函数的重载,常用的构造函数如下:
string();//string的构造函数
string(const string& str);//string的拷贝构造函数
string(const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);//复制从字符位置 pos 开始并跨越 len字符的str部分
(如果 str 太短或 len 是 string::npos,则复制到 str 的末尾)。
string(const char* s);//复制由s指向的以 null 结尾的字符序列(s指向的字符串)。
string(const char* s, size_t n);//从s指向的字符串中复制前 n 个字符。
string(size_t n, char c);//生成n个c字符的字符串。
示例:
int main()
{
string s0; //string();
string s1("hello string");
string s2(s1); //string(const string& str);
string s3(s2, 5, 7); //string(const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
const char* s = "hello lzg";
string s4(s); //string(const char* s);
string s5(s,5); //string(const char* s, size_t n);
string s6(10, 'x'); //string(size_t n, char c);
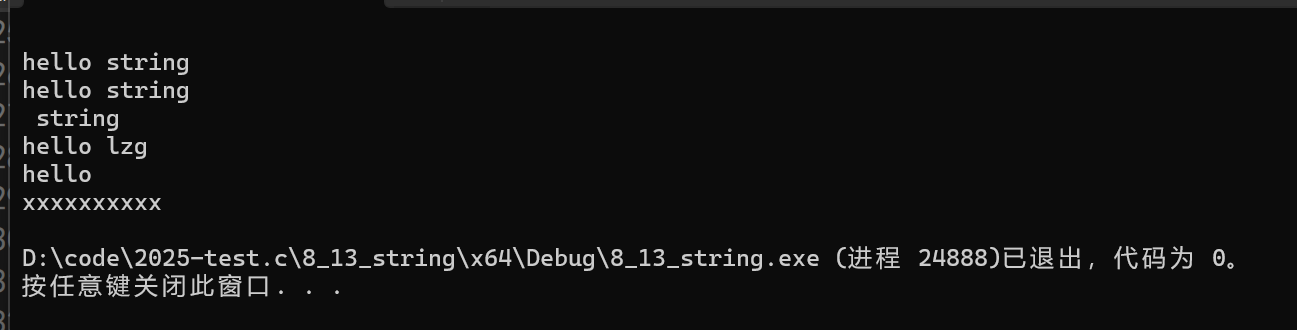
cout << s0 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
cout << s6 << endl;
return 0;
}
二、string的operator[]
说明:返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用
class string
{
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos<_size);
return _str[pos];
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{
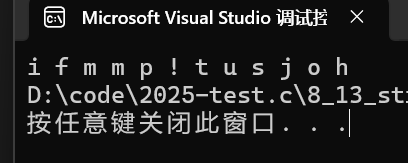
string s1("hello string");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << ' ';
}
}
三、string中与迭代器相关的函数

1、与正向迭代器相关的函数
begin函数:返回一个指向字符串第一个字符的迭代器。
end函数:返回一个指向字符串结束字符的迭代器,即’\0’
使用示例:
int main()
{
string s1("hello string");
string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
(*it1)--;
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
}2、与反向迭代器相关的函数
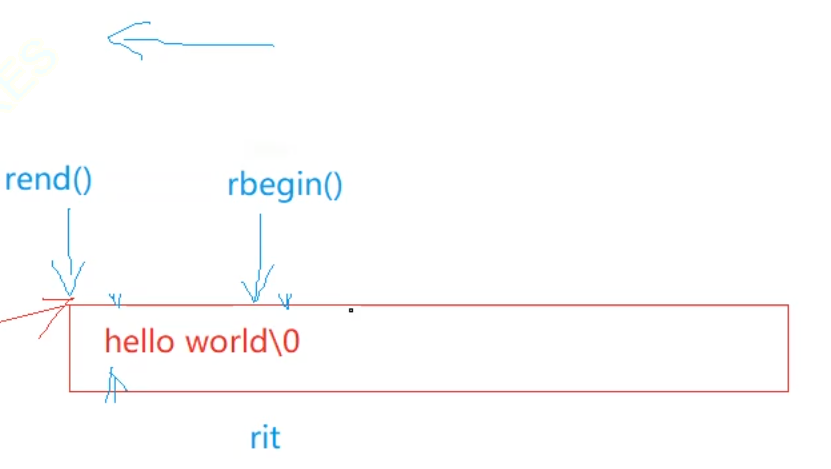
rbegin函数:返回指向字符串最后一个字符的反向迭代器。
rend函数:返回指向字符串第一个字符前面的理论元素的反向迭代器。
使用示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello string");
//反向迭代器
string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit;
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
四、"语法糖"auto和范围for
auto和范围for都是c++11才支持的
auto是自动推到类型
范围for是自动取容器的数据赋值给左边变量
自动++,自动判断结束
使用示例:
int main()
{
int i = 0;
auto a = i; //a是int类型
std::map<std::string, std::string> dict;
//std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator dict = dict.begin();
//auto dict = dict.begin();
string s1("hello world");
//for(char& e:s1)
for (auto& e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}注意:改变e并不影响s1,因为是把s1赋值给了e
五、string的大小和容量
1、使用size函数或length函数获取当前有效字符的个数
size_t size() const; size_t length() const;
int main()
{
string s0;
string s1("hello string");
cout << s1.size()<<endl; //12
cout << s1.length()<< endl; //12
return 0;
}2、使用max_size函数获取string对象对多可包含的字符数
size_t max_size() const;
int main()
{
string s0;
string s1("hello string");
cout << s1.max_size()<<endl;//x86环境下2147483647
return 0;
}
x86和x64环境下大小不一样,这个接口几乎用不到
3、使用capacity函数获取当前对象所分配的存储空间的大小
size_t capacity() const;
int main()
{
string s0;
string s1("hello string");
cout << s1.capacity()<<endl;//15
return 0;
}
六、string的插入
1、使用push_back进行尾插
void push_back (char c);
int main()
{
string s0;
string s1("hello ");
s1.push_back('w');
s1.push_back('o');
s1.push_back('r');
s1.push_back('d');
cout << s1 << endl;//hello word
return 0;
}
2、使用insert插入
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str);
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s);
iterator insert (iterator p, char c);
int main()
{
//string& insert(size_t pos, const string& str);
//在指定位置后插入string类对象
string s1("jingfeng ");
string s0("CSDN");
s1.insert(9,s0);
cout << s1 << endl;//jingfeng CSDN
//string& insert(size_t pos, const char* s);
//在指定位置后插入字符串
string s2("jingfeng");
const char* s = "CSDN博主:";
s2.insert(0, s);
cout << s2 << endl;//CSDN博主:jingfeng
//iterator insert(iterator p, char c);
//用iterator指定位置插入字符
string s3("ello");
string::iterator it1 = s3.begin();
s3.insert(it1, 'h');
cout << s3 << endl;//hello
return 0;
}七、string的拼接
使用append函数完成string的拼接:
string& append (const string& str);
string& append (const char* s);
string& append (size_t n, char c);
int main()
{
//string& append(const string& str);
//在s1后面拼接string类的str对象
string s1("hello ");
string str("world ");
s1.append(str);
cout << s1 << endl;//hello world
//string& append(const char* s);
//在s2后面拼接字符串s
string s2("hello ");
const char* s = "append";
s2.append(s);
cout << s2 << endl;
//string& append(size_t n, char c);
//将n个字符char拼接到string对象后面
string s3("CSD");
char c = 'N';
s3.append(1,c);
cout << s3 << endl;//CSDN
return 0;
}八、string的删除
1、使用pop_back进行尾删
void pop_back();
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
cout << s1 << endl;//hello
}2、使用erase删除
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
iterator erase (iterator p);
iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);
int main()
{
//string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
//在pos位置(包括pos)删除后面len个字符
string s1("hello world");
s1.erase(5, 6);
cout << s1 << endl;//hello后没有空格
//iterator erase(iterator p);
//指定删除iterator位置上的数据
string s2("CSSDN");
string::iterator it = s2.begin();
s2.erase(++it);
cout << s2 << endl;//CSDN
//iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);
//删除[first,last)上的数据
string s3("123333333333456");//10个3
string::iterator it1 = s3.begin();
string::iterator it2 = s3.end();
s3.erase(it1+2,it2-3);
cout << s3 << endl;//123456
return 0;
}九、string的查找
1、使用find函数正向搜索第一个匹配项
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
int main()
{
string s1("https://blog.csdn.net/jingfeng514");
//size_t find(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
//find(string)正向搜索与string对象所匹配的第一个位置
string s2("/");
int n = s1.find(s2);
cout << n << endl;//6
//size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//find(char* s)正向搜索与字符串str所匹配的第一个位置
const char* s = "tt";
int n1 = s1.find(s);
cout << n1 << endl;//1
//size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
//find(char)正向搜索与字符s所匹配的第一个位置
const char c = '.';
int n2 = s1.find(c);
cout << n2 << endl;//12
return 0;
}十、string的比较
使用compare函数完成比较:
int compare (const string& str) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen) const;
比较规则:
1、比较字符串中第一个不匹配的字符值较小,或者所有比较字符都匹配,但比较字符串较短,则返回小于0的值。
2、比较字符串中第一个不匹配的字符值较大,或者所有比较字符都匹配,但比较字符串较长,则返回大于0的值。
3、比较的两个字符串相等,则返回0。
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello CSDN");
//"hello world"和"hello CSDN"比较
cout << s1.compare(s2) << endl; //1
//"ell"和"hello CSDN"比较
cout << s1.compare(1, 3, s2) << endl; //-1
//"hello"和"hello"比较
cout << s1.compare(0, 4, s2, 0, 4) << endl; //0
return 0;
}