一、数据准备
xiaopiao.png

二、案例详解
现在需要对这张小票进行识别达到下图的效果
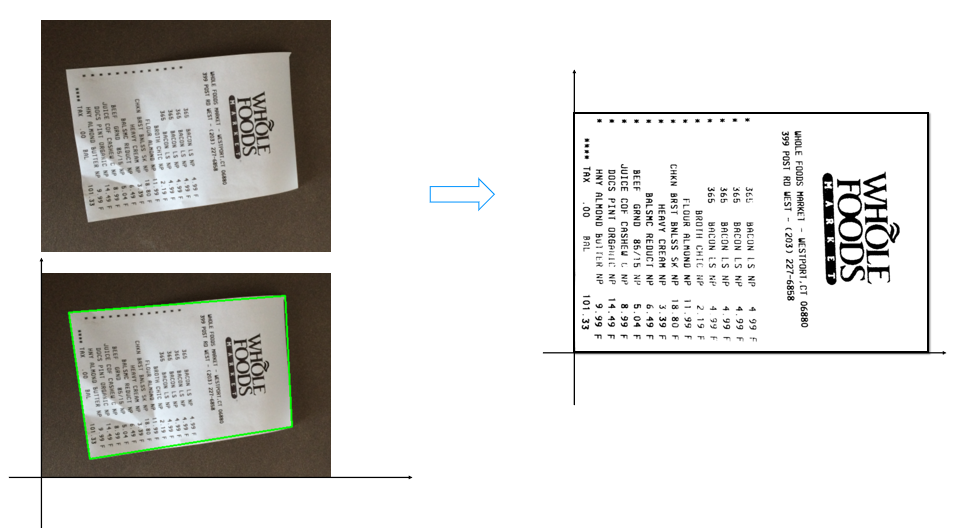
设计思路:
1、整体处理框架
- 图像读取与缩放:先读取原始图像,为提高处理效率,将图像按比例缩小
- 轮廓检测:通过边缘检测找到图像中所有物体的轮廓
- 目标定位:筛选出面积最大的轮廓(票据主体),并提取其四个顶点
- 透视矫正:利用透视变换将倾斜的票据转换为正视角的矩形
- 图像优化:通过二值化和形态学操作,增强票据文字与背景的对比度
2、分步处理思路详解
1. 图像准备阶段
读取原始图像:使用
cv2.imread加载票据图片缩放处理:将图像按比例缩小到高度 500 像素(通过
resize函数)目的:减少计算量,加快后续处理速度
关键:记录缩放比例(原始高度 / 500),用于后续坐标还原
2. 轮廓检测阶段
灰度化:将彩色图像转为灰度图(
cv2.cvtColor),简化处理通道二值化:用 OTSU 算法自动阈值分割(
cv2.threshold),将图像转为黑白对比明显的二值图轮廓提取:使用
cv2.findContours找出图像中所有轮廓,这些轮廓代表了不同物体的边缘
3. 目标轮廓筛选
按面积排序:票据通常是图像中面积最大的物体,因此取面积最大的轮廓
轮廓近似:通过
cv2.approxPolyDP将复杂轮廓简化为多边形目标:得到 4 个顶点(票据的四个角)
原理:用 Douglas-Peucker 算法,通过设定精度(周长的 5%)来简化轮廓
4. 透视变换矫正
坐标排序:通过
order_points函数将 4 个顶点按 "左上→右上→右下→左下" 排序计算目标尺寸:根据原始顶点坐标计算票据的实际宽高(用勾股定理算边长)
透视变换:
用
cv2.getPerspectiveTransform计算变换矩阵用
cv2.warpPerspective将倾斜票据转换为正矩形关键:使用之前记录的缩放比例,将缩小图像的坐标还原为原始图像坐标
5. 图像优化处理
再次二值化:将矫正后的图像转为黑白二值图,突出文字信息
腐蚀操作:用
cv2.erode去除细小噪点,使文字边缘更清晰旋转调整:根据需要旋转图像(
cv2.rotate),使票据方向符合阅读习惯
3、核心技术点
- 透视变换:解决票据因拍摄角度导致的倾斜和透视变形问题
- 轮廓检测与筛选:准确识别票据主体,排除背景干扰
- 坐标计算:通过几何方法确定票据的顶点位置和实际尺寸
- 图像预处理:通过二值化和形态学操作优化图像质量
三、完整代码
import numpy as np
import cv2
def cv_show(name, img):
"""显示图像"""
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def order_points(pts):
# 一共4个坐标点
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype="float32") # 用来存储排序之后的坐标
# 按顺序找到对应坐标0123分别是 左上,右上,右下,左下
s = pts.sum(axis=1) # 对pts矩阵的每一行进行求和操作。(x+y)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
diff = np.diff(pts, axis=1) # 对pts矩阵的每一行进行求差操作。(y - x)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
def four_point_transform(image,pts):
rect = order_points(pts)
(tl,tr,br,bl) = rect
widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0]-bl[0])**2)+((br[1]-bl[1])**2))
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2))
maxWidth = max(int(widthA),int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2))
heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB))
dst = np.array([[0,0],[maxWidth+1,0],
[maxWidth+1,maxHeight+1],[0,maxHeight+1]],dtype="float32")
M= cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect,dst)
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image,M,(maxWidth,maxHeight))
return warped
def resize(image, width=None, height=None, inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim = None
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r = height / float(h)
dim = (int(w * r), height)
else:
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
resized = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=inter)
return resized
#数据读取
image = cv2.imread('xiaopiao.jpg')
cv_show('image',image)
#图片缩小处理
ratio = image.shape[0]/500
orig = image.copy()
image = resize(orig,height=500)
cv_show('1',image)
#轮毂检测
print('STEP 1: 轮毂检测')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edged = cv2.threshold(gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(),cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
image_contours = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(),cnts,-1,(0,0,255),1)
cv_show('image_contours',image_contours)
print("STEP 2:获取最大轮毂")
screenCnt = sorted(cnts,key=cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)[0]
print(screenCnt.shape)
peri = cv2.arcLength(screenCnt,True)
screenCnt = cv2.approxPolyDP(screenCnt,0.05*peri,True)
print(screenCnt.shape)
image_contour = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(),[screenCnt],-1,(0,0,255),2)
cv_show('image_contour',image_contour)
warped = four_point_transform(orig,screenCnt.reshape(4,2)*ratio)
image = np.rot90(warped, k=1)
cv2.imwrite('invoice_new.jpg',image)
cv2.namedWindow('xx',cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv_show('xx',image)
# 三值处理
warped =cv2.cvtColor(warped,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ref = cv2.threshold(warped, 0, 255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY |cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show( 'ref',ref)
ref=resize(ref,width=900)
kernel=np.ones((2,2),np.uint8)# 设置kenenel大小
ref_new =cv2.erode(ref,kernel,iterations=1)#腐蚀
# cv_show('ref new',ref new)
rotated_image = cv2.rotate(ref_new, cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
cv2.imshow("result",rotated_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)四、完整效果
小票的轮毂定位

定位后将其完整切下来并调整比例
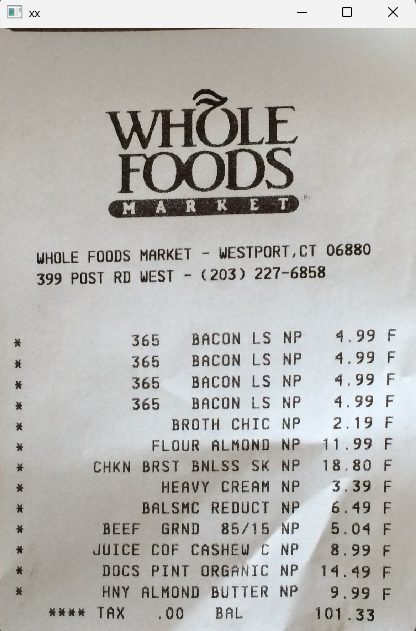
突出文字效果
