
本系列博客为复习操作系统导论的笔记,内容主要参考自:
- Remzi H. Arpaci-Dusseau and Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau, Operating Systems: Three Easy PiecesA. Silberschatz, P. Galvin, and G. Gagne,
- Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014, ISBN 978-1-118-09375-7.Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. .
目录
0x02 多级页表(Multi-level Page Tables)
0x05 三级页表(Three-level Page Table)
0x06 反向页表(Inverted Page Table)
0x00 引入:页表太大怎么办
我们现在来解决分页的第二个问题 —— 页表太大!
我们通常为系统中的每个进程设置一个页表,假设32位地址空间有4KB的页和4字节的页表项。
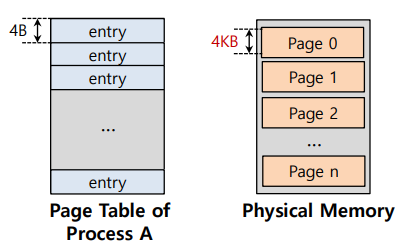
页表大小为:
Page table are too big and thus consume too much memory.
0x01 试试使用更大的页?
❓ 简单的解决方案:如果我们使用更大的页呢?
💡 假设32位地址空间有 16KB 页和 4 字节的页表项。
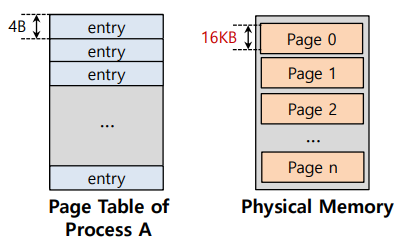
页表大小为:
然而,这种方法的问题在于,大内存页会导致每页内的浪费!
因为浪费问题存在于分配单元的内部,所以这被称为 "内部碎片问题"(internal fragmentation),
因此,结果是应用程序回分配页,但只用每页的一小部分,而内存就会充满这些过大的页。
这未免有些太奢侈了哈,就像一道菜只吃两口就扔了一样,这很浪费的说……
Big pages lead to internal fragmentation.
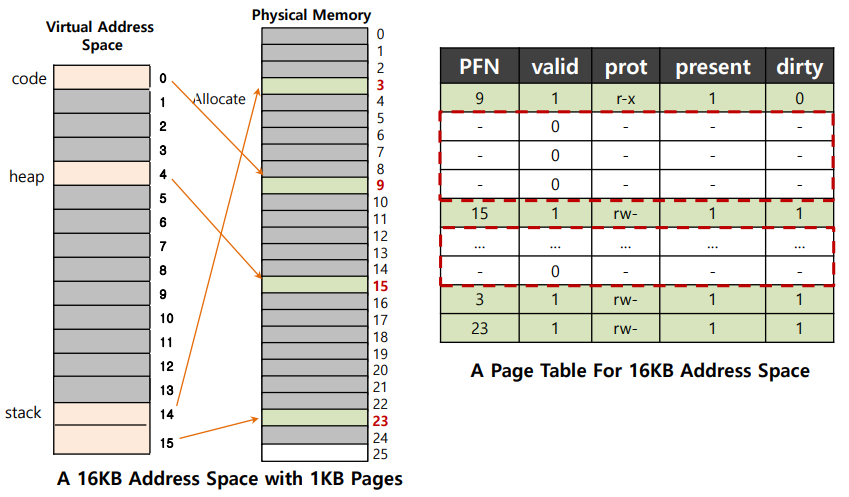
Most of the page table is unused, full of invalid entries!
0x01 混合方法:分页和分段
Page table for each segment
- The base register for each of these segments contains the physical address of the page table of that segment.
- The bound register: indicate the end of the page table (# of valid entries).
例子:每个进程有3个与之相关的页表
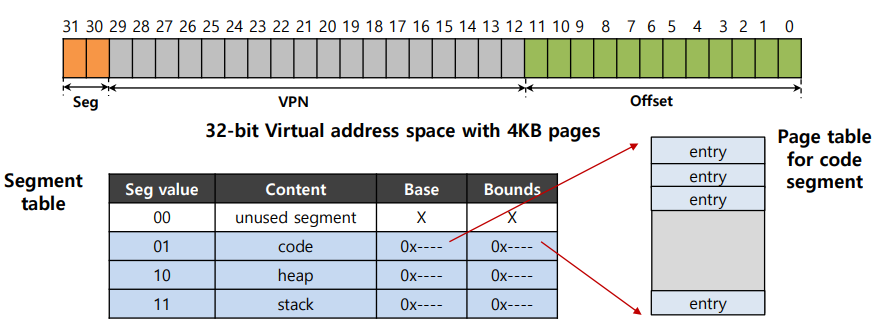
Address translation
- The hardware uses the segment bits (SN) to determine which base and bounds pair to use.
- The hardware then takes the physical address of the page table and combines it with the VPN as follows to form the address of the page table
硬件使用段位(SN)来决定使用哪一对基数和边界。
然后,硬件将页表的物理地址与VPN结合,如下所示形成页表的地址:
01: SN = (VirtualAddress & SEG_MASK) >> SN_SHIFT
02: VPN = (VirtualAddress & VPN_MASK) >> VPN_SHIFT
03: AddressOfPTE = Base[SN] + (VPN * sizeof(PTE))
遗憾的是,这种方法并非十全十美。首先,它仍然要使用分段。正如我们讨论的那样,分段并不像我们需要的那要灵活,因为他假定地址空间有一定的使用模式。例如,如果有一个大而稀疏的堆,仍然可能导致大量的页表浪费。其次,这种混合导致外部碎片再次出现。
0x02 多级页表(Multi-level Page Tables)
来大哥了,既然前面介绍的两个都挺摆烂的,这个多级页表可能会让你眼前一亮。
❓ 思考:如何摆脱页表中所有这些无效的区域,而不是将它们全部保留在内存中?而不是把它们全部保留在内存中?
💡 把线性页表变成像树一样的玩意!
- Chop up the page table into page-sized units. 把线性页面表变成类似树的东西。
- If an entire page of page-table entries is invalid, don’t allocate that page of the page table at all. 如果一整页的页表项是无效的,就根本不要分配页表的那一页。
- To track whether a page of the page table is valid, use a new structure, called page directory. 为了跟踪页表的某一页是否有效,使用一个新的结构,称为页目录。
- The page directory contains one entry per page of the page table. 页目录 包含页表的每一页的一个项。
- It consists of a number of page directory entries (PDE). 它由一些 页目录项(PDE)组成。
- PDE has a valid bit and page frame number (PFN). PDE有一个有效的位和 页帧号(PFN)。
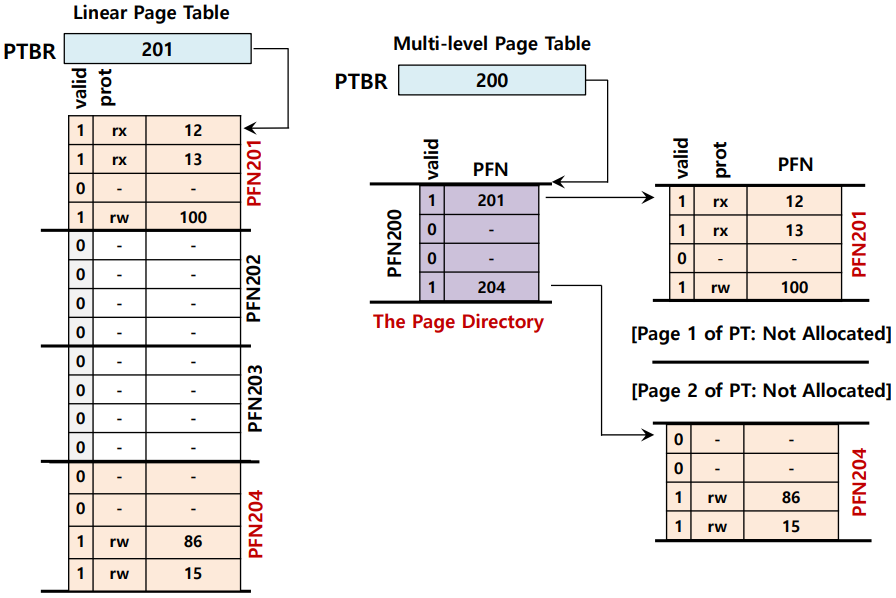
优点:
- Only allocates page-table space in proportion to the amount of address space you are using. 只按照你所使用的地址空间的比例分配页表空间
- The OS can grab the next free page when it needs to allocate or grow a page table. 当操作系统需要分配或增长页表时,它可以抓取下一个空闲页。
缺陷:
- Multi-level table is a small example of a time-space trade-off (时空折中).
- On a TLB miss, two loads from memory will be required to get the right translation information from the page table. 在TLB缺失时,需要从内存中加载两次,以便从页表中获得正确的翻译信息。
- On a TLB hit, performance is obviously identical. 在TLB击中时,性能显然是相同的。
- Complexity (复杂).
理解时空折中
在构建数据结构时,应始终考虑时间和空间的折中(time-space trade-off)。通常,如果你希望更快地访问特定的数据结构,就必须为该结构付出空间的代价。(正所谓以时间换空间)
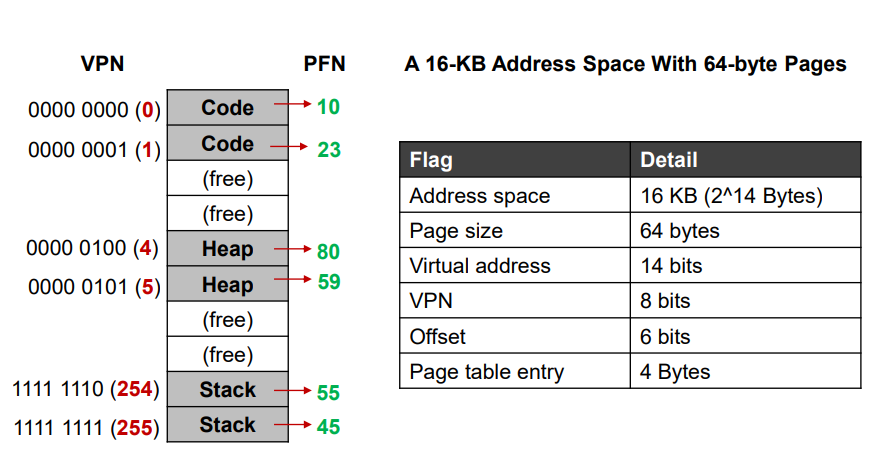
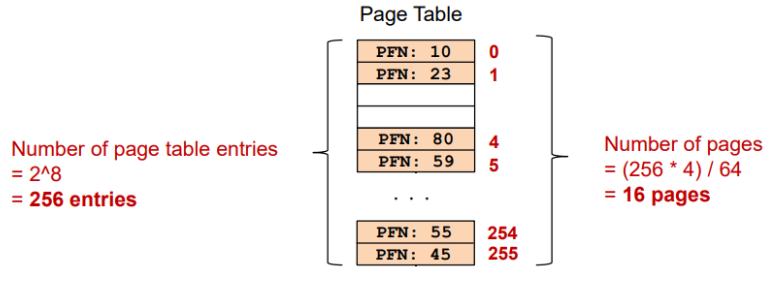
0x03 例子:单级页表
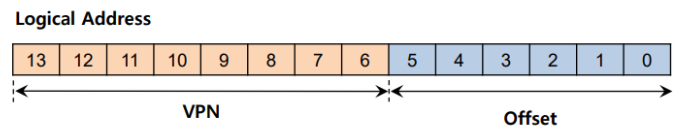
- 页表项:
项
- 页表大小:
0x04 例子:二级页表
Chop up the page table into page-sized units and create a page directory.
If an entire page of page-table entries is invalid, don’t allocate that page of the page table at all.
- 访问无效时会抛出一个异常
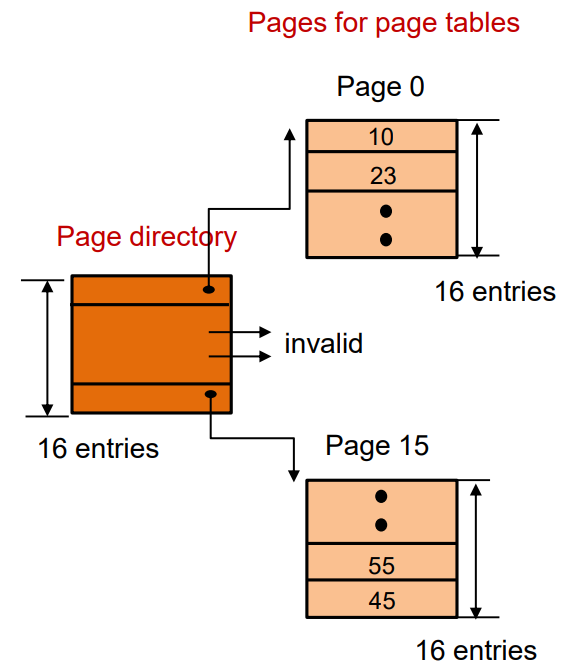
页目录(Page directory):
- 由 16 个项组成 → 每页页表有一个项(即页表的PFN)。
- 需要 16*4 字节 = 64字节 → 可以装入一个页面。
- 需要 4 bits的页目录索引 → 用于查找页表项的地址。
二级页表寻址(Addressing):
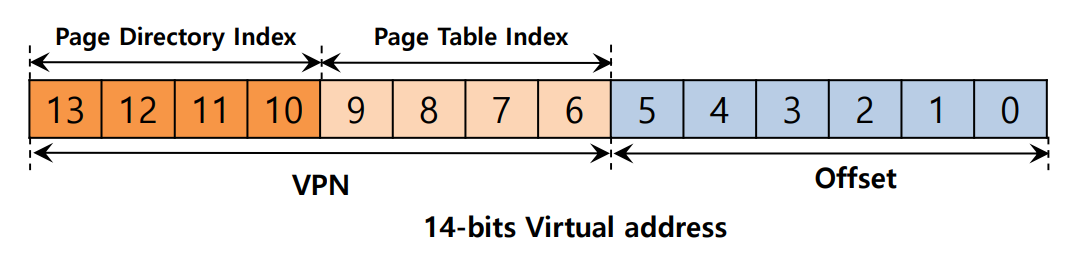
页目录索引(PDIndex)
它用于从VPN中找到页面目录条目(PDE)的地址。
PDEAddr = PageDirBase + (PDIndex * sizeof(PDE))页表索引 (PTIndex)
它用于索引页表本身,给我们的 PTE 的地址。
PTEAddr = (PDE.PFN << SHIFT) + (PTIndex * sizeof(PTE))PhysAddr = (PTE.PFN << SHIFT) + offset二级页表 - 详细的内存视图:

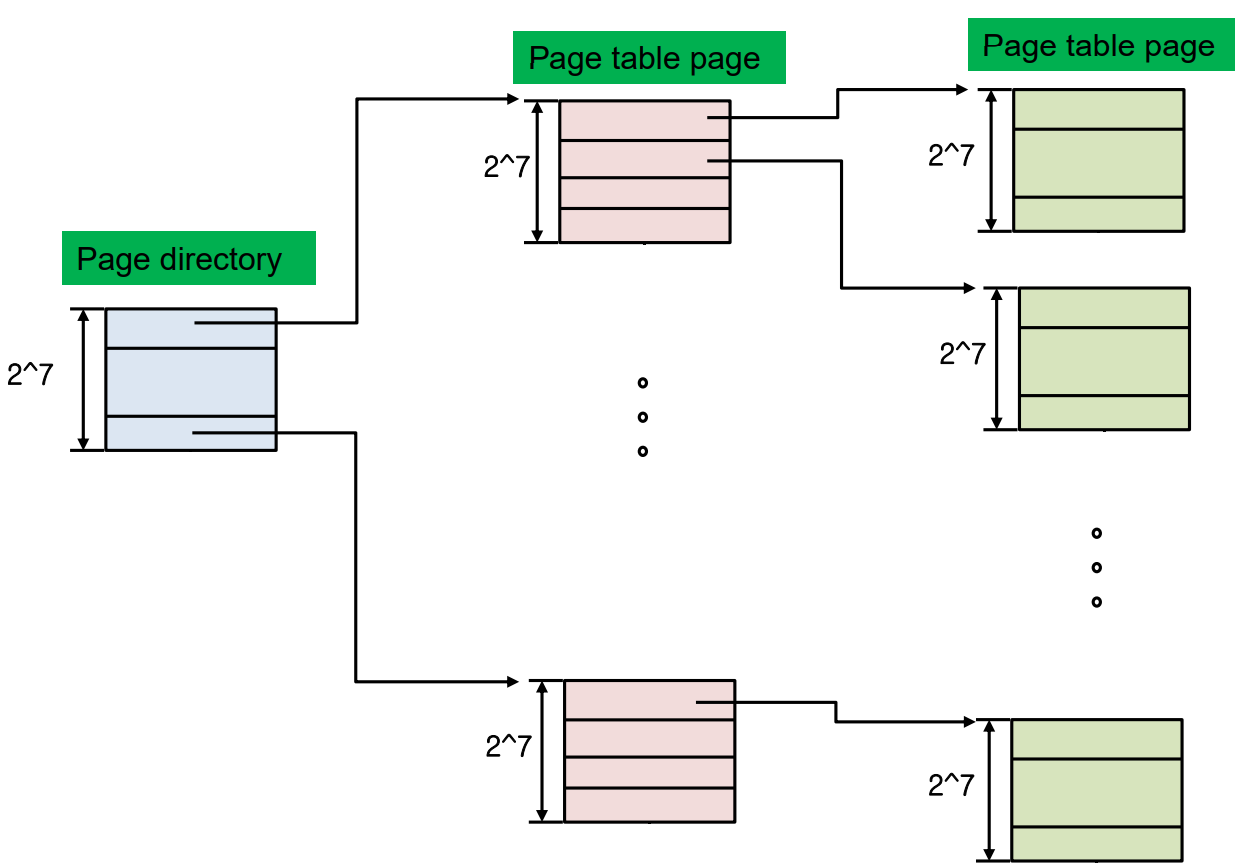
0x05 三级页表(Three-level Page Table)
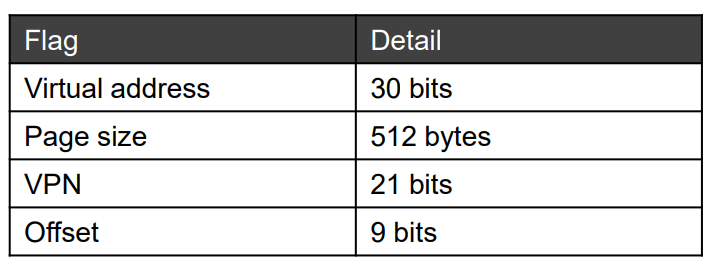
Make each piece of the page table and page directory fit within a page !
❓ 一级两级三级……我们到底需要多少级?
单个页面中的 PTE 数量 ( ) → 页表索引(7 bit)。
页目录索引需要 14 位(个项目 -
个页)→ 太大!
页目录: 页目录中的条目 → 适合于一个页面内的项!
我们需要三级!
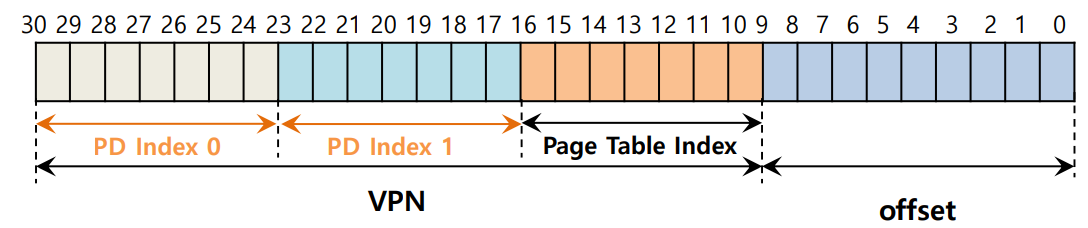
三级页表的例子:
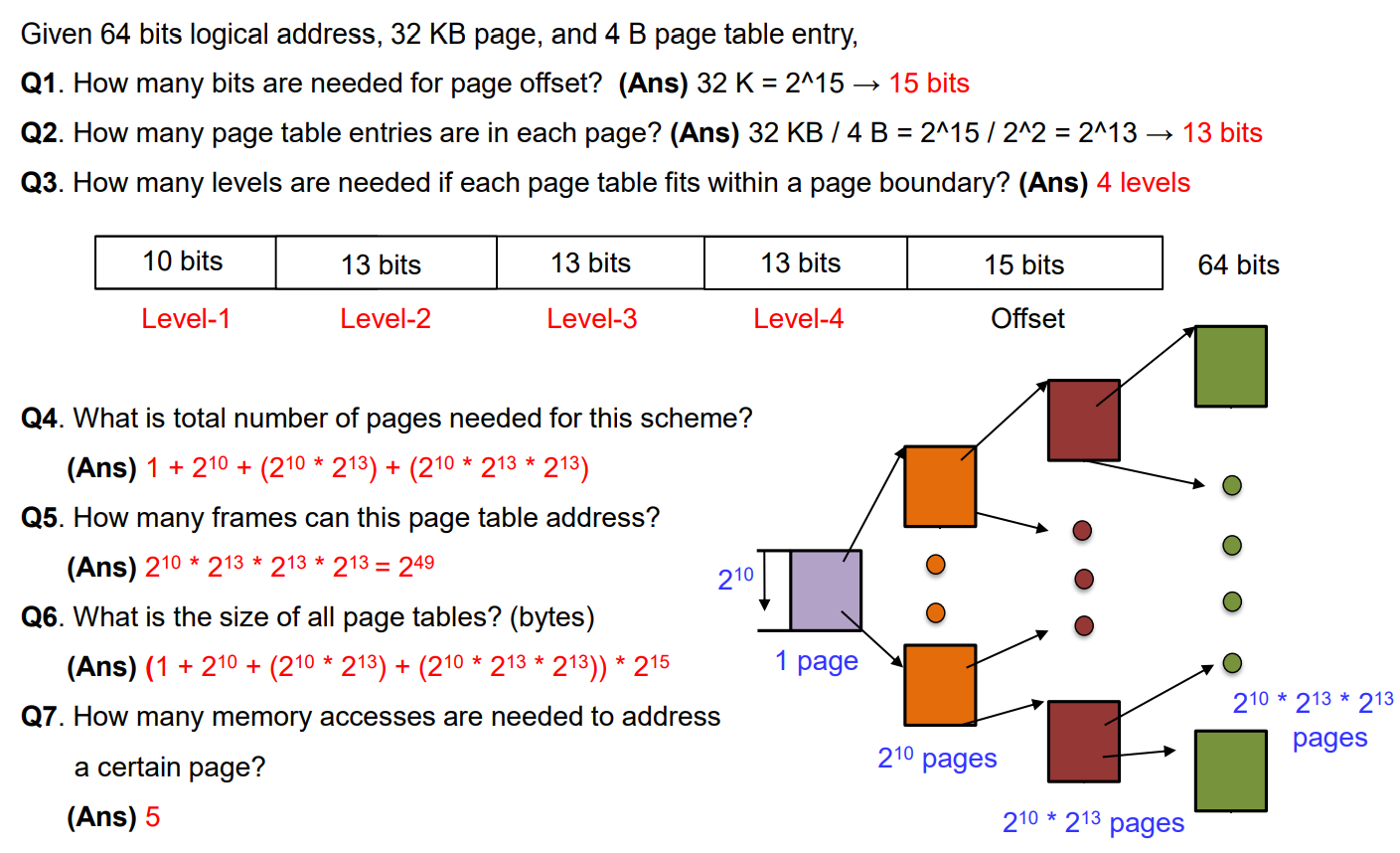
多级页表控制流程 - TLB命中:
VPN = (VirtualAddress & VPN_MASK) >> SHIFT
(Success,TlbEntry) = TLB_Lookup(VPN)
if ( Success == True ) // TLB Hit
if ( CanAccess(TlbEntry.ProtectBits) == True )
Offset = VirtualAddress & OFFSET_MASK
PhysAddr = (TlbEntry.PFN << SHIFT) | Offset
Register = AccessMemory(PhysAddr)
else
RaiseException(PROTECTION_FAULT);
else
// TLB Miss : perform the full multi-level lookup多级页表控制流程 - TLB未命中:
else // perform the full multi-level lookup
PDIndex = (VPN & PD_MASK) >> PD_SHIFT
PDEAddr = PDBR + (PDIndex * sizeof(PDE))
PDE = AccessMemory(PDEAddr) // fetch PDE from PD
if ( PDE.Valid == False ) RaiseException(SEGMENTATION_FAULT)
else // PDE is Valid
PTIndex = (VPN & PT_MASK) >> PT_SHIFT
PTEAddr = (PDE.PFN << SHIFT) + (PTIndex * sizeof(PTE))
PTE = AccessMemory(PTEAddr) // fetch PTE from PT
if ( PTE.Valid == False )
RaiseException(SEGMENTATION_FAULT)
else if ( CanAccess(PTE.ProtectBits) == False )
RaiseException(PROTECTION_FAULT);
else // now refresh TLB and restart
TLB_Insert(VPN, PTE.PFN, PTE.ProtectBits)
RetryInstruction()练习:
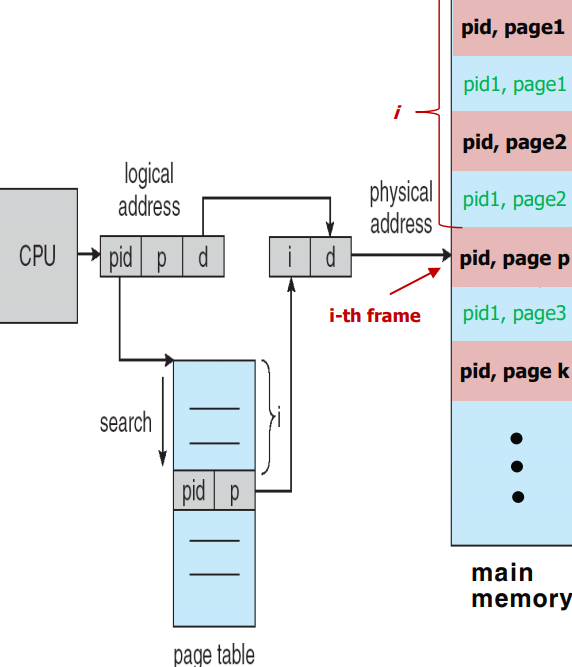
0x06 反向页表(Inverted Page Table)
 "生灵有倒悬之急"
"生灵有倒悬之急"
One entry for each real page of memory.
每个表项由存储在该真实内存位置的页面的虚拟地址组成,并附有关于拥有该页面的进程的信息(即pid或asid)。
减少了存储每个页表所需的内存,但增加了在发生页引用时搜索表所需的时间。
使用哈希表将搜索限制在一个或最多几个(例如64位 UltraSPARC 和 PowerPC)。

📌 [ 笔者 ] 王亦优
📃 [ 更新 ] 2022.11.8
❌ [ 勘误 ] /* 暂无 */
📜 [ 声明 ] 由于作者水平有限,本文有错误和不准确之处在所难免,
本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!📜 参考资料 Remzi H. Arpaci-Dusseau and Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau, Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces A. Silberschatz, P. Galvin, and G. Gagne, Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014, ISBN 978-1-118-09375-7. Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. . 百度百科[EB/OL]. []. https://baike.baidu.com/. |